apsimNGpy: API Reference
apsimNGpy.core.apsim
Interface to APSIM simulation models using Python.NET author: Richard Magala email: magalarich20@gmail.com
Classes
- class apsimNGpy.core.apsim.ApsimModel
This class inherits from
CoreModeland extends its capabilities.High-level methods/attributes flow between the
ApsimModelclass and its parents, and child class is illustrated below:PlotManager ---> CoreModel ---> ApsimModel ---> ExperimentManager
PlotManager. Produces visual outputs from model results. (Not exposed in the public API reference.)CoreModel. Provides core methods for running and manipulating APSIM models. (Not exposed in the public API reference.)ApsimModel. ExtendsCoreModelwith higher-level functionality.ExperimentManager. Creates and manages multi-factor experiments from a base scenario.
from pathlib import Path from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel # Initialize a model model = ApsimModel( 'Maize', out_path=Path.home() / 'apsim_model_example.apsimx' ) # Run the model model.run(report_name='Report') # 'Report' is the default table name; adjust if needed # Get all results res = model.results # Or fetch a specific report table from the APSIM database report_df = model.get_simulated_output('Report')
List of Public Attributes:
is_recent_versionstr_model
List of Public Methods
- __init__(self, model: os.PathLike | dict | str, out_path: str | pathlib.Path = None, set_wd=None, **kwargs)
Initialize self. See help(type(self)) for accurate signature.
- evaluate_simulated_output(self, ref_data: pandas.core.frame.DataFrame, table, ref_data_col, target_col, index_col, expr=None)
Evaluate APSIM-simulated output against a reference (observed) dataset.
This method compares observed data (
ref_data) with simulated predictions obtained either from a provided DataFrame or from a table name that is used to extract simulation output throughget_simulated_output(). The comparison is performed throughfinal_evalfromapsimNGpy.optimizer.problems.back_end, which computes common evaluation metrics (e.g., RMSE, RRMSE, WIA, CCC, bias), depending on the implementation offinal_eval.Added in v0.39.12.21+
Parameters
- ref_datapandas.DataFrame
The reference or observed dataset against which predictions will be evaluated. Must contain at least the column specified by
ref_data_coland the index column.- tablestr or pandas.DataFrame
- Either:
A string referring to an APSIM output table name. In this case, simulated output is retrieved using :meth:`~apsimNGpy.core.apsim.ApsimModel.get_simulated_output`(table).
A DataFrame containing simulated predictions directly.
Any other type will raise a
TypeError.- ref_data_colstr
Column name in
ref_datacontaining the observed values.- target_colstr
Column name in the simulated dataset indicating the predicted values to be compared against the observations.
- index_colstr
Column used to join observed and simulated data (e.g., date, sample number, simulation ID). Both datasets must contain this column.
- exprcallable or str, optional
An optional transformation or expression to apply before comparison. Can be a lambda function, a string expression, or
None. Default isNone.
Returns
- dict or pandas.DataFrame
The output of
final_eval, typically containing evaluation metrics such as RMSE, RRMSE, WIA, CCC, ME, and bias.
Raises
- TypeError
If
tableis neither a string nor a pandas DataFrame.
Notes
This method streamlines comparison between observed and simulated APSIM outputs during model calibration or performance assessment. It allows the user to directly pass simulation tables or retrieve them automatically by name, ensuring a consistent evaluation workflow. Examples ——– .. code-block:: python
from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel from apsimNGpy.tests.unittests.test_factory import obs model = ApsimModel(‘Maize’) # need to add column year to act as common index with observed data model.add_report_variable(variable_spec=’[Clock].Today.Year as year’, report_name=’Report’) model.evaluate_simulated_output(ref_data=obs, table=’Report’, index_col=[‘year’],
target_col=’Yield’, ref_data_col=’observed’)
Model Evaluation Metrics ---------------------------------------- RMSE : 0.0003 MAE : 0.0003 MSE : 0.0000 RRMSE : 0.0000 bias : -0.0001 ME : 1.0000 WIA : 1.0000 R2 : 1.0000 CCC : 1.0000 SLOPE : 1.0000
Added in version v0.39.12.21+.
Set parameters for the given model by passing a dictionary or keyword arguments.
Parameters
- paramsdict, optional
A dictionary mapping APSIM parameter names to their corresponding values. If
paramsisNone, thenkwargsis expected, following the same signature asedit_model_by_path().- **kwargs :
Additional keyword arguments equivalent to entries in
params. These are interpreted according to the same signature asedit_model_by_path().
Returns
- selfApsimModel
Returns the same instance for method chaining.
Raises
- TypeError if any of the above arguments does not resolve to a dictionary. Other errors maybe raised gracefully
by
edit_model_by_path().
Notes
This flexible design allows users to supply parameters either as standard keyword arguments or as dictionary objects. The dictionary-based approach is particularly useful when working with JSON-compatible data structures, as commonly required during large-scale model optimization, calibration, or parameter sensitivity analysis workflows. In such cases, parameter sets can be programmatically generated, serialized, and reused without manual modification of code.
- get_soil_from_web(self, simulation_name: str | tuple | NoneType = None, *, lonlat: System.Tuple[Double, Double] | None = None, soil_series: str | None = None, thickness_sequence: Sequence[float] | None = 'auto', thickness_value: int = None, max_depth: int | None = 2400, n_layers: int = 10, thinnest_layer: int = 100, thickness_growth_rate: float = 1.5, edit_sections: Sequence[str] | None = None, attach_missing_sections: bool = True, additional_plants: tuple = None, adjust_dul: bool = True)
Download SSURGO-derived soil for a given location and populate the APSIM NG soil sections in the current model.
This method updates the target Simulation(s) in-place by attaching a Soil node (if missing) and writing section properties from the downloaded profile.
Parameters
- simulationstr | sequence[str] | None, default None
Target simulation name(s). If
None, all simulations are updated.- lonlattuple[float, float] | None
Location for SSURGO download, as
(lon, lat)in decimal degrees (e.g.,(-93.045, 42.012)).- soil_seriesstr | None, optional
Optional component/series filter. If
None, the dominant series by area is used. If a non-existent series is supplied, an error is raised.- thickness_sequencesequence[float] | str | None, default “auto”
Explicit layer thicknesses (mm). If
"auto", thicknesses are generated from the layer controls (e.g., number of layers, growth rate, thinnest layer, andmax_depth). IfNone, you must providethickness_valueandmax_depthto construct a uniform sequence.- thickness_valueint | None, optional
Uniform thickness (mm) for all layers. Ignored if
thickness_sequenceis provided; used only whenthickness_sequenceisNone.- max_depthint, default 2400
Maximum soil depth (mm) to cover with the thickness sequence.
- edit_sectionssequence[str], optional
Sections to edit. Default:
("physical", "organic", "chemical", "water", "water_balance", "solutes", "soil_crop", "meta_info"). Note: if sections are edited with differing layer counts, APSIM may error at run time.- attach_missing_sectionsbool, default True
If
True, create and attach missing section nodes before editing.- additional_plantssequence[str] | None, optional
Plant names for which to create/populate
SoilCropentries (e.g., to set KL/XF).- adjust_dulbool, optional
If
True, adjust layer values whereSATexceedsDULto prevent APSIM runtime errors.
Returns
- self
The same instance, to allow method chaining.
Raises
- ValueError
thickness_sequenceprovided with any non-positive value(s).thickness_sequenceisNoneandthickness_valueisNone.Units mismatch or inconsistency between
thickness_valueandmax_depth.
Notes
Assumes soil sections live under a Soil node; when
attach_missing_sections=Truea Soil node is created if missing.Uses the optimized SoilManager routines (vectorized assignments / .NET double[] marshaling).
- Side effects (in place on the APSIM model):
Creates/attaches Soil when needed.
Creates/updates child sections (
Physical,Organic,Chemical,Water,WaterBalance,SoilCrop) as listed inedit_sections.Overwrites section properties (e.g., layer arrays such as
Depth,BD,LL15,DUL,SAT; solutes; crop KL/XF) with downloaded values.Add SoilCrop children for any names in
additional_plants.Performs network I/O to retrieve SSURGO tables when
lonlatis provided.Emits log messages (warnings/info) when attaching nodes, resolving thickness controls, or skipping missing columns.
Caches the computed soil profile in the helper during execution; the in-memory APSIM tree remains modified after return.
Does not write files; call
save()on the model if you want to persist changes.The existing soil-profile structure is completed override by the newly generated soil profile. So, variables like soil thickness, number of soil layers, etc. might be different from the old one.
This method checks whether the soil
SATis above or belowDULand decreasesDULvalues accordinglyNeed to call this method everytime
SATis changed, orDULis changed accordingly.
simulations: str, name of the simulation where we want to adjust DUL and SAT according.returns:model the object for method chaining
- @deprecated and will be removed in the future versions
Updates soil parameters and configurations for downloaded soil data in simulation models.
This method adjusts soil physical and organic parameters based on provided soil tables and applies these adjustments to specified simulation models.
Parameters:
soil_tables(list): A list containing soil data tables. Expected to contain: see the naming convention in the for APSIM - [0]: DataFrame with physical soil parameters. - [1]: DataFrame with organic soil parameters. - [2]: DataFrame with crop-specific soil parameters. - simulation_names (list of str): Names or identifiers for the simulations to be updated.sReturns: - self: Returns an instance of the class for
chainingmethods.This method directly modifies the simulation instances found by
find_simulationsmethod calls, updating physical and organic soil properties, as well as crop-specific parameters like lower limit (LL), drain upper limit (DUL), saturation (SAT), bulk density (BD), hydraulic conductivity at saturation (KS), and more based on the provided soil tables.
->> key-word argument
set_sw_con: Boolean, set the drainage coefficient for each layeradJust_kl:: Bollean, adjust, kl based on productivity indexCultvarName: cultivar name which is in the sowing module for adjusting the ruetillage: specify whether you will be carried to adjust some physical parameters- read_apsimx_data(self, table=None)
Read APSIM NG datastore for the current model. Raises FileNotFoundError if the model was initialized from default models because those need to be executed first to generate a database.
The rationale for this method is that you can just access the results from the previous session without running it if the database is in the same location as the apsimx file.
Since apsimNGpy clones the apsimx file, the original file is kept with attribute name
_model, that is what is being used to access the datasettable: (str) name of the database table to read if none of all tables are returned
Returns: pandas.DataFrame
KeyError: if table is not found in the database
- property simulations(inherited)
Retrieve simulation nodes in the APSIMx
Model.Core.Simulationsobject.We search all-Models.Core.Simulation in the scope of Model.Core.Simulations. Please note the difference Simulations is the whole json object Simulation is the child with the field zones, crops, soils and managers.
Any structure of apsimx file can be handled.
Note
The simulations are c# referenced objects, and their manipulation maybe for advanced users only.
- property simulation_names(inherited)
@deprecated will be removed in future releases. Please use inspect_model function instead.
retrieves the name of the simulations in the APSIMx file @return: list of simulation names
- property tables_list(inherited)
quick property returns available database report tables name
- property managers_scripts_list(inherited)
quick property returns available database manager script names
- property simulations_list(inherited)
quick property for returning a list of available simulation names @return:
- restart_model(self, model_info=None) (inherited)
Reinitialize the APSIM model instance after edits or management updates.
Parameters
- model_infocollections.NamedTuple, optional
A named tuple returned by
load_apsim_modelfrom themodel_loadermodule. Contains references to the APSIM model, datastore, and file path. If not provided, the method reinitializes the model using the existingself.model_infoobject.
Notes
This method is essential when the model needs to be reloaded after modifying management scripts or saving an edited APSIM file.
It may be invoked automatically by internal methods such as
save_edited_file,save, andupdate_mgt.Reinitializing ensures that all APSIM NG components and datastore references are refreshed and consistent with the modified file.
Returns
- selfobject
Returns the updated ApsimModel instance.
- save(self, file_name: 'Union[str, Path, None]' = None, reload=True) (inherited)
Saves the current APSIM NG model (
Simulations) to disk and refresh runtime state.This method writes the model to a file, using a version-aware strategy:
After writing, the model is recompiled via
recompile(self)()and the in-memory instance is refreshed usingrestart_model(), ensuring the object graph reflects the just-saved state. This is now only impozed if the user specifiedrelaod = True.Parameters
- file_namestr or pathlib.Path, optional
Output path for the saved model file. If omitted (
None), the method uses the instance’s existingpath. The resolved path is also written back to instancepathattribute for consistency if reload is True.- reload: bool Optional default is True
resets the reference path to the one provided after serializing to disk. This implies that the instance
pathwill be the providedfile_name
Returns
- Self
The same model/manager instance to support method chaining.
Raises
- OSError
If the file cannot be written due to I/O errors, permissions, or invalid path.
- AttributeError
If required attributes (e.g.,
self.Simulations) or methods are missing.- Exception
Any exception propagated by
save_model_to_file(),recompile(), orrestart_model().
Side Effects
Sets
self.pathto the resolved output path (string).Writes the model file to disk (overwrites if it exists).
If reload is True (default), recompiles the model and restarts the in-memory instance.
Notes
Path normalization: The path is stringified via
str(file_name)just in case it is a pathlib object.Reload semantics: Post-save recompilation and restart ensure any code generation or cached reflection is refreshed to match the serialized model.
Examples
- check the current path before saving the model
>>> from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel >>> from pathlib import Path >>> model = ApsimModel("Maize", out_path='saved_maize.apsimx') >>> model.path scratch\saved_maize.apsimx
- Save to a new path and continue working with the refreshed instance
>>> model.save(file_name='out_maize.apsimx', reload=True) # check the path >>> model.path 'out_maize.apsimx' # possible to run again the refreshed model. >>> model.run()
- Save to a new path without refreshing the instance path
>>> model = ApsimModel("Maize", out_path='saved_maize.apsimx') >>> model.save(file_name='out_maize.apsimx', reload=False) # check the current reference path for the model. >>> model.path 'scratch\saved_maize.apsimx' # When reload is False, the original referenced path remains as shown above
As shown above, everything is saved in the scratch folder; if the path is not abolutely provided, e.g., a relative path. If the path is not provided as shown below, the reference path is the current path for the isntance model.
>>> model = ApsimModel("Maize", out_path='saved_maize.apsimx') >>> model.path 'scratch\saved_maize.apsimx' # save the model without providing the path. >>> model.save()# uses the default, in this case the defaul path is the existing path >>> model.path 'scratch\saved_maize.apsimx'
In the above case, both reload =
FalseorTrue, will produce the same reference path for the live instance class.- property results(inherited)
Legacy method for retrieving simulation results.
This method is implemented as a
propertyto enable lazy loading—results are only loaded into memory when explicitly accessed. This design helps optimizememoryusage, especially forlargesimulations.It must be called only after invoking
run(). If accessed before the simulation is run, it will raise an error.Notes
The
run()method should be called with a validreport nameor a list of report names.If
report_namesis not provided (i.e.,None), the system will inspect the model and automatically detect all available report components. These reports will then be used to collect the data.If multiple report names are used, their corresponding data tables will be concatenated along the rows.
Returns
- pd.DataFrame
A DataFrame containing the simulation output results.
Examples
>>> from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel # create an instance of ApsimModel class >>> model = ApsimModel("Maize", out_path="my_maize_model.apsimx") # run the simulation >>> model.run() # get the results >>> df = model.results # do something with the results e.g. get the mean of numeric columns >>> df.mean(numeric_only=True) Out[12]: CheckpointID 1.000000 SimulationID 1.000000 Maize.AboveGround.Wt 1225.099950 Maize.AboveGround.N 12.381196 Yield 5636.529504 Maize.Grain.Wt 563.652950 Maize.Grain.Size 0.284941 Maize.Grain.NumberFunction 1986.770519 Maize.Grain.Total.Wt 563.652950 Maize.Grain.N 7.459296 Maize.Total.Wt 1340.837427
If there are more than one database tables or
reportsas called in APSIM, results are concatenated along the axis 0, implying along rows. The example below mimics this scenario.>>> model.add_db_table( ... variable_spec=['[Clock].Today.Year as year', ... 'sum([Soil].Nutrient.TotalC)/1000 from 01-jan to [clock].Today as soc'], ... rename='soc' ... ) # inspect the reports >>> model.inspect_model('Models.Report', fullpath=False) ['Report', 'soc'] >>> model.run() >>> model.results CheckpointID SimulationID Zone ... source_table year soc 0 1 1 Field ... Report NaN NaN 1 1 1 Field ... Report NaN NaN 2 1 1 Field ... Report NaN NaN 3 1 1 Field ... Report NaN NaN 4 1 1 Field ... Report NaN NaN 5 1 1 Field ... Report NaN NaN 6 1 1 Field ... Report NaN NaN 7 1 1 Field ... Report NaN NaN 8 1 1 Field ... Report NaN NaN 9 1 1 Field ... Report NaN NaN 10 1 1 Field ... soc 1990.0 77.831512 11 1 1 Field ... soc 1991.0 78.501766 12 1 1 Field ... soc 1992.0 78.916339 13 1 1 Field ... soc 1993.0 78.707094 14 1 1 Field ... soc 1994.0 78.191686 15 1 1 Field ... soc 1995.0 78.573085 16 1 1 Field ... soc 1996.0 78.724598 17 1 1 Field ... soc 1997.0 79.043935 18 1 1 Field ... soc 1998.0 78.343111 19 1 1 Field ... soc 1999.0 78.872767 20 1 1 Field ... soc 2000.0 79.916413 [21 rows x 17 columns]
By default all the tables are returned and the column
source_tabletells us the source table for each row. Sinceresultsis a property attribute, which does not take in any argument, we can only decide this when calling therunmethod as shown below.>>> model.run(report_name='soc') >>> model.results CheckpointID SimulationID Zone year soc source_table 0 1 1 Field 1990.0 77.831512 soc 1 1 1 Field 1991.0 78.501766 soc 2 1 1 Field 1992.0 78.916339 soc 3 1 1 Field 1993.0 78.707094 soc 4 1 1 Field 1994.0 78.191686 soc 5 1 1 Field 1995.0 78.573085 soc 6 1 1 Field 1996.0 78.724598 soc 7 1 1 Field 1997.0 79.043935 soc 8 1 1 Field 1998.0 78.343111 soc 9 1 1 Field 1999.0 78.872767 soc 10 1 1 Field 2000.0 79.916413 soc
The above example has dataset only from one database table specified at run time.
See also
Related API:
get_simulated_output().- get_simulated_output(self, report_names: 'Union[str, list]', axis=0, **kwargs)
Reads report data from CSV files generated by the simulation. More Advanced table-merging arguments will be introduced soon.
Parameters:
- report_names: (str, iterable)
Name or list names of report tables to read. These should match the report names in the simulation output.
- axis: int, Optional. Default to 0
concatenation axis numbers for multiple reports or database tables. if axis is 0, source_table column is populated to show source of the data for each row
Returns:
pd.DataFrameConcatenated DataFrame containing the data from the specified reports.
Raises:
- ValueError
If any of the requested report names are not found in the available tables.
- RuntimeError
If the simulation has not been
runsuccessfully before attempting to read data.
Examples
>>> from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel >>> model = ApsimModel(model='Maize') # replace with your path to the apsim template model >>> model.run() # if we are going to use get_simulated_output, no need to provide the report name in ``run()`` method >>> df = model.get_simulated_output(report_names="Report") SimulationName SimulationID CheckpointID ... Maize.Total.Wt Yield Zone 0 Simulation 1 1 ... 1728.427 8469.616 Field 1 Simulation 1 1 ... 920.854 4668.505 Field 2 Simulation 1 1 ... 204.118 555.047 Field 3 Simulation 1 1 ... 869.180 3504.000 Field 4 Simulation 1 1 ... 1665.475 7820.075 Field 5 Simulation 1 1 ... 2124.740 8823.517 Field 6 Simulation 1 1 ... 1235.469 3587.101 Field 7 Simulation 1 1 ... 951.808 2939.152 Field 8 Simulation 1 1 ... 1986.968 8379.435 Field 9 Simulation 1 1 ... 1689.966 7370.301 Field [10 rows x 16 columns]
This method also handles more than one reports as shown below.
>>> model.add_db_table( ... variable_spec=[ ... '[Clock].Today.Year as year', ... 'sum([Soil].Nutrient.TotalC)/1000 from 01-jan to [clock].Today as soc' ... ], ... rename='soc' ... ) # inspect the reports >>> model.inspect_model('Models.Report', fullpath=False) ['Report', 'soc'] >>> model.run() >>> model.get_simulated_output(["soc", "Report"], axis=0) CheckpointID SimulationID ... Maize.Grain.N Maize.Total.Wt 0 1 1 ... NaN NaN 1 1 1 ... NaN NaN 2 1 1 ... NaN NaN 3 1 1 ... NaN NaN 4 1 1 ... NaN NaN 5 1 1 ... NaN NaN 6 1 1 ... NaN NaN 7 1 1 ... NaN NaN 8 1 1 ... NaN NaN 9 1 1 ... NaN NaN 10 1 1 ... NaN NaN 11 1 1 ... 11.178291 1728.427114 12 1 1 ... 6.226327 922.393712 13 1 1 ... 0.752357 204.108770 14 1 1 ... 4.886844 869.242545 15 1 1 ... 10.463854 1665.483701 16 1 1 ... 11.253916 2124.739830 17 1 1 ... 5.044417 1261.674967 18 1 1 ... 3.955080 951.303260 19 1 1 ... 11.080878 1987.106980 20 1 1 ... 9.751001 1693.893386 [21 rows x 17 columns]
>>> model.get_simulated_output(['soc', 'Report'], axis=1) CheckpointID SimulationID ... Maize.Grain.N Maize.Total.Wt 0 1 1 ... 11.178291 1728.427114 1 1 1 ... 6.226327 922.393712 2 1 1 ... 0.752357 204.108770 3 1 1 ... 4.886844 869.242545 4 1 1 ... 10.463854 1665.483701 5 1 1 ... 11.253916 2124.739830 6 1 1 ... 5.044417 1261.674967 7 1 1 ... 3.955080 951.303260 8 1 1 ... 11.080878 1987.106980 9 1 1 ... 9.751001 1693.893386 10 1 1 ... NaN NaN [11 rows x 19 columns]
See also
Related API:
results.- run(self, report_name: 'Union[tuple, list, str]' = None, simulations: 'Union[tuple, list]' = None, clean_up: 'bool' = True, verbose: 'bool' = False, timeout: 'int' = 800, cpu_count: 'int' = -1, **kwargs)
- Run APSIM model simulations to write the results either to SQLite database or csv file. Does not collect the
simulated output into memory. Please see related APIs:
resultsandget_simulated_output().
Parameters
- report_name: Union[tuple, list, str], optional
Defaults to APSIM default Report Name if not specified. - If iterable, all report tables are read and aggregated into one DataFrame.
- simulations: Union[tuple, list], optional
List of simulation names to run. If None, runs all simulations.
- clean_up: bool, optional
If True, removes the existing database before running.
- verbose: bool, optional
If True, enables verbose output for debugging. The method continues with debugging info anyway if the run was unsuccessful
- timeout: int, default is 800 seconds
Enforces a timeout and returns a CompletedProcess-like object.
- cpu_count: int, Optional default is -1, referring to all threads
This parameter is useful when the number of simulations are more than 1, below that performance differences are minimal added in 0.39.11.21+
- kwargs: **dict
Additional keyword arguments, e.g., to_csv=True, use this flag to correct results from a csv file directly stored at the location of the running apsimx file.
Warning:
In my experience with Models.exe, CSV outputs are not always overwritten; after edits, stale results can persist. Proceed with caution.
Returns
Instance of the respective model class e.g., ApsimModel, ExperimentManager.
RuntimeErrorRaised if the
APSIMrun is unsuccessful. Common causes includemissing meteorological files, mismatched simulationstartdates withweatherdata, or otherconfiguration issues.
Example:
Instantiate an
apsimNGpy.core.apsim.ApsimModelobject and run:from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel model = ApsimModel(model= 'Maize')# replace with your path to the apsim template model model.run(report_name = "Report") # check if the run was successful model.ran_ok 'True'
Note
Updates the
ran_okflag toTrueif no error was encountered.See also
Related APIs:
resultsandget_simulated_output().- rename_model(self, model_type, *, old_name, new_name) (inherited)
Renames a model within the APSIM simulation tree.
This method searches for a model of the specified type and current name, then updates its name to the new one provided. After renaming, it saves the updated simulation file to enforce the changes.
- model_typestr
The type of the model to rename (e.g., “Manager”, “Clock”, etc.).
- old_namestr
The current name of the model to be renamed.
- new_namestr
The new name to assign to the model.
- selfobject
Returns the modified object to allow for method chaining.
- ValueError
If the model of the specified type and name is not found.
Tip
This method uses
get_or_check_modelwith action=’get’ to locate the model, and then updates the model’sNameattribute. The model is serialized using thesave()immediately after to apply and enfoce the change.>>> from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel >>> model = ApsimModel(model = 'Maize', out_path='my_maize.apsimx') >>> model.rename_model(model_type="Models.Core.Simulation", old_name ='Simulation', new_name='my_simulation') # check if it has been successfully renamed >>> model.inspect_model(model_type='Models.Core.Simulation', fullpath = False) ['my_simulation'] # The alternative is to use model.inspect_file to see your changes >>> model.inspect_file()
└── Models.Core.Simulations: .Simulations ├── Models.Storage.DataStore: .Simulations.DataStore ├── Models.Core.Folder: .Simulations.Replacements │ └── Models.PMF.Plant: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize │ └── Models.Core.Folder: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Atrium │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.CG4141 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Dekalb_XL82 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.GH_5009 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.GH_5019WX │ ├── Models.Core.Folder: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_100 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_103 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_105 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_108 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_110 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_112 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_115 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_120 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_130 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_80 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_90 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_95 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_100 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_103 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_105 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_108 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_110 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_112 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_115 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_120 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_130 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_80 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_90 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_95 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.HY_110 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.LY_110 │ │ └── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.P1197 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Hycorn_40 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Hycorn_53 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Katumani │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Laila │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Makueni │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Melkassa │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.NSCM_41 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_3153 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_33M54 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_34K77 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_38H20 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_39G12 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_39V43 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.malawi_local │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh12 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh16 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh17 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh18 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh19 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.r201 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.r215 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc401 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc501 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc601 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc623 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc625 │ └── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.sr52 └── Models.Core.Simulation: .Simulations.Simulation ├── Models.Clock: .Simulations.Simulation.Clock ├── Models.Core.Zone: .Simulations.Simulation.Field │ ├── Models.Manager: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Fertilise at sowing │ ├── Models.Fertiliser: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Fertiliser │ ├── Models.Manager: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Harvest │ ├── Models.PMF.Plant: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize │ │ └── Models.Core.Folder: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Atrium │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.CG4141 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Dekalb_XL82 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.GH_5009 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.GH_5019WX │ │ ├── Models.Core.Folder: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_100 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_103 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_105 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_108 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_110 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_112 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_115 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_120 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_130 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_80 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_90 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_95 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_100 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_103 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_105 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_108 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_110 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_112 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_115 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_120 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_130 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_80 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_90 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_95 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.HY_110 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.LY_110 │ │ │ └── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.P1197 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Hycorn_40 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Hycorn_53 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Katumani │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Laila │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Makueni │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Melkassa │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.NSCM_41 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_3153 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_33M54 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_34K77 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_38H20 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_39G12 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_39V43 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.malawi_local │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh12 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh16 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh17 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh18 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh19 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.r201 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.r215 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc401 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc501 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc601 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc623 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc625 │ │ └── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.sr52 │ ├── Models.Report: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Report │ ├── Models.Soils.Soil: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Chemical: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Chemical │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Solute: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.NH4 │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Solute: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.NO3 │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Organic: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Organic │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Physical: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Physical │ │ │ └── Models.Soils.SoilCrop: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Physical.MaizeSoil │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Solute: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Urea │ │ └── Models.Soils.Water: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Water │ ├── Models.Manager: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Sow using a variable rule │ └── Models.Surface.SurfaceOrganicMatter: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.SurfaceOrganicMatter ├── Models.Graph: .Simulations.Simulation.Graph │ └── Models.Series: .Simulations.Simulation.Graph.Series ├── Models.MicroClimate: .Simulations.Simulation.MicroClimate ├── Models.Soils.Arbitrator.SoilArbitrator: .Simulations.Simulation.SoilArbitrator ├── Models.Summary: .Simulations.Simulation.Summary └── Models.Climate.Weather: .Simulations.Simulation.WeatherSee also
Related APIs:
add_model(),clone_model(), andmove_model().- clone_model(self, model_type, model_name, adoptive_parent_type, rename=None, adoptive_parent_name=None) (inherited)
Clone an existing
modeland move it to a specified parent within the simulation structure. The function modifies the simulation structure by adding the cloned model to the designated parent.This function is useful when a model instance needs to be duplicated and repositioned in the
APSIMsimulation hierarchy without manually redefining its structure.Parameters:
- model_type: Models
The type of the model to be cloned, e.g.,
Models.SimulationorModels.Clock.- model_name: str
The unique identification name of the model instance to be cloned, e.g.,
"clock1".- adoptive_parent_type: Models
The type of the new parent model where the cloned model will be placed.
- rename: str, optional
The new name for the cloned model. If not provided, the clone will be renamed using the original name with a
_clonesuffix.- adoptive_parent_name: str, optional
The name of the parent model where the cloned model should be moved. If not provided, the model will be placed under the default parent of the specified type.
- in_place: bool, optional
If
True, the cloned model remains in the same location but is duplicated. Defaults toFalse.
Returns:
None
Example:
Create a cloned version of
"clock1"and place it under"Simulation"with the new name"new_clock:>>> from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel >>> model = ApsimModel('Maize', out_path='my_maize.apsimx') >>> model.clone_model(model_type='Models.Core.Simulation', model_name="Simulation", ... rename="Sim2", adoptive_parent_type = 'Models.Core.Simulations', ... adoptive_parent_name='Simulations') >>> model.inspect_file() └── Simulations: .Simulations ├── DataStore: .Simulations.DataStore ├── Sim2: .Simulations.Sim2 │ ├── Clock: .Simulations.Sim2.Clock │ ├── Field: .Simulations.Sim2.Field │ │ ├── Fertilise at sowing: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Fertilise at sowing │ │ ├── Fertiliser: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Fertiliser │ │ ├── Harvest: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Harvest │ │ ├── Maize: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Maize │ │ ├── Report: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Report │ │ ├── Soil: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Soil │ │ │ ├── Chemical: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Soil.Chemical │ │ │ ├── NH4: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Soil.NH4 │ │ │ ├── NO3: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Soil.NO3 │ │ │ ├── Organic: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Soil.Organic │ │ │ ├── Physical: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Soil.Physical │ │ │ │ └── MaizeSoil: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Soil.Physical.MaizeSoil │ │ │ ├── Urea: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Soil.Urea │ │ │ └── Water: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Soil.Water │ │ ├── Sow using a variable rule: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Sow using a variable rule │ │ ├── SurfaceOrganicMatter: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.SurfaceOrganicMatter │ │ └── soc_table: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.soc_table │ ├── Graph: .Simulations.Sim2.Graph │ │ └── Series: .Simulations.Sim2.Graph.Series │ ├── MicroClimate: .Simulations.Sim2.MicroClimate │ ├── SoilArbitrator: .Simulations.Sim2.SoilArbitrator │ ├── Summary: .Simulations.Sim2.Summary │ └── Weather: .Simulations.Sim2.Weather └── Simulation: .Simulations.Simulation ├── Clock: .Simulations.Simulation.Clock ├── Field: .Simulations.Simulation.Field │ ├── Fertilise at sowing: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Fertilise at sowing │ ├── Fertiliser: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Fertiliser │ ├── Harvest: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Harvest │ ├── Maize: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize │ ├── Report: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Report │ ├── Soil: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil │ │ ├── Chemical: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Chemical │ │ ├── NH4: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.NH4 │ │ ├── NO3: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.NO3 │ │ ├── Organic: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Organic │ │ ├── Physical: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Physical │ │ │ └── MaizeSoil: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Physical.MaizeSoil │ │ ├── Urea: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Urea │ │ └── Water: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Water │ ├── Sow using a variable rule: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Sow using a variable rule │ ├── SurfaceOrganicMatter: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.SurfaceOrganicMatter │ └── soc_table: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.soc_table ├── Graph: .Simulations.Simulation.Graph │ └── Series: .Simulations.Simulation.Graph.Series ├── MicroClimate: .Simulations.Simulation.MicroClimate ├── SoilArbitrator: .Simulations.Simulation.SoilArbitrator ├── Summary: .Simulations.Simulation.Summary └── Weather: .Simulations.Simulation.Weather
See also
Related APIs:
add_model()andmove_model().- static find_model(model_name: 'str') (inherited)
Find a model from the Models namespace and return its path.
Parameters:
- model_name: (str)
The name of the model to find.
- model_namespace: (object, optional):
The root namespace (defaults to Models).
- path: (str, optional)
The accumulated path to the model.
- Returns:
str: The full path to the model if found, otherwise None.
Example:
>>> from apsimNGpy import core # doctest: >>> model =core.apsim.ApsimModel(model = "Maize", out_path ='my_maize.apsimx') >>> model.find_model("Weather") 'Models.Climate.Weather' >>> model.find_model("Clock") 'Models.Clock'
- add_model(self, model_type, adoptive_parent, rename=None, adoptive_parent_name=None, verbose=False, source='Models', source_model_name=None, override=True, **kwargs) (inherited)
Adds a model to the Models Simulations namespace.
Some models are restricted to specific parent models, meaning they can only be added to compatible models. For example, a Clock model cannot be added to a Soil model.
Parameters:
- model_type: (str or Models object)
The type of model to add, e.g.,
Models.Clockor just"Clock". if the APSIM Models namespace is exposed to the current script, then model_class can be Models.Clock without strings quotes- rename (str):
The new name for the model.
- adoptive_parent: (Models object)
The target parent where the model will be added or moved e.g
Models.ClockorClockas string all are valid- adoptive_parent_name: (Models object, optional)
Specifies the parent name for precise location. e.g.,
Models.Core.SimulationorSimulationsall are valid- source: Models, str, CoreModel, ApsimModel object: defaults to Models namespace.
The source can be an existing Models or string name to point to one of the default model examples, which we can extract the model from
- override: bool, optional defaults to
True. When
True(recommended), it deletes any model with the same name and type at the suggested parent location before adding the new model ifFalseand proposed model to be added exists at the parent location;APSIMautomatically generates a new name for the newly added model. This is not recommended.- Returns:
None:
Modelsare modified in place, so models retains the same reference.Caution
Added models from
Models namespaceare initially empty. Additional configuration is required to set parameters. For example, after adding a Clock module, you must set the start and end dates.Example
>>> from apsimNGpy import core >>> from apsimNGpy.core.core import Models >>> model = core.apsim.ApsimModel("Maize") >>> model.remove_model(Models.Clock) # first delete the model >>> model.add_model(Models.Clock, adoptive_parent=Models.Core.Simulation, rename='Clock_replaced', verbose=False)
>>> model.add_model(model_class=Models.Core.Simulation, adoptive_parent=Models.Core.Simulations, rename='Iowa')
>>> model.preview_simulation()
>>> model.add_model( ... Models.Core.Simulation, ... adoptive_parent='Simulations', ... rename='soybean_replaced', ... source='Soybean') # basically adding another simulation from soybean to the maize simulation
See also
Related APIs:
clone_model()andmove_model().- detect_model_type(self, model_instance: 'Union[str, Models]') (inherited)
Detects the model type from a given APSIM model instance or path string.
- edit_model_by_path(self, path: 'str', **kwargs) (inherited)
Edit a model component located by an APSIM path, dispatching to type-specific editors.
This method resolves a node under
instance.Simulationsusing an APSIM path, then edits that node by delegating to an editor based on the node’s runtime type. It supports common APSIM NG components (e.g., Weather, Manager, Cultivar, Clock, Soil subcomponents, Report, SurfaceOrganicMatter). Unsupported types raiseNotImplementedError.Parameters
- pathstr
APSIM path to a target node under
self.Simulations(e.g., ‘.Simulations.Simulations.Weather’ or a similar canonical path).
kwargs
Additional keyword arguments specific to the model type. Atleast one key word argument is required. These vary by component:
- Models.Climate.Weather:
weather_file(str): Path to the weather.metfile.- Models.Clock:
Date properties such as
StartandEndin ISO format (e.g., ‘2021-01-01’).- Models.Manager:
Variables to update in the Manager script using
update_mgt_by_path.- Soils.Physical | Soils.Chemical | Soils.Organic | Soils.Water:
Variables to replace using
replace_soils_values_by_path.Valid
parametersare shown below;Soil Model Type
Supported key word arguments
Physical
AirDry, BD, DUL, DULmm, Depth, DepthMidPoints, KS, LL15, LL15mm, PAWC, PAWCmm, SAT, SATmm, SW, SWmm, Thickness, ThicknessCumulative
Organic
CNR, Carbon, Depth, FBiom, FInert, FOM, Nitrogen, SoilCNRatio, Thickness
Chemical
Depth, PH, Thickness
- Models.Report:
- report_name (str):
Name of the report model (optional depending on structure).
- variable_spec` (list[str] or str):
Variables to include in the report.
- set_event_names` (list[str], optional):
Events that trigger the report.
- Models.PMF.Cultivar:
- commands (str):
APSIM path to the cultivar parameter to update.
- values: (Any)
Value to assign.
- cultivar_manager: (str)
Name of the Manager script managing the cultivar, which must contain the
CultivarNameparameter. Required to propagate updated cultivar values, as APSIM treats cultivars as read-only.
Warning
- ValueError
If the model instance is not found, required kwargs are missing, or
kwargsis empty.- NotImplementedError
If the logic for the specified
model_classis not implemented.
Examples
Edit a Manager script parameter:
model.edit_model_by_path( ".Simulations.Simulation.Field.Sow using a variable rule", verbose=True, Population=10)
Point a Weather component to a new
.metfile:model.edit_model_by_path( path=".Simulations.Simulation.Weather", FileName="data/weather/Ames_2020.met")
Change Clock dates:
model.edit_model_by_path( ".Simulations.Simulation.Clock", StartDate="2020-01-01", EndDate="2020-12-31")
Update soil water properties at a specific path:
model.edit_model_by_path( ".Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Physical", LL15="[0.26, 0.18, 0.10, 0.12]")
Apply cultivar edits:
model.edit_model_by_path( ".Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh18", sowed=True, **{"Phenology.EmergencePhase.Photo-period": "Short"} )
See also
Related API:
edit_model().- add_base_replacements(self) (inherited)
Add base replacements with all available models of type Plants and then start from there to add more @return: self
- edit_model(self, model_type: 'str', model_name: 'str', simulations: 'Union[str, list]' = 'all', exclude=None, verbose=False, **kwargs) (inherited)
Modify various APSIM model components by specifying the model type and name across given simulations.
Tip
Editing APSIM models in apsimNGpy does not require placing the target model inside a Replacements folder or node. However, when modifying cultivar parameters, it can be helpful to include a Replacements folder containing the relevant plant definition hosting that cultivar. In many cases, apsimNGpy will handle this automatically.
Selective Editing
Selective editing allows you to apply modifications only to certain simulations. This is not possible when the same model instance is shared through a common Replacements folder. For reliable selective editing, each simulation should ideally reference a uniquely named model. However, even when model names are not unique, apsimNGpy still enables targeted editing through two mechanisms:
Exclusion strategy You can explicitly exclude simulations to which the edits should not be applied.
Specification strategy You can explicitly specify which simulations should have their models edited or replaced with new parameters.
Parameters
- model_type: str, required
Type of the model component to modify (e.g., ‘Clock’, ‘Manager’, ‘Soils.Physical’, etc.).
- simulations: Union[str, list], optional
A simulation name or list of simulation names in which to search. Defaults to all simulations in the model.
- model_name: str, required
Name of the model instance to modify.
- verbose: bool, optional
print the status of the editing activities
- exclude: Union[str, None, Iterable[str]], optional,default is None
Added in ‘V0.39.10.20’+. It is used to specify which simulation should be skipped during the editing process, in case there are more than simulations
kwargs
Additional keyword arguments specific to the model type. Atleast one key word argument is required. These vary by component:
- Models.Climate.Weather:
weather_file(str): Path to the weather.metfile.- Models.Clock:
Date properties such as
StartandEndin ISO format (e.g., ‘2021-01-01’).- Models.Manager:
Variables to update in the Manager script using
update_mgt_by_path.- Soils.Physical | Soils.Chemical | Soils.Organic | Soils.Water:
Variables to replace using
replace_soils_values_by_path.Valid
parametersare shown below;Soil Model Type
Supported key word arguments
Physical
AirDry, BD, DUL, DULmm, Depth, DepthMidPoints, KS, LL15, LL15mm, PAWC, PAWCmm, SAT, SATmm, SW, SWmm, Thickness, ThicknessCumulative
Organic
CNR, Carbon, Depth, FBiom, FInert, FOM, Nitrogen, SoilCNRatio, Thickness
Chemical
Depth, PH, Thickness
- Models.Report:
- report_name (str):
Name of the report model (optional depending on structure).
- variable_spec` (list[str] or str):
Variables to include in the report.
- set_event_names` (list[str], optional):
Events that trigger the report.
- Models.PMF.Cultivar:
- commands (str):
APSIM path to the cultivar parameter to update.
- values: (Any)
Value to assign.
- cultivar_manager: (str)
Name of the Manager script managing the cultivar, which must contain the
CultivarNameparameter. Required to propagate updated cultivar values, as APSIM treats cultivars as read-only.
Warning
- ValueError
If the model instance is not found, required kwargs are missing, or
kwargsis empty.- NotImplementedError
If the logic for the specified
model_classis not implemented.
Examples:
from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel model = ApsimModel(model='Maize')
Example of how to edit a cultivar model:
model.edit_model(model_type='Cultivar', simulations='Simulation', commands='[Phenology].Juvenile.Target.FixedValue', values=256, model_name='B_110', new_cultivar_name='B_110_edited', cultivar_manager='Sow using a variable rule')
Edit a soil organic matter module:
model.edit_model( model_type='Organic', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Organic', Carbon=1.23)
Edit multiple soil layers:
model.edit_model( model_type='Organic', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Organic', Carbon=[1.23, 1.0])
Example of how to edit solute models:
model.edit_model( model_type='Solute', simulations='Simulation', model_name='NH4', InitialValues=0.2) model.edit_model( model_class='Solute', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Urea', InitialValues=0.002)
Edit a manager script:
model.edit_model( model_type='Manager', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Sow using a variable rule', population=8.4)
Edit surface organic matter parameters:
model.edit_model( model_type='SurfaceOrganicMatter', simulations='Simulation', model_name='SurfaceOrganicMatter', InitialResidueMass=2500) model.edit_model( model_type='SurfaceOrganicMatter', simulations='Simulation', model_name='SurfaceOrganicMatter', InitialCNR=85)
Edit Clock start and end dates:
model.edit_model( model_type='Clock', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Clock', Start='2021-01-01', End='2021-01-12')
Edit report _variables:
model.edit_model( model_type='Report', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Report', variable_spec='[Maize].AboveGround.Wt as abw')
Multiple report _variables:
model.edit_model( model_type='Report', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Report', variable_spec=[ '[Maize].AboveGround.Wt as abw', '[Maize].Grain.Total.Wt as grain_weight'])
the best way to edit cultivar with minimal error is to use a dict of commands as follows.
params = { "[Leaf].Photosynthesis.RUE.FixedValue": 1.8984705340394, "[Phenology].GrainFilling.Target.FixedValue": 710, "[Grain].MaximumGrainsPerCob.FixedValue": 810, "[Phenology].FloweringToGrainFilling.Target.FixedValue": 215, "[Phenology].MaturityToHarvestRipe.Target.FixedValue": 100, "[Maize].Grain.MaximumPotentialGrainSize.FixedValue": 0.867411373063701, "[Grain].MaximumNConc.InitialPhase.InitialNconc.FixedValue": 0.05, '[Maize].Root.SpecificRootLength.FixedValue': 135, '[Maize].Root.RootFrontVelocity.PotentialRootFrontVelocity.PreFlowering.RootFrontVelocity.FixedValue': 22, '[Rachis].DMDemands.Structural.DMDemandFunction.MaximumOrganWt.FixedValue': 36
}
- model.edit_model_by_path(model_type=’Models.PMF.Cultivar, model_name=’Dekalb_XL82’,
commands=params, cultivar_manager=’Sow using a variable rule, parameter_name=’CultivarName’ )
See also
Related API:
edit_model_by_path().- static inspect_settable_attributes(model_type) (inherited)
Inspect and return all settable attributes for a given APSIM model type.
This method identifies which attributes of a model can be modified by the user. APSIM model classes typically expose writable parameters through setter methods following the naming convention
set_<AttributeName>(). This function extracts all such attributes and returns them in a clean, user-friendly list.Added in v0.39.12.21
Parameters
- model_typetype or str
The APSIM model class or the registered model name. This value is validated and resolved to a concrete APSIM model class via
validate_model_obj().
Returns
- list of str
A list of attribute names that can be set on the specified model. These correspond to all public APSIM parameters for which a
set_<AttributeName>method exists. Theset_prefix is removed for clarity, so the list contains clean parameter names.
Notes
This method does not set or modify any attributes—its purpose is diagnostic and introspective.
Useful for error reporting, documentation, and informing users which parameters are valid inputs for
edit_model()or related methods.
Examples
from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel sm = ApsimModel('Maize') sm.inspect_settable_attributes(model_type='Models.Surface.SurfaceOrganicMatter')
['Canopies', 'Children', 'Enabled', 'InitialCNR', 'InitialCPR', 'InitialResidueMass', 'InitialResidueName', 'InitialResidueType', 'InitialStandingFraction', 'IsHidden', 'Name', 'Node', 'Parent', 'ReadOnly', 'ResourceName', 'Structure']
sm.inspect_settable_attributes(Models.WaterModel.WaterBalance)
['CN2Bare', 'CNCov', 'CNRed', 'CatchmentArea', 'Children', 'Depth', 'DiffusConst', 'DiffusSlope', 'DischargeWidth', 'Enabled', 'Eo', 'IsHidden', 'KLAT', 'Name', 'Node', 'PSIDul', 'Parent', 'PoreInteractionIndex', 'PotentialInfiltration', 'PrecipitationInterception', 'ReadOnly', 'ResourceName', 'Runon', 'SW', 'SWCON', 'Salb', 'Structure', 'SummerCona', 'SummerDate', 'SummerU', 'Thickness', 'Water', 'WaterTable', 'WinterCona', 'WinterDate', 'WinterU']
Added in version 0.39.12.21.
- find_model_in_replacements(self, model_type, model_name) (inherited)
checks whether the model to be edited is in the replacement, there is no point to contnue editing from individual simulations
- add_report_variable(self, variable_spec: 'Union[list, str, tuple]', report_name: 'str' = None, set_event_names: 'Union[str, list]' = None, simulations=None) (inherited)
This adds a report variable to the end of other _variables, if you want to change the whole report use change_report
Parameters
- variable_spec: str, required.
list of text commands for the report _variables e.g., ‘[Clock].Today as Date’
- param report_name: str, optional.
Name of the report variable if not specified, the first accessed report object will be altered
- set_event_names: list or str, optional.
A list of APSIM events that trigger the recording of _variables. Defaults to [‘[Clock].EndOfYear’] if not provided.
Returns
returns instance of apsimNGpy.core.core.apsim.ApsimModel or apsimNGpy.core.core.apsim.CoreModel
Raise
raises an
ValueErrorif a report is not foundExamples
>>> from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel >>> model = ApsimModel('Maize') >>> model.add_report_variable(variable_spec = '[Clock].Today as Date', report_name = 'Report') # isnepct the report >>> model.inspect_model_parameters(model_type='Models.Report', model_name='Report') {'EventNames': ['[Maize].Harvesting'], 'VariableNames': ['[Clock].Today', '[Maize].Phenology.CurrentStageName', '[Maize].AboveGround.Wt', '[Maize].AboveGround.N', '[Maize].Grain.Total.Wt*10 as Yield', '[Maize].Grain.Wt', '[Maize].Grain.Size', '[Maize].Grain.NumberFunction', '[Maize].Grain.Total.Wt', '[Maize].Grain.N', '[Maize].Total.Wt', '[Clock].Today as Date']} The new report variable is appended at the end of the existing ones
See also
Related APIs:
remove_report_variable()andadd_db_table().- remove_report_variable(self, variable_spec: 'Union[list, tuple, str]', report_name: 'str | None' = None) (inherited)
Remove one or more variable expressions from an APSIM Report component.
Parameters
- variable_specstr | list[str] | tuple[str, …]
Variable expression(s) to remove, e.g.
"[Clock].Today"or"[Clock].Today as Date". You may pass a single string or a list/tuple. Matching is done by exact text after whitespace normalization (consecutive spaces collapsed), so minor spacing differences are tolerated.- report_namestr, optional
Name of the Report component to modify. If
None, the default resolver (self._get_report) is used to locate the target report.
Returns
- list[str]
The updated list of variable expressions remaining in the report (in original order, without duplicates).
Notes
Variables not present are ignored (no error raised).
Order is preserved; duplicates are removed.
The model is saved at the end of this call.
Examples
>>> model= CoreModel('Maize') >>> model.add_report_variable(variable_spec='[Clock].Today as Date', report_name='Report') >>> model.inspect_model_parameters('Models.Report', 'Report')['VariableNames'] ['[Clock].Today', '[Maize].Phenology.CurrentStageName', '[Maize].AboveGround.Wt', '[Maize].AboveGround.N', '[Maize].Grain.Total.Wt*10 as Yield', '[Maize].Grain.Wt', '[Maize].Grain.Size', '[Maize].Grain.NumberFunction', '[Maize].Grain.Total.Wt', '[Maize].Grain.N', '[Maize].Total.Wt', '[Clock].Today as Date'] >>> model.remove_report_variable(variable_spec='[Clock].Today as Date', report_name='Report') >>> model.inspect_model_parameters('Models.Report', 'Report')['VariableNames'] ['[Clock].Today', '[Maize].Phenology.CurrentStageName', '[Maize].AboveGround.Wt', '[Maize].AboveGround.N', '[Maize].Grain.Total.Wt*10 as Yield', '[Maize].Grain.Wt', '[Maize].Grain.Size', '[Maize].Grain.NumberFunction', '[Maize].Grain.Total.Wt', '[Maize].Grain.N', '[Maize].Total.Wt']
See also
Related APIs:
add_report_variable()andadd_db_table().- remove_model(self, model_type: 'Models', model_name) (inherited)
Removes a model from the APSIM Models.Simulations namespace.
- model_type: Models
The type of the model to remove (e.g.,
Models.Clock). This parameter is required.- model_name: str, optional
The name of the specific model instance to remove (e.g.,
"Clock"). If not provided, all models of the specified type may be removed.
Returns:
None
Example:
from apsimNGpy import core from apsimNGpy.core.core import Models model = core.base_data.load_default_simulations(crop = 'Maize') model.remove_model(Models.Clock) #deletes the clock node model.remove_model(Models.Climate.Weather) #deletes the weather node
See also
Related APIs:
clone_model()andadd_model().- move_model(self, model_type: 'Models', new_parent_type: 'Models', model_name: 'str' = None, new_parent_name: 'str' = None, verbose: 'bool' = False, simulations: 'Union[str, list]' = None) (inherited)
Args:
- model_type: Models
type of model tied to Models Namespace
- new_parent_type: Models.
New model parent type (Models)
- model_name: str
Name of the model e.g., Clock, or Clock2, whatever name that was given to the model
- new_parent_name``: str
The new parent names =Field2, this field is optional but important if you have nested simulations
Returns:
returns instance of apsimNGpy.core.core.apsim.ApsimModel or apsimNGpy.core.core.apsim.CoreModel
- replicate_file(self, k: 'int', path: 'os.PathLike' = None, suffix: 'str' = 'replica') (inherited)
Replicates a file
ktimes. Parameters ———- path:str default is NoneIf specified, the copies will be placed in that dir_path with incremented filenames. If no path is specified, copies are created in the same dir_path as the original file, also with incremented filenames.
- k int:
The number of copies to create.
- suffix: str, optional
a suffix to attach with the copies. Default to “replicate”
Returns:
A generator(str) is returned.
- get_crop_replacement(self, Crop) (inherited)
- param Crop:
crop to get the replacement
- return:
System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerable APSIM plant object
- inspect_model_parameters(self, model_type: 'Union[Models, str]', model_name: 'str', simulations: 'Union[str, list]' = <UserOptionMissing>, parameters: 'Union[list, set, tuple, str]' = 'all', exclude: 'list | set | tuple | str' = None, **kwargs) (inherited)
Inspect the input parameters of a specific
APSIMmodel type instance within selected simulations.This method consolidates functionality previously spread across
examine_management_info,read_cultivar_params, and other inspectors, allowing a unified interface for querying parameters of interest across a wide range of APSIM models.Parameters
- model_type: str required
The name of the model class to inspect (e.g., ‘Clock’, ‘Manager’, ‘Physical’, ‘Chemical’, ‘Water’, ‘Solute’). Shorthand names are accepted (e.g., ‘Clock’, ‘Weather’) as well as fully qualified names (e.g., ‘Models.Clock’, ‘Models.Climate.Weather’).
- simulations: Union[str, list]
A single simulation name or a list of simulation names within the APSIM context to inspect.
- model_name: str
The name of the specific model instance within each simulation. For example, if
model_class='Solute',model_namemight be ‘NH4’, ‘Urea’, or another solute name.- parameters: Union[str, set, list, tuple], optional
A specific parameter or a collection of parameters to inspect. Defaults to
'all', in which case all accessible attributes are returned. For layered models like Solute, valid parameters includeDepth,InitialValues,SoluteBD,Thickness, etc.- exclude: Union[str, list, tuple], optional
used to exclude a few simulations and include only the rest of the simulations Added in v0.39.10.20+
- kwargs:
Reserved for future compatibility; currently unused.
Returns
Union[dict, list, pd.DataFrame, Any] The format depends on the model type as shown below:
- Weather:
file path(s) as string(s)
- Clock:
dictionary with start and end datetime objects (or a single datetime if only one is requested).
- Manager:
dictionary of script parameters.
- Soil-related:
pandas DataFrame of layered values.
- Report:
A dictionary with
VariableNamesandEventNames.
Cultivar: dictionary of parameter strings.
Raises
ValueErrorIf the specified model or simulation is not found or arguments are invalid.
NotImplementedErrorIf the model type is unsupported by the current interface.
Requirements
APSIM Next Generation Python bindings (
apsimNGpy)Python 3.10+
Examples:
from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel model_instance = ApsimModel('Maize')
Inspect full soil
Organicprofile:model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Organic', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Organic') CNR Carbon Depth FBiom ... FOM Nitrogen SoilCNRatio Thickness 0 12.0 1.20 0-150 0.04 ... 347.129032 0.100 12.0 150.0 1 12.0 0.96 150-300 0.02 ... 270.344362 0.080 12.0 150.0 2 12.0 0.60 300-600 0.02 ... 163.972144 0.050 12.0 300.0 3 12.0 0.30 600-900 0.02 ... 99.454133 0.025 12.0 300.0 4 12.0 0.18 900-1200 0.01 ... 60.321981 0.015 12.0 300.0 5 12.0 0.12 1200-1500 0.01 ... 36.587131 0.010 12.0 300.0 6 12.0 0.12 1500-1800 0.01 ... 22.191217 0.010 12.0 300.0 [7 rows x 9 columns]
Inspect soil
Physicalprofile:model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Physical', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Physical') AirDry BD DUL ... SWmm Thickness ThicknessCumulative 0 0.130250 1.010565 0.521000 ... 78.150033 150.0 150.0 1 0.198689 1.071456 0.496723 ... 74.508522 150.0 300.0 2 0.280000 1.093939 0.488438 ... 146.531282 300.0 600.0 3 0.280000 1.158613 0.480297 ... 144.089091 300.0 900.0 4 0.280000 1.173012 0.471584 ... 141.475079 300.0 1200.0 5 0.280000 1.162873 0.457071 ... 137.121171 300.0 1500.0 6 0.280000 1.187495 0.452332 ... 135.699528 300.0 1800.0 [7 rows x 17 columns]
Inspect soil
Chemicalprofile:model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Chemical', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Chemical') Depth PH Thickness 0 0-150 8.0 150.0 1 150-300 8.0 150.0 2 300-600 8.0 300.0 3 600-900 8.0 300.0 4 900-1200 8.0 300.0 5 1200-1500 8.0 300.0 6 1500-1800 8.0 300.0
Inspect one or more specific parameters:
model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Organic', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Organic', parameters='Carbon') Carbon 0 1.20 1 0.96 2 0.60 3 0.30 4 0.18 5 0.12 6 0.12
Inspect more than one specific properties:
model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Organic', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Organic', parameters=['Carbon', 'CNR']) Carbon CNR 0 1.20 12.0 1 0.96 12.0 2 0.60 12.0 3 0.30 12.0 4 0.18 12.0 5 0.12 12.0 6 0.12 12.0
Inspect Report module attributes:
model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Report', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Report') {'EventNames': ['[Maize].Harvesting'], 'VariableNames': ['[Clock].Today', '[Maize].Phenology.CurrentStageName', '[Maize].AboveGround.Wt', '[Maize].AboveGround.N', '[Maize].Grain.Total.Wt*10 as Yield', '[Maize].Grain.Wt', '[Maize].Grain.Size', '[Maize].Grain.NumberFunction', '[Maize].Grain.Total.Wt', '[Maize].Grain.N', '[Maize].Total.Wt']}
Specify only EventNames:
model_instance.inspect_model_parameters(‘Report’, simulations=’Simulation’, model_name=’Report’, parameters=’EventNames’) {‘EventNames’: [‘[Maize].Harvesting’]}
Inspect a weather file path:
model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Weather', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Weather') '%root%/Examples/WeatherFiles/AU_Dalby.met'
Inspect manager script parameters:
model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Manager', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Sow using a variable rule') {'Crop': 'Maize', 'StartDate': '1-nov', 'EndDate': '10-jan', 'MinESW': '100.0', 'MinRain': '25.0', 'RainDays': '7', 'CultivarName': 'Dekalb_XL82', 'SowingDepth': '30.0', 'RowSpacing': '750.0', 'Population': '10'}
Inspect manager script by specifying one or more parameters:
model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Manager', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Sow using a variable rule', parameters='Population') {'Population': '10'}
Inspect cultivar parameters:
model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Cultivar', simulations='Simulation', model_name='B_110') # lists all path specifications for B_110 parameters abd their values model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Cultivar', simulations='Simulation', model_name='B_110', parameters='[Phenology].Juvenile.Target.FixedValue') {'[Phenology].Juvenile.Target.FixedValue': '210'}
Inspect surface organic matter module:
model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Models.Surface.SurfaceOrganicMatter', simulations='Simulation', model_name='SurfaceOrganicMatter') {'NH4': 0.0, 'InitialResidueMass': 500.0, 'StandingWt': 0.0, 'Cover': 0.0, 'LabileP': 0.0, 'LyingWt': 0.0, 'InitialCNR': 100.0, 'P': 0.0, 'InitialCPR': 0.0, 'SurfOM': <System.Collections.Generic.List[SurfOrganicMatterType] object at 0x000001DABDBB58C0>, 'C': 0.0, 'N': 0.0, 'NO3': 0.0}
Inspect a few parameters as needed:
model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Models.Surface.SurfaceOrganicMatter', simulations='Simulation', ... model_name='SurfaceOrganicMatter', parameters={'InitialCNR', 'InitialResidueMass'}) {'InitialCNR': 100.0, 'InitialResidueMass': 500.0}
Inspect a clock:
model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Clock', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Clock') {'End': datetime.datetime(2000, 12, 31, 0, 0), 'Start': datetime.datetime(1990, 1, 1, 0, 0)}
Inspect a few Clock parameters as needed:
model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Clock', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Clock', parameters='End') datetime.datetime(2000, 12, 31, 0, 0)
Access specific components of the datetime object e.g., year, month, day, hour, minute:
model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Clock', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Clock', parameters='Start').year # gets the start year only 1990
Inspect solute models:
model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Solute', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Urea') Depth InitialValues SoluteBD Thickness 0 0-150 0.0 1.010565 150.0 1 150-300 0.0 1.071456 150.0 2 300-600 0.0 1.093939 300.0 3 600-900 0.0 1.158613 300.0 4 900-1200 0.0 1.173012 300.0 5 1200-1500 0.0 1.162873 300.0 6 1500-1800 0.0 1.187495 300.0 model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Solute', simulations='Simulation', model_name='NH4', parameters='InitialValues') InitialValues 0 0.1 1 0.1 2 0.1 3 0.1 4 0.1 5 0.1 6 0.1
See also
Related API:
inspect_model_parameters_by_path()- inspect_model_parameters_by_path(self, path, *, parameters: 'Union[list, set, tuple, str]' = None) (inherited)
Inspect and extract parameters from a model component specified by its path.
Parameters:
- path: str required
The path relative to the Models.Core.Simulations Node
- parameters: Union[str, set, list, tuple], optional
A specific parameter or a collection of parameters to inspect. Defaults to
'all', in which case all accessible attributes are returned. For layered models like Solute, valid parameters includeDepth,InitialValues,SoluteBD,Thickness, etc.- kwargs:
Reserved for future compatibility; currently unused.
Returns
Union[dict, list, pd.DataFrame, Any] The format depends on the model type as shown below:
- Weather:
file path(s) as string(s)
- Clock:
dictionary with start and end datetime objects (or a single datetime if only one is requested).
- Manager:
dictionary of script parameters.
- Soil-related:
pandas DataFrame of layered values.
- Report:
A dictionary with
VariableNamesandEventNames.
Cultivar: dictionary of parameter strings.
Raises
ValueErrorIf the specified model or simulation is not found or arguments are invalid.
NotImplementedErrorIf the model type is unsupported by the current interface.
Requirements
APSIM Next Generation Python bindings (
apsimNGpy)Python 3.10+
See also
Related API:
inspect_model_parameters()Others:inspect_model(),inspect_file()- edit_cultivar(self, *, CultivarName: 'str', commands: 'str', values: 'Any', **kwargs) (inherited)
@deprecated Edits the parameters of a given cultivar. we don’t need a simulation name for this unless if you are defining it in the manager section, if that it is the case, see update_mgt.
- Requires:
required a replacement for the crops
Args:
CultivarName (str, required): Name of the cultivar (e.g., ‘laila’).
variable_spec (str, required): A strings representing the parameter paths to be edited.
Returns: instance of the class CoreModel or ApsimModel
Example:
('[Grain].MaximumGrainsPerCob.FixedValue', '[Phenology].GrainFilling.Target.FixedValue') - values: values for each command (e.g., (721, 760)).
- update_cultivar(self, *, parameters: 'dict', simulations: 'Union[list, tuple]' = None, clear=False, **kwargs) (inherited)
Update cultivar parameters
- parameters: (dict, required)
dictionary of cultivar parameters to update.
- simulationsstr optional
List or tuples of simulation names to update if
Noneupdate all simulations.- clear (bool, optional)
If
Trueremove all existing parameters, by defaultFalse.
- recompile_edited_model(self, out_path: 'os.PathLike') (inherited)
Args:
out_path: os.PathLike object this method is called to convert the simulation object from ConverterReturnType to model like objectreturn:self- update_mgt_by_path(self, *, path: 'str', fmt='.', **kwargs) (inherited)
Parameters
- path: str
A complete node path to the script manager e.g. ‘.Simulations.Simulation.Field.Sow using a variable rule’
- fmt: str
seperator for formatting the path e.g., “.”. Other characters can be used with caution, e.g., / and clearly declared in fmt argument. If you want to use the forward slash, it will be ‘/Simulations/Simulation/Field/Sow using a variable rule’, fmt = ‘/’
- **kwargs:
Corresponding keyword arguments representing the paramters in the script manager and their values. Values is what you want to change to; Example here
Population=8.2, values should be entered with their corresponding data types e.g., int, float, bool,str etc.
Returns:
Instance of apsimNgpy.core.ApsimModel or apsimNgpy.core.experimentmanager.ExperimentManager
- replace_model_from(self, model, model_type: 'str', model_name: 'str' = None, target_model_name: 'str' = None, simulations: 'str' = None) (inherited)
@deprecated and will be removed function has not been maintained for a long time, use it at your own risk
Replace a model, e.g., a soil model with another soil model from another APSIM model. The method assumes that the model to replace is already loaded in the current model and the same class as a source model. e.g., a soil node to soil node, clock node to clock node, et.c
Parameters:
model: Path to the APSIM model file or a CoreModel instance.
- model_type: (str):
Class name (as string) of the model to replace (e.g., “Soil”).
- model_name: (str, optional)
Name of the model instance to copy from the source model. If not provided, the first match is used.
- target_model_name: (str, optional)
Specific simulation name to target for replacement. Only used when replacing Simulation-level objects.
- simulations (str, optional):
Simulation(s) to operate on. If None, applies to all.
- Returns:
self: To allow method chaining.
- Raises:
ValueError: Ifmodel_classis “Simulations” which is not allowed for replacement.
- update_mgt(self, *, management: 'Union[dict, tuple]', simulations: '[list, tuple]' = <UserOptionMissing>, out: '[Path, str]' = None, reload: 'bool' = True, **kwargs) (inherited)
Update management settings in the model. This method handles one management parameter at a time.
Parameters
- management: dict or tuple
A dictionary or tuple of management parameters to update. The dictionary should have ‘Name’ as the key for the management script’s name and corresponding values to update. Lists are not allowed as they are mutable and may cause issues with parallel processing. If a tuple is provided, it should be in the form (param_name, param_value).
- simulations: list of str, optional
List of simulation names to update. If
None, updates all simulations. This is not recommended for large numbers of simulations as it may result in a high computational load.- out: str or pathlike, optional
Path to save the edited model. If
None, uses the default output path specified inself.out_pathorself.model_info.path. No need to callsave_edited_fileafter updating, as this method handles saving.
Returns
Returns the instance of the respective model class for method chaining.
..note:
Ensure that the `management` parameter is provided in the correct format to avoid errors. - This method does not perform `validation` on the provided `management` dictionary beyond checking for key existence. - If the specified management script or parameters do not exist, they will be ignored.
- preview_simulation(self, watch=False) (inherited)
Open the current simulation in the APSIM Next Gen GUI.
This first saves the in-memory simulation to
out_pathand then launches the APSIM Next Gen GUI (viaget_apsim_bin_path()) so you can inspect the model tree and make quick edits side by side.Parameters
- watchbool, default False
If True, Python will listen for GUI edits and sync them back into the model instance in (near) real time. This feature is experimental.
Returns
- None
This function performs a side effect (opening the GUI) and does not return a value.
Raises
- FileNotFoundError
If the file does not exist after
save().- RuntimeError
If the APSIM Next Gen executable cannot be located or the GUI fails to start.
Tip
The file opened in the GUI is a saved copy of this Python object. Changes made in the GUI are not propagated back to the
ApsimModelinstance unless you setwatch=True. Otherwise, to continue working in Python with GUI edits, save the file in APSIM and re-load it, for example:ApsimModel("gui_edited_file_path.apsimx")
Examples
1. Preview only
from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel model = ApsimModel("Maize", out_path="test_.apsimx") model.preview_simulation()
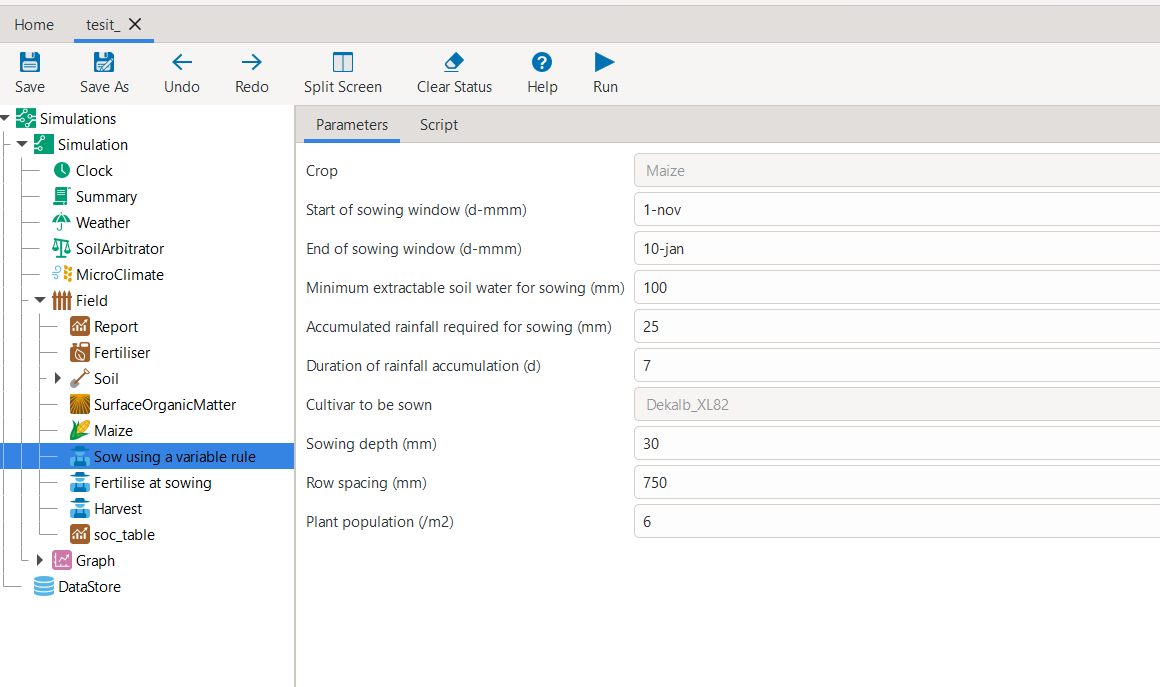
2. Preview and edit simultaneously
After opening the APSIMX file in the GUI via the watching mode (
watch=True), you can modify any parameters using GUI interface. The Example given below involved changing parameters such as Plant population (/m²), Cultivar to be sown, and Row spacing (mm) in the Sow using a variable rule script and finally, checked whether the changes were successful by inspecting the model.model.preview_simulation(watch=True)
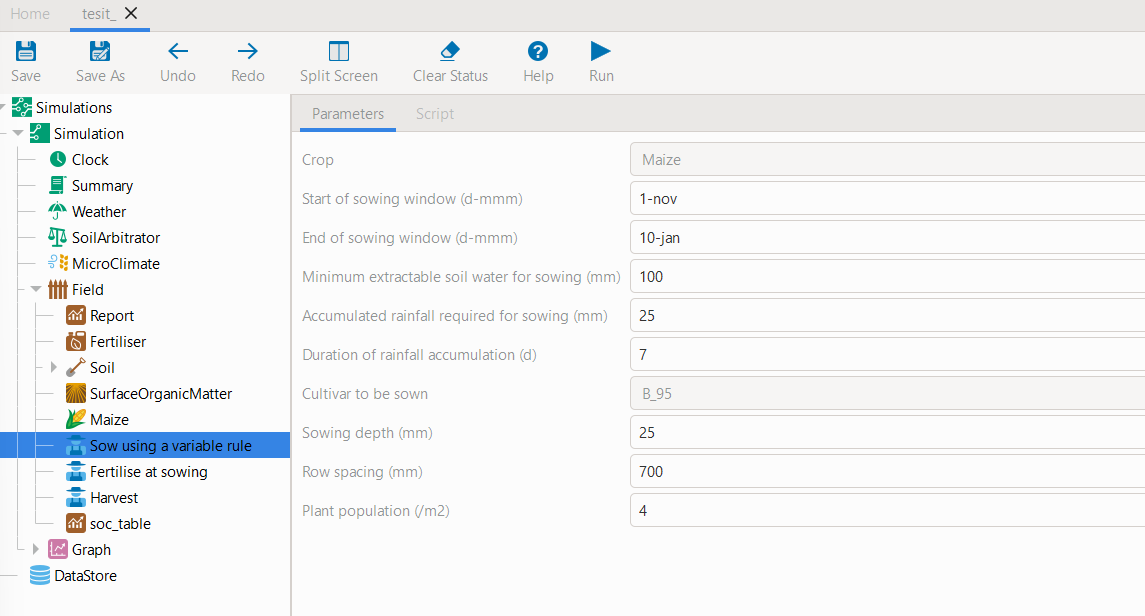
Example console output when
watch=True:2025-10-24 13:05:08,480 - INFO - Watching for GUI edits... Save in APSIM to sync back. 2025-10-24 13:05:08,490 - INFO - Press Ctrl+C in this cell to stop. APSIM GUI saved. Syncing model... 2025-10-24 13:05:24,112 - INFO - Watching terminated successfully.
Tip
When
watch=True, follow the console instructions. One critical step is that you must pressCtrl+Cto stop watching.Checking if changes were successfully propagated back
model.inspect_model_parameters("Models.Manager", "Sow using a variable rule")
{'Crop': '[Maize]', 'StartDate': '1-nov', 'EndDate': '10-jan', 'MinESW': '100', 'MinRain': '25', 'RainDays': '7', 'CultivarName': 'B_95', 'SowingDepth': '25', 'RowSpacing': '700', 'Population': '4'}Tip
Depending on your environment, you may need to close the GUI window to continue or follow the prompts shown after termination.
- replace_met_file(self, *, weather_file: 'Union[Path, str]', simulations=<UserOptionMissing>, exclude: 'set | str | tuple | list' = None, **kwargs) (inherited)
Deprecated since version 0.**x**: This helper will be removed in a future release. Prefer newer weather configuration utilities or set the
FileNameproperty on weather nodes directly.Replace the
FileNameof everyModels.Climate.Weathernode under one or more simulations so they point to a new.metfile.This method traverses the APSIM NG model tree under each selected simulation and updates the weather component(s) in-place. Version-aware traversal is used:
If
APSIM_VERSION_NO > BASE_RELEASE_NOorAPSIM_VERSION_NO == GITHUB_RELEASE_NO: useModelTools.find_all_in_scope()to findModels.Climate.Weathernodes.Otherwise: fall back to
sim.FindAllDescendants[Models.Climate.Weather]().
Parameters
- weather_fileUnion[pathlib.Path, str]
Path to the
.metfile. May be absolute or relative to the current working directory. The path must exist at call time; otherwise aFileNotFoundErroris raised.- simulationsAny, optional
Simulation selector forwarded to
find_simulations(). If left asMissingOption(default) (or if your implementation acceptsNone), all simulations yielded byfind_simulations()are updated. Acceptable types depend on yourfind_simulations()contract (e.g., iterable of names, single name, or sentinel).- exclude: (str, tuple, list), optional
used to eliminate a given simulation from getting updated Added in 0.39.10.20+
- **kwargs
Ignored. Reserved for backward compatibility and future extensions.
Returns
- Self
The current model/manager instance to support method chaining.
Raises
- FileNotFoundError
If
weather_filedoes not exist.- Exception
Any exception raised by
find_simulations()or underlying APSIM traversal utilities is propagated unchanged.
Side Effects
Mutates the model by setting
met.FileName = os.path.realpath(weather_file)for each matchedModels.Climate.Weathernode.Notes
No-op safety: If a simulation has no Weather nodes, that simulation is silently skipped.
Path normalization: The stored path is the canonical real path (
os.path.realpath).Thread/process safety: This operation mutates in-memory model state and is not inherently thread-safe. Coordinate external synchronization if calling concurrently.
Examples
Update all simulations to use a local
Ames.met:model.replace_met_file(weather_file="data/weather/Ames.met")
Update only selected simulations:
model.replace_met_file( weather_file=Path("~/wx/Boone.met").expanduser(), simulations=("Sim_A", "Sim_B") )
See Also
find_simulations : Resolve and yield simulation objects by name/selector. ModelTools.find_all_in_scope : Scope-aware traversal utility. Models.Climate.Weather : APSIM NG weather component.
- get_weather_from_file(self, weather_file, simulations=None)
Point targeted APSIM Weather nodes to a local
.metfile.The function name mirrors the semantics of
get_weather_from_webbut sources the weather from disk. If the provided path lacks the.metsuffix, it is appended. The file must exist on disk.Parameters
- weather_file: str | Path
Path (absolute or relative) to a
.metfile. If the suffix is missing,.metis appended. AFileNotFoundErroris raised if the final path does not exist. The path is resolved to an absolute path to avoid ambiguity.- simulations: None | str | Iterable[str], optional
Which simulations to update: -
None(default): update all Weather nodes found underSimulations. -stror iterable of names: only update Weather nodes within the namedsimulation(s). A
ValueErroris raised if a requested simulation has no Weather nodes.
Returns
Instance of the model for method chaining
Raises
- FileNotFoundError
If the resolved
.metfile does not exist.- ValueError
If any requested simulation exists but contains no Weather nodes.
Side Effects
Sets
w.FileNamefor each targetedModels.Climate.Weathernode to the resolved path ofweather_file. The file is not copied; only the path inside the APSIM document is changed.Notes
APSIM resolves relative paths relative to the
.apsimxfile. Using an absolute path (the default here) reduces surprises across working directories.Replacement folders that contain Weather nodes are also updated when
simulationsisNone(i.e., “update everything in scope”).
Examples
Update all Weather nodes:
from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel model = ApsimModel("Maize") model.get_weather_from_file("data/ames_2020.met")
Update only two simulations (suffix added automatically):
model.get_weather_from_file("data/ames_2020", simulations=("Simulation",))
See also
Related APIs:
edit_model()andedit_model_by_path().- get_weather_from_web(self, lonlat: 'tuple', start: 'int', end: 'int', simulations=<UserOptionMissing>, source='nasa', filename=None) (inherited)
Replaces the weather (met) file in the model using weather data fetched from an online source. Internally, calls get_weather_from_file after downloading the weather
Parameters:
- lonlat: tuple
A tuple containing the longitude and latitude coordinates.
- start: int
Start date for the weather data retrieval.
- end: int
End date for the weather data retrieval.
- simulations: str | list[str] default is all or None list of simulations or a singular simulation
name, where to place the weather data, defaults to None, implying
allthe available simulations- source: str default is ‘nasa’
Source of the weather data.
- filename: str default is generated using the base name of the apsimx file in use, and the start and
end years Name of the file to save the retrieved data. If None, a default name is generated.
- Returns:
model object with the corresponding file replaced with the fetched weather data.
Examples
>>> from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel >>> model = ApsimModel(model= "Maize") >>> model.get_weather_from_web(lonlat = (-93.885490, 42.060650), start = 1990, end = 2001)
Changing weather data with non-matching start and end dates in the simulation will lead to RuntimeErrors. To avoid this, first check the start and end date before proceeding as follows:
>>> dt = model.inspect_model_parameters(model_class='Clock', model_name='Clock', simulations='Simulation') >>> start, end = dt['Start'].year, dt['End'].year # output: 1990, 2000
- change_report(self, *, command: 'str', report_name='Report', simulations=None, set_DayAfterLastOutput=None, **kwargs) (inherited)
Set APSIM report _variables for specified simulations.
This function allows you to set the variable names for an APSIM report in one or more simulations.
Parameters
- command: str
The new report string that contains variable names.
- report_name: str
The name of the APSIM report to update defaults to Report.
- simulations: list of str, optional
A list of simulation names to update. If
None, the function will update the report for all simulations.
Returns
None
- extract_soil_physical(self, simulations: '[tuple, list]' = None) (inherited)
Find physical soil
Parameters
simulation, optionalSimulation name, if
Noneuse the first simulation.
Returns
APSIM Models.Soils.Physical object
- extract_any_soil_physical(self, parameter, simulations: '[list, tuple]' = <UserOptionMissing>) (inherited)
Extracts soil physical parameters in the simulation
- Args::
parameter(_string_): string e.g. DUL, SATsimulations(string, optional): Targeted simulation name. Defaults to None.
- inspect_model(self, model_type: 'Union[str, Models]', fullpath=True, **kwargs) (inherited)
Inspect the model types and returns the model paths or names.
When is it needed?
useful if you want to identify the paths or name of the model for further editing the model e.g., with the
in edit_modelmethod.Parameters
- model_classtype | str
The APSIM model type to search for. You may pass either a class (e.g., Models.Clock, Models.Manager) or a string. Strings can be short names (e.g., “Clock”, “Manager”) or fully qualified (e.g., “Models.Core.Simulation”, “Models.Climate.Weather”, “Models.Core.IPlant”). Please see from The list of classes or model types from the Models Namespace below. Red represents the modules, and this method
will throw an error if only a module is supplied. The list constitutes the classes or model types under each module
- Models:
Models.Clock
Models.Fertiliser
Models.Irrigation
Models.Manager
Models.Memo
Models.MicroClimate
Models.Operations
Models.Report
Models.Summary
- Models.Climate:
Models.Climate.Weather
- Models.Core:
Models.Core.Folder
Models.Core.Simulation
Models.Core.Simulations
Models.Core.Zone
- Models.Factorial:
Models.Factorial.Experiment
Models.Factorial.Factors
Models.Factorial.Permutation
- Models.PMF:
Models.PMF.Cultivar
Models.PMF.Plant
- Models.Soils:
Models.Soils.Arbitrator.SoilArbitrator
Models.Soils.CERESSoilTemperature
Models.Soils.Chemical
Models.Soils.Nutrients.Nutrient
Models.Soils.Organic
Models.Soils.Physical
Models.Soils.Sample
Models.Soils.Soil
Models.Soils.SoilCrop
Models.Soils.Solute
Models.Soils.Water
- Models.Storage:
Models.Storage.DataStore
- Models.Surface:
Models.Surface.SurfaceOrganicMatter
- Models.WaterModel:
Models.WaterModel.WaterBalance
- fullpathbool, optional (default: False)
If False, return the model name only. If True, return the model’s full path relative to the Simulations root.
Returns
- list[str]
A list of model names or full paths, depending on
fullpath.
Examples:
from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel from apsimNGpy.core.core import Models
load default
maizemodule:model = ApsimModel('Maize')
Find the path to all the manager scripts in the simulation:
model.inspect_model(Models.Manager, fullpath=True) [.Simulations.Simulation.Field.Sow using a variable rule', '.Simulations.Simulation.Field.Fertilise at sowing', '.Simulations.Simulation.Field.Harvest']
Inspect the full path of the Clock Model:
model.inspect_model(Models.Clock) # gets the path to the Clock models ['.Simulations.Simulation.Clock']
Inspect the full path to the crop plants in the simulation:
model.inspect_model(Models.Core.IPlant) # gets the path to the crop model ['.Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize']
Or use the full string path as follows:
model.inspect_model(Models.Core.IPlant, fullpath=False) # gets you the name of the crop Models ['Maize']
Get the full path to the fertilizer model:
model.inspect_model(Models.Fertiliser, fullpath=True) ['.Simulations.Simulation.Field.Fertiliser']
The models from APSIM Models namespace are abstracted to use strings. All you need is to specify the name or the full path to the model enclosed in a stirng as follows:
model.inspect_model('Clock') # get the path to the clock model ['.Simulations.Simulation.Clock']
Alternatively, you can do the following:
model.inspect_model('Models.Clock') ['.Simulations.Simulation.Clock']
Repeat inspection of the plant model while using a
string:model.inspect_model('IPlant') ['.Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize']
Inspect using the full model namespace path:
model.inspect_model('Models.Core.IPlant')
What about the weather model?:
model.inspect_model('Weather') # inspects the weather module ['.Simulations.Simulation.Weather']
Alternative:
# or inspect using full model namespace path model.inspect_model('Models.Climate.Weather') ['.Simulations.Simulation.Weather']
Try finding the path to the cultivar model:
model.inspect_model('Cultivar', fullpath=False) # list all available cultivar names ['Hycorn_53', 'Pioneer_33M54', 'Pioneer_38H20','Pioneer_34K77', 'Pioneer_39V43','Atrium', 'Laila', 'GH_5019WX']
# we can get only the names of the cultivar models using the full string path:
model.inspect_model('Models.PMF.Cultivar', fullpath = False) ['Hycorn_53','Pioneer_33M54', 'Pioneer_38H20','Pioneer_34K77', 'Pioneer_39V43','Atrium', 'Laila', 'GH_5019WX']
Tip
- Models can be inspected either by importing the Models namespace or by using string paths. The most reliable
approach is to provide the full model path—either as a string or as the
Modelsobject.- However, remembering full paths can be tedious, so allowing partial model names or references can significantly
save time during development and exploration.
Note
You do not need to import
Modelsif you pass a string; both short and fully qualified names are supported.“Full path” is the APSIM tree path relative to the Simulations node (be mindful of the difference between Simulations (root) and an individual Simulation).
See also
Related APIs:
inspect_file(),inspect_model_parameters(),inspect_model_parameters_by_path()- property configs(inherited)
records activities or modifications to the model including changes to the file
- replace_soils_values_by_path(self, node_path: 'str', indices: 'list' = None, **kwargs) (inherited)
set the new values of the specified soil object by path. only layers parameters are supported.
Unfortunately, it handles one soil child at a time e.g.,
Physicalat a goParameters:
- node_path: (str, required):
complete path to the soil child of the Simulations e.g.,Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Organic. Use`copy path to node function in the GUI to get the real path of the soil node.
- indices: (list, optional)
defaults to none but could be the position of the replacement values for arrays
- **kwargs: (key word arguments)
This carries the parameter and the values e.g., BD = 1.23 or BD = [1.23, 1.75] if the child is
Physical, orCarbonif the child isOrganicraises: `ValueError if none of the key word arguments, representing the paramters are specified
- returns:
Instance of the model object
Example:
from apsimNGpy.core.base_data import load_default_simulations model = load_default_simulations(crop ='Maize', simulations_object=False) # initiate model. model = CoreModel(model) # ``replace`` with your intended file path model.replace_soils_values_by_path(node_path='.Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Organic', indices=[0], Carbon =1.3) sv= model.get_soil_values_by_path('.Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Organic', 'Carbon') output # {'Carbon': [1.3, 0.96, 0.6, 0.3, 0.18, 0.12, 0.12]}
- replace_soil_property_values(self, *, parameter: 'str', param_values: 'list', soil_child: 'str', simulations: 'list' = <UserOptionMissing>, indices: 'list' = None, crop=None, **kwargs) (inherited)
Replaces values in any soil property array. The soil property array.
parameter: str: parameter name e.g., NO3, ‘BD’param_values: list or tuple: values of the specified soil property name to replacesoil_child: str: sub child of the soil component e.g., organic, physical etc.simulations: list: list of simulations to where the child is found ifnot found, all current simulations will receive the new values, thus defaults to None
indices: list. Positions in the array which will be replaced. Please note that unlike C#, python satrt counting from 0crop(str, optional): string for soil water replacement. Default is None- clean_up(self, db=True, verbose=False, csv=True) (inherited)
Clears the file cloned the datastore and associated csv files are not deleted if db is set to False defaults to True.
- Returns:
>>None: This method does not return a value.
Caution
Please proceed with caution, we assume that if you want to clear the model objects, then you don’t need them, but by making copy compulsory, then, we are clearing the edited files
- create_experiment(self, permutation: 'bool' = True, base_name: 'str' = None, **kwargs) (inherited)
@deprecated and will be removed in future versions for this class.
Initialize an
ExperimentManagerinstance, adding the necessary models and factors.Args:
kwargs: Additional parameters for CoreModel.permutation(bool). If True, the experiment uses a permutation node to run unique combinations of the specified factors for the simulation. For example, if planting population and nitrogen fertilizers are provided, each combination of planting population level and fertilizer amount is run as an individual treatment.base_name(str, optional): The name of the base simulation to be moved into the experiment setup. if notprovided, it is expected to be Simulation as the default.
Warning
base_nameis optional but the experiment may not be created if there are more than one base simulations. Therefore, an error is likely.- refresh_model(self) (inherited)
for methods that will alter the simulation objects and need refreshing the second time we call @return: self for method chaining
- add_factor(self, specification: 'str', factor_name: 'str' = None, **kwargs) (inherited)
Adds a factor to the created experiment. Thus, this method only works on factorial experiments
It could raise a value error if the experiment is not yet created.
Under some circumstances, experiment will be created automatically as a permutation experiment.
Parameters:
- specification``: (str), required*
- A specification can be:
multiple values or categories e.g., “[Sow using a variable rule].Script.Population =4, 66, 9, 10”
Range of values e.g, “[Fertilise at sowing].Script.Amount = 0 to 200 step 20”,
- factor_name: (str), required
expected to be the user-desired name of the factor being specified e.g., population
This method is overwritten in
ExperimentManagerclass.@deprecated and will be removed in future versions for this class.
Example:
from apsimNGpy.core import base_data apsim = base_data.load_default_simulations(crop='Maize') apsim.create_experiment(permutation=False) apsim.add_factor(specification="[Fertilise at sowing].Script.Amount = 0 to 200 step 20", factor_name='Nitrogen') apsim.add_factor(specification="[Sow using a variable rule].Script.Population =4 to 8 step 2", factor_name='Population') apsim.run() # doctest: +SKIP
- add_fac(self, model_type, parameter, model_name, values, factor_name=None) (inherited)
Add a factor to the initiated experiment. This should replace add_factor. which has less abstractionn @param model_type: model_class from APSIM Models namespace @param parameter: name of the parameter to fill e.g CNR @param model_name: name of the model @param values: values of the parameter, could be an iterable for case of categorical variables or a string e.g, ‘0 to 100 step 10 same as [0, 10, 20, 30, …]. @param factor_name: name to identify the factor in question @return:
- set_continuous_factor(self, factor_path, lower_bound, upper_bound, interval, factor_name=None) (inherited)
Wraps around
add_factorto add a continuous factor, just for clarity- Args:
factor_path: (str): The path of the factor definition relative to its child node,e.g.,
"[Fertilise at sowing].Script.Amount".
factor_name: (str): The name of the factor.lower_bound: (int or float): The lower bound of the factor.upper_bound: (int or float): The upper bound of the factor.interval: (int or float): The distance between the factor levels.Returns:ApsimModelorCoreModel: An instance ofapsimNGpy.core.core.apsim.ApsimModelorCoreModel.
Example:
from apsimNGpy.core import base_data apsim = base_data.load_default_simulations(crop='Maize') apsim.create_experiment(permutation=False) apsim.set_continuous_factor(factor_path = "[Fertilise at sowing].Script.Amount", lower_bound=100, upper_bound=300, interval=10)
- set_categorical_factor(self, factor_path: 'str', categories: 'Union[list, tuple]', factor_name: 'str' = None) (inherited)
wraps around
add_factor()to add a continuous factor, just for clarity.factor_path: (str, required): path of the factor definition relative to its child node “[Fertilise at sowing].Script.Amount”factor_name: (str) name of the factor.categories: (tuple, list, required): multiple values of a factorreturns:ApsimModelorCoreModel: An instance ofapsimNGpy.core.core.apsim.ApsimModelorCoreModel.
Example:
from apsimNGpy.core import base_data apsim = base_data.load_default_simulations(crop='Maize') apsim.create_experiment(permutation=False) apsim.set_continuous_factor(factor_path = "[Fertilise at sowing].Script.Amount", lower_bound=100, upper_bound=300, interval=10)
- add_crop_replacements(self, _crop: 'str') (inherited)
Adds a replacement folder as a child of the simulations.
Useful when you intend to edit cultivar parameters.
- Args:
_crop(str): Name of the crop to be added to the replacement folder.Returns:ApsimModel: An instance of
apsimNGpy.core.core.apsim.ApsimModelorCoreModel.
Raises:ValueError: If the specified crop is not found.
- get_model_paths(self, cultivar=False)
Select out a few model types to use for building the APSIM file inspections
- inspect_file(self, *, cultivar=False, console=True, **kwargs) (inherited)
Inspects the file by traversing the entire simulation tree, using
inspect_model()under the hoodThis method is important in inspecting the
whole fileand also getting thescripts paths.Parameters
- cultivar: (bool)
To include cultivar paths.
- console: (bool)
Prints to the console if True
Examples
from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel model = ApsimModel('Maize') model.inspect_file(cultivar=False)
# output
└── Models.Core.Simulations: .Simulations ├── Models.Storage.DataStore: .Simulations.DataStore ├── Models.Core.Folder: .Simulations.Replacements │ └── Models.PMF.Plant: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize └── Models.Core.Simulation: .Simulations.Simulation ├── Models.Clock: .Simulations.Simulation.Clock ├── Models.Core.Zone: .Simulations.Simulation.Field │ ├── Models.Manager: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Fertilise at sowing │ ├── Models.Fertiliser: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Fertiliser │ ├── Models.Manager: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Harvest │ ├── Models.PMF.Plant: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize │ ├── Models.Report: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Report │ ├── Models.Soils.Soil: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Chemical: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Chemical │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Solute: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.NH4 │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Solute: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.NO3 │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Organic: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Organic │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Physical: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Physical │ │ │ └── Models.Soils.SoilCrop: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Physical.MaizeSoil │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Solute: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Urea │ │ └── Models.Soils.Water: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Water │ ├── Models.Manager: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Sow using a variable rule │ └── Models.Surface.SurfaceOrganicMatter: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.SurfaceOrganicMatter ├── Models.Graph: .Simulations.Simulation.Graph │ └── Models.Series: .Simulations.Simulation.Graph.Series ├── Models.MicroClimate: .Simulations.Simulation.MicroClimate ├── Models.Soils.Arbitrator.SoilArbitrator: .Simulations.Simulation.SoilArbitrator ├── Models.Summary: .Simulations.Simulation.Summary └── Models.Climate.Weather: .Simulations.Simulation.WeatherTurn cultivar paths on as follows:
model.inspect_file(cultivar=True)
# output
└── Models.Core.Simulations: .Simulations ├── Models.Storage.DataStore: .Simulations.DataStore ├── Models.Core.Folder: .Simulations.Replacements │ └── Models.PMF.Plant: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize │ └── Models.Core.Folder: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Atrium │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.CG4141 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Dekalb_XL82 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.GH_5009 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.GH_5019WX │ ├── Models.Core.Folder: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_100 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_103 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_105 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_108 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_110 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_112 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_115 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_120 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_130 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_80 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_90 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_95 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_100 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_103 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_105 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_108 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_110 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_112 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_115 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_120 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_130 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_80 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_90 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_95 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.HY_110 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.LY_110 │ │ └── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.P1197 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Hycorn_40 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Hycorn_53 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Katumani │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Laila │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Makueni │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Melkassa │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.NSCM_41 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_3153 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_33M54 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_34K77 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_38H20 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_39G12 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_39V43 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.malawi_local │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh12 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh16 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh17 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh18 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh19 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.r201 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.r215 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc401 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc501 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc601 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc623 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc625 │ └── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.sr52 └── Models.Core.Simulation: .Simulations.Simulation ├── Models.Clock: .Simulations.Simulation.Clock ├── Models.Core.Zone: .Simulations.Simulation.Field │ ├── Models.Manager: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Fertilise at sowing │ ├── Models.Fertiliser: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Fertiliser │ ├── Models.Manager: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Harvest │ ├── Models.PMF.Plant: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize │ │ └── Models.Core.Folder: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Atrium │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.CG4141 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Dekalb_XL82 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.GH_5009 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.GH_5019WX │ │ ├── Models.Core.Folder: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_100 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_103 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_105 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_108 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_110 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_112 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_115 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_120 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_130 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_80 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_90 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_95 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_100 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_103 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_105 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_108 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_110 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_112 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_115 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_120 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_130 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_80 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_90 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_95 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.HY_110 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.LY_110 │ │ │ └── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.P1197 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Hycorn_40 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Hycorn_53 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Katumani │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Laila │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Makueni │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Melkassa │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.NSCM_41 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_3153 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_33M54 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_34K77 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_38H20 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_39G12 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_39V43 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.malawi_local │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh12 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh16 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh17 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh18 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh19 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.r201 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.r215 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc401 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc501 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc601 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc623 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc625 │ │ └── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.sr52 │ ├── Models.Report: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Report │ ├── Models.Soils.Soil: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Chemical: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Chemical │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Solute: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.NH4 │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Solute: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.NO3 │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Organic: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Organic │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Physical: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Physical │ │ │ └── Models.Soils.SoilCrop: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Physical.MaizeSoil │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Solute: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Urea │ │ └── Models.Soils.Water: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Water │ ├── Models.Manager: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Sow using a variable rule │ └── Models.Surface.SurfaceOrganicMatter: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.SurfaceOrganicMatter ├── Models.Graph: .Simulations.Simulation.Graph │ └── Models.Series: .Simulations.Simulation.Graph.Series ├── Models.MicroClimate: .Simulations.Simulation.MicroClimate ├── Models.Soils.Arbitrator.SoilArbitrator: .Simulations.Simulation.SoilArbitrator ├── Models.Summary: .Simulations.Simulation.Summary └── Models.Climate.Weather: .Simulations.Simulation.WeatherSee also
Related APIs:
inspect_model(),inspect_model_parameters()
- summarize_numeric(self, data_table: 'Union[str, tuple, list]' = None, columns: 'list' = None, percentiles=(0.25, 0.5, 0.75), round=2)
Summarize numeric columns in a simulated pandas DataFrame. Useful when you want to quickly look at the simulated data
Parameters:
data_table (list, tuple, str): The names of the data table attached to the simulations. defaults to all data tables.
specific (list) columns to summarize.
percentiles (tuple): Optional percentiles to include in the summary.
round (int): number of decimal places for rounding off.
Returns:
pd.DataFrame: A summary DataFrame with statistics for each numeric column.
- add_db_table(self, variable_spec: 'list' = None, set_event_names: 'list' = None, rename: 'str' = None, simulation_name: 'Union[str, list, tuple]' = <UserOptionMissing>) (inherited)
Adds a new database table, which
APSIMcallsReport(Models.Report) to theSimulationunder a Simulation Zone.This is different from
add_report_variablein that it creates a new, named report table that collects data based on a given list of _variables and events. actuParameters:
- variable_spec: (list or str)
A list of APSIM variable paths to include in the report table. If a string is passed, it will be converted to a list.
- set_event_names: (list or str, optional):
- A list of APSIM events that trigger the recording of _variables.
Defaults to [‘[Clock].EndOfYear’] if not provided. other examples include ‘[Clock].StartOfYear’, ‘[Clock].EndOfsimulation’, ‘[crop_name].Harvesting’ etc.
rename: (str): The name of the report table to be added. Defaults to ‘my_table’.
- simulation_name: (str,tuple, or list, Optional)
if specified, the name of the simulation will be searched and will become the parent candidate for the report table. If it is none, all Simulations in the file will be updated with the new db_table
Raises:
ValueError: If no variable_spec is provided.RuntimeError: If no Zone is found in the current simulation scope.Examples:
from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel model = ApsimModel('Maize') model.add_db_table(variable_spec=['[Clock].Today', '[Soil].Nutrient.TotalC[1]/1000 as SOC1'], rename='report2') model.add_db_table(variable_spec=['[Clock].Today', '[Soil].Nutrient.TotalC[1]/1000 as SOC1', '[Maize].Grain.Total.Wt*10 as Yield'], rename='report2', set_event_names=['[Maize].Harvesting','[Clock].EndOfYear' ])
See also
Related APIs:
remove_report_variables()andadd_report_variables().- plot_mva(self, table: pandas.core.frame.DataFrame, time_col: Hashable, response: Hashable, *, expression: str = None, window: int = 5, min_period: int = 1, grouping: Hashable | collections.abc.Sequence[Hashable] | NoneType = None, preserve_start: bool = True, kind: str = 'line', estimator='mean', plot_raw: bool = False, raw_alpha: float = 0.35, raw_linewidth: float = 1.0, auto_datetime: bool = False, ylabel: str | None = None, return_data: bool = False, **kwargs)
Plot a centered moving-average (MVA) of a response using
seaborn.relplot.Enhancements over a direct
relplotcall: - Computes and plots a smoothed series viaapsimNGpy.stats.data_insights.mva(). - Supports multi-column grouping; will auto-construct a composite hue if needed. - Optional overlay of the raw (unsmoothed) series for comparison. - Stable (mergesort) time ordering.Parameters
- tablepandas.DataFrame or str
Data source or table name; if
None, use :pyattr:`results`.- time_colhashable
Time (x-axis) column.
- responsehashable
Response (y) column to smooth.
- expression: str default is None
simple mathematical expression to create new columns from existing columns
- windowint, default=5
MVA window size.
- min_periodint, default=1
Minimum periods for the rolling mean.
- groupinghashable or sequence of hashable, optional
One or more grouping columns.
- preserve_startbool, default=True
Preserve initial values when centering.
- kind{“line”,”scatter”}, default=”line”
Passed to
sns.relplot.- estimatorstr or None, default=”mean”
Passed to
sns.relplot(set toNoneto plot raw observations).- plot_rawbool, default=False
Overlay the raw series on each facet.
- raw_alphafloat, default=0.35
Alpha for the raw overlay.
- raw_linewidthfloat, default=1.0
Line width for the raw overlay.
- auto_datetimebool, default=False
Attempt to convert
time_colto datetime.- ylabelstr, optional
Custom y-axis label; default is generated from window/response.
- return_databool, default=False
If
True, return(FacetGrid, smoothed_df).
Returns
- seaborn.FacetGrid
The relplot grid, or
(grid, smoothed_df)ifreturn_data=True.
Notes
This function calls
seaborn.relplot()and accepts its keyword arguments via**kwargs. See link below for details:https://seaborn.pydata.org/generated/seaborn/relplot.html
- boxplot(self, column, *, table=None, expression: str = None, by=None, figsize=(10, 8), grid=False, **kwargs) (inherited)
Plot a boxplot from simulation results using
pandas.DataFrame.boxplot.Parameters
- columnstr
Column to plot.
- tablestr or pandas.DataFrame, optional
Table name or DataFrame; if omitted, use :pyattr:`results`.
- bystr, optional
Grouping column.
figsize : tuple, default=(10, 8) grid : bool, default=False **kwargs
Forwarded to
pandas.DataFrame.boxplot().Returns
matplotlib.axes.Axes
See also
Related APIs:
cat_plot().- distribution(self, x, *, table=None, expression: str = None, **kwargs) (inherited)
Plot a uni-variate distribution/histogram using
seaborn.histplot().Parameters
- xstr
Numeric column to plot.
- tablestr or pandas.DataFrame, optional
Table name or DataFrame; if omitted, use :pyattr:`results`.
- expression: str default is None
simple mathematical expression to create new columns from existing columns
- **kwargs
Forwarded to
seaborn.histplot().
Raises
- ValueError
If
xis a string-typed column.
Notes
This function calls
seaborn.histplot()and accepts its keyword arguments via**kwargs. See link below for details:https://seaborn.pydata.org/generated/seaborn/histplot.html
- series_plot(self, table=None, expression: str = None, *, x: str = None, y: Union[str, list] = None, hue=None, size=None, style=None, units=None, weights=None, palette=None, hue_order=None, hue_norm=None, sizes=None, size_order=None, size_norm=None, dashes=True, markers=None, style_order=None, estimator='mean', errorbar=('ci', 95), n_boot=1000, seed=None, orient='x', sort=True, err_style='band', err_kws=None, legend='auto', ci='deprecated', ax=None, **kwargs) (inherited)
Just a wrapper for seaborn.lineplot that supports multiple y columns that could be provided as a list
- tablestr | [str] |None | None| pandas.DataFrame, optional. Default is None
If the table names are provided, results are collected from the simulated data, using that table names. If None, results will be all the table names inside concatenated along the axis 0 (not recommended).
- expression: str default is None
simple mathematical expression to create new columns from existing columns
If
yis a list of columns, the data are melted into long form and
the different series are colored by variable name.
- **Kwargs
Additional keyword args and all other arguments are for Seaborn.lineplot. See the reference below for all the kwargs.
reference; https://seaborn.pydata.org/generated/seaborn.lineplot.html
Examples
>>> model.series_plot(x='Year', y='Yield', table='Report') >>> model.series_plot(x='Year', y=['SOC1', 'SOC2'], table='Report')
Examples:
>>> from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel >>> model = ApsimModel(model= 'Maize') # run the results >>> model.run(report_names='Report') >>>model.series_plot(x='Maize.Grain.Size', y='Yield', table='Report') >>>model.render_plot(show=True, ylabel = 'Maize yield', xlabel ='Maize grain size')
Plot two variables:
>>>model.series_plot(x=’Yield’, y=[‘Maize.Grain.N’, ‘Maize.Grain.Size’], table= ‘Report’)
Notes
This function calls
seaborn.lineplot()and accepts its keyword arguments via**kwargs. See link below for detailed explanations:https://seaborn.pydata.org/generated/seaborn/lineplot.html
See also
Related APIs:
plot_mva().- scatter_plot(self, table=None, expression: str = None, *, x=None, y=None, hue=None, size=None, style=None, palette=None, hue_order=None, hue_norm=None, sizes=None, size_order=None, size_norm=None, markers=True, style_order=None, legend='auto', ax=None, **kwargs) (inherited)
Scatter plot using
seaborn.scatterplot()with flexible aesthetic mappings.Parameters
- tablestr | [str] |None | None| pandas.DataFrame, optional. Default is None
If the table names are provided, results are collected from the simulated data, using that table names. If None, results will be all the table names inside concatenated along the axis 0 (not recommended).
- x, y, hue, size, style, palette, hue_order, hue_norm, sizes, size_order, size_norm, markers, style_order, legend, ax
Passed through to
seaborn.scatterplot().- expression: str default is None
simple mathematical expression to create new columns from existing columns
- ** Kwargs
Additional keyword args for Seaborn.
See the reference below for all the kwargs. reference; https://seaborn.pydata.org/generated/seaborn.scatterplot.html
- cat_plot(self, table=None, expression=None, *, x=None, y=None, hue=None, row=None, col=None, kind='strip', estimator='mean', errorbar=('ci', 95), n_boot=1000, seed=None, units=None, weights=None, order=None, hue_order=None, row_order=None, col_order=None, col_wrap=None, height=5, aspect=1, log_scale=None, native_scale=False, formatter=None, orient=None, color=None, palette=None, hue_norm=None, legend='auto', legend_out=True, sharex=True, sharey=True, margin_titles=False, facet_kws=None, **kwargs) (inherited)
Categorical plot wrapper over
seaborn.catplot().
Parameters
table : str or pandas.DataFrame, optional
- expression: str default is None
simple mathematical expression to create new columns from existing columns
x, y, hue, row, col, kind, estimator, errorbar, n_boot, seed, units, weights, order, hue_order, row_order, col_order, col_wrap, height, aspect, log_scale, native_scale, formatter, orient, color, palette, hue_norm, legend, legend_out, sharex, sharey, margin_titles, facet_kws
Passed through to
seaborn.catplot().- **kwargs
Additional keyword args for Seaborn.
Returns
seaborn.axisgrid.FacetGrid
reference https://seaborn.pydata.org/generated/seaborn.catplot.html
Related APIs:
distribution().- reg_plot(self, table=None, expression=None, **kwargs) (inherited)
Wrapper around seaborn.lmplot. V 0.39.10.19+
Kwargs passed to seaborn.lmplot
- xstr or None, optional
Name of column in
datato plot on the x-axis.- ystr or None, optional
Name of column in
datato plot on the y-axis.- huestr or None, optional
Grouping variable that will produce elements with different colors.
- colstr or None, optional
Variable that defines columns of the facet grid.
- rowstr or None, optional
Variable that defines rows of the facet grid.
- palettestr, list, dict, or None, optional
Color palette for different
huelevels.- col_wrapint or None, optional
Wrap the column facets after this many columns.
- heightfloat, default=5
Height (in inches) of each facet.
- aspectfloat, default=1
Aspect ratio of each facet, so width = aspect * height.
- markersstr or list, default=’o’
Marker(s) used for the scatter plot points.
- sharexbool or None, optional
If True, share x-axis limits across facets.
- shareybool or None, optional
If True, share y-axis limits across facets.
- hue_orderlist or None, optional
Order to plot the levels of
hue.- col_orderlist or None, optional
Order to plot the levels of
col.- row_orderlist or None, optional
Order to plot the levels of
row.- legendbool, default=True
If True, add a legend for the
huevariable.- legend_outbool or None, optional
If True, place the legend outside the grid.
- x_estimatorcallable or None, optional
Function to compute a central tendency of
yfor each uniquex(e.g.np.mean). Plot points at that value instead of raw data.- x_binsint or None, optional
Bin the
xvariable into discrete bins before plotting.- x_ci‘ci’, ‘sd’, float, or None, default=’ci’
Size/definition of the confidence band around the estimator in
x_estimator.- scatterbool, default=True
If True, draw the scatter points.
- fit_regbool, default=True
If True, fit and plot a regression line.
- ciint or None, default=95
Size of the bootstrap confidence interval for the regression estimate.
- n_bootint, default=1000
Number of bootstrap samples to compute
ci.- unitsstr or None, optional
Column in
dataidentifying sampling units. Used for clustered bootstrap.- seedint, RandomState, or None, optional
Random seed for reproducible bootstrapping.
- orderint, default=1
Polynomial order of the regression (1 = linear).
- logisticbool, default=False
If True, fit a logistic regression.
- lowessbool, default=False
If True, fit a locally weighted regression (LOWESS).
- robustbool, default=False
If True, use a robust regression estimator.
- logxbool, default=False
If True, estimate the model in log10(x) space.
- x_partialstr, list of str, or None, optional
Columns in
datato regress out ofxbefore plotting.- y_partialstr, list of str, or None, optional
Columns in
datato regress out ofybefore plotting.- truncatebool, default=True
If True, limit the regression line to the data range.
- x_jitterfloat or None, optional
Amount of horizontal jitter to add to scatter points.
- y_jitterfloat or None, optional
Amount of vertical jitter to add to scatter points.
- scatter_kwsdict or None, optional
Additional keyword args passed to the scatter plot (e.g. alpha, s).
- line_kwsdict or None, optional
Additional keyword args passed to the regression line plot.
- facet_kwsdict or None, optional
Additional keyword args passed to seaborn.FacetGrid.
See Also
- seaborn.lmplotHigh-level interface for plotting linear models with faceting.
Tutorial: https://seaborn.pydata.org/tutorial/regression.html#regression-tutorial
- relplot(self, table=None, **kwargs) (inherited)
Plots a relation plot
apsimNGpy.core.config
Module attributes
- apsimNGpy.core.config.configuration
Default value:
Configuration(bin_path='D:\\My_BOX\\Box\\PhD thesis\\Objective two\\morrow plot…
Functions
- apsimNGpy.core.config.any_bin_path_from_env() 'Path'
Finalize resolving the real APSIM bin path or raise a clear error.
APSIM bin path expected in environment variables:keys include:
APSIM_BIN_PATH / APSIM_PATH / APSIM/ Models
- apsimNGpy.core.config.get_apsim_bin_path()
Returns the path to the apsim bin folder from either auto-detection or from the path already supplied by the user through the apsimNGpy config.ini file in the user home directory.
This function is silent does not raise any exception but return empty string in all cases if bin_path is empty or was not found.
Example:
bin_path = get_apsim_bin_path()
See also
- apsimNGpy.core.config.get_bin_use_history()
shows the bins that have been used only those still available on the computer as valid paths are shown.
@return: list[paths]
- apsimNGpy.core.config.list_drives()
for windows-only @return: list of available drives on windows pc
- apsimNGpy.core.config.load_crop_from_disk(crop: 'str', out: 'Union[str, Path]', bin_path=None, cache_path=True, suffix='.apsimx')
Load a default APSIM crop simulation file from disk by specifying only the crop name. This fucntion can literally load anything that resides under the /Examples directory.
Locates and copies an
.apsimxfile associated with the specified crop from the APSIM /Examples directory into a working directory. It is useful when programmatically running default simulations for different crops without manually opening them in GUI.Parameters
- crop: (str)
The name of the crop to load (e.g., ‘Maize’, ‘Soybean’, ‘Barley’, ‘Mungbean’, ‘Pinus’, ‘Eucalyptus’). The name is case-insensitive and must-match an existing
.apsimxfile in the APSIM Examples folder.- out: (str, optional)
A custom output path where the
.apsimxfile should be copied. If not provided, a temporary file will be created in the working directory. this is stamped with the APSIM version being used- bin_path: (str, optional):
no restriction we can laod from another bin path
cache_path: (str, optional):
keep the path in memory for the next request
Returns
str: The path to the copied.apsimxfile ready for further manipulation or simulation.Caution
The method catches the results, so if the file is removed from the disk, there may be issues> If this case is anticipated, turn off the cach_path to False.
Raises
FileNotFoundError: If the APSIM binary path cannot be resolved or the crop simulation file does not exist.Example:
>>> load_crop_from_disk("Maize", out ='my_maize_example.apsimx') 'C:/path/to/temp_uuid_Maize.apsimx'
- apsimNGpy.core.config.scan_drive_for_bin()
This function uses scan_dir_for_bin to scan all drive directories. for Windows only
- apsimNGpy.core.config.set_apsim_bin_path(path: 'Union[str, Path]', raise_errors: 'bool' = True, verbose: 'bool' = False) 'bool'
Validate and write the bin path to the config file, where it is accessed by
get_apsim_bin_path.- pathUnion[str, Path]
The provided
pathshould point to (or contain) the APSIMbindirectory that includes the required binaries:Windows: Models.dll AND Models.exe
macOS/Linux: Models.dll AND Models (unix executable)
If
pathis a parent directory, the function will search recursively to locate a matchingbindirectory. The first match is used.- raise_errorsbool, default is True
Whether to raise an error in case of errors. for testing purposes only
- verbose: bool
whether to print messages to the console or not
- bool
True if the configuration was updated (or already valid and set to the same resolved path), False if validation failed and
raise_errors=False.
- ValueError
If no valid APSIM binary directory is found and
raise_errors=True.
>>> from apsimNGpy.core import config >>> # Check the current path >>> current = config.get_apsim_bin_path() >>> # Set the desired path (either the bin folder or a parent) >>> config.set_apsim_bin_path('/path/to/APSIM/2025/bin', verbose=True)
See also
Classes
- class apsimNGpy.core.config.Configuration
- In the future, this module will contain all the constants required by the package.
Users will be able to override these values if needed by importing this module before running any simulations.
Initialize self. See help(type(self)) for accurate signature.
- bin_path
Default:
None- set_temporal_bin_path(self, temporal_bin_path)
Set a temporary APSIM-NG binary path for this package/module.
This updates the module-level resolution of APSIM assemblies to use the provided path for the current process/session. It does not permanently change the global APSIM bin path on disk. Use this when you need to pin a workflow to a specific APSIM build for reproducibility.
Parameters
- temporal_bin_pathstr | os.PathLike
Absolute or relative path to the APSIM
bindirectory to use temporarily (e.g.,C:/APSIM/2025.09.01/bin).Reference (for the global fallback, not changed by this method):
get_apsim_bin_path()typically resolves from configuration or environment variablesAPSIM_BIN_PATH,MODELS, orAPSIM.
Returns
None
Raises
- FileNotFoundError
If
temporal_bin_pathdoes not exist.- NotADirectoryError
If
temporal_bin_pathis not a directory.- PermissionError
If the process lacks read/execute permission on the path.
- ValueError
If the directory does not appear to be a valid APSIM
bin(e.g., required assemblies are missing).
Notes
Assemblies already loaded after pointing to this path will remain bound in memory for the lifetime of the process.
To limit the override to a block of code, prefer a context manager that restores the prior path on exit.
Examples
from apsimNGpy.core.config import configuration configuration.set_temporal_bin_path(r"C:/APSIM/2025.09.01/bin") # proceed with imports/execution; assemblies are resolved from that path
See also
- release_temporal_bin_path(self)
release and set back to the global bin path
- class apsimNGpy.core.config.apsim_bin_context
Temporarily configure the APSIM-NG bin path used by
apsimNGpyso imports (e.g.,ApsimModel) can resolve APSIM .NET assemblies. Restores the previous configuration on exit.- apsim_bin_pathstr | os.PathLike | None, optional
Explicit path to the APSIM
bindirectory (e.g.,C:/APSIM/2025.05.1234/binor/opt/apsim/2025.05.1234/bin). Used if no valid value is resolved fromdotenv_path.- dotenv_pathstr | os.PathLike | None, optional
Path to a
.envfile to load before resolution. If provided, the manager will read (in order):bin_key(if non-empty), thenAPSIM_BIN_PATH, thenAPSIM_MODEL_PATHfrom that file.- bin_keystr, default ‘’
Custom environment variable name to read from the loaded
.env(e.g.,"APSIM_BIN_PATH_2025"). Ignored when empty.- timeoutfloat, default 0.003
Small sleep (seconds) after setting the bin path to avoid races with immediate imports on some filesystems. Set to 0 to disable.
- None
The context manager returns
None; import within thewithblock.
- ValueError
If no path can be resolved from
dotenv_path,apsim_bin_path, or the process environment.- FileNotFoundError
If the resolved path does not exist.
Python.NET assemblies cannot be unloaded from a running process; this context only restores path configuration for future imports.
Do not nest this context across threads; the underlying config is global.
Use an explicit path:
with apsim_bin_context(r"C:/APSIM/2025.05.1234/bin"): from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel model = ApsimModel(...)
Use a .env file with a custom key:
from pathlib import Path with apsim_bin_context(dotenv_path=Path(".env"), bin_key="APSIM_BIN_PATH"): from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel
If you have .env files located in the root of your script:
with apsim_bin_context(): from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel Verify restoration:: prev = get_apsim_bin_path() with apsim_bin_context(r"C:/APSIM/X.Y.Z/bin"): assert get_apsim_bin_path() == prev
added in v0.39.10.20+
- __init__(self, apsim_bin_path: 'str | os.PathLike | None' = None, dotenv_path: 'str | os.PathLike | None' = None, bin_key: 'str' = '') 'None'
Initialize self. See help(type(self)) for accurate signature.
apsimNGpy.core.experimentmanager
Classes
- class apsimNGpy.core.experimentmanager.ExperimentManager
This class inherits methods and attributes from:
ApsimModelto manage APSIM Experiments with pure factors or permutations. You first need to initiate the instance of this class and then initialize the experiment itself with:init_experiment(), which creates a new experiment from the suggested base simulation andpermutationtypeThe flow of method for
ExperimentManagerclass is shown in the diagram below:PlotManager ---> CoreModel ---> ApsimModel ---> ExperimentManager
PlotManager→ Produces visual outputs from model results (Not exposed in the API reference)CoreModel→ contains methods for running and manipulating models (Not exposed in the API reference)ApsimModel→ ExtendsCoremodelcapabilities with more functionalitiesExperimentManager→ Manages and creates a new experiment from the suggested base.
List of Public Attributes:
is_recent_versionstr_model
List of Public Methods
- __init__(self, model, out_path=None)
Initialize self. See help(type(self)) for accurate signature.
Initializes the factorial experiment structure inside the APSIM file.
Parameters
- permutation: (bool)
If True, enables permutation mode; otherwise, uses standard factor crossing.
- base_simulation: (str)
The base simulation name to use for the experiment. If None, the base simulation is selected from the available simulations
Side Effects:
Replaces any existing ExperimentManager node with a new configuration.
Clones the base simulation and adds it under the experiment.
Never mind, though all this edits are made on a cloned model.
In the presence of replacements, they are moved or retained directly at the simulations node
Examples:
from apsimNGpy.core.experimentmanager import ExperimentManager # initialize the model experiment = ExperimentManager('Maize', out_path = 'my_experiment.apsimx') # initialize experiment without permutation crossing of the factors experiment.init_experiment(permutation=False) # initialize experiment with permutation =True experiment.init_experiment(permutation=True) # initialize experiment with a preferred base simulation name experiment.init_experiment(permutation=False, base_simulation='Simulation') # view the simulation tree experiment.inspect_file()
The method
inspect_file()is inherited from theApsimModelclass , but it is still useful here, for example, you can see that we added an experiment Model under Simulations as shown below.└── Simulations: .Simulations ├── DataStore: .Simulations.DataStore └── Experiment: .Simulations.Experiment ├── Factors: .Simulations.Experiment.Factors └── Simulation: .Simulations.Experiment.Simulation ├── Clock: .Simulations.Experiment.Simulation.Clock ├── Field: .Simulations.Experiment.Simulation.Field │ ├── Fertilise at sowing: .Simulations.Experiment.Simulation.Field.Fertilise at sowing │ ├── Fertiliser: .Simulations.Experiment.Simulation.Field.Fertiliser │ ├── Harvest: .Simulations.Experiment.Simulation.Field.Harvest │ ├── Maize: .Simulations.Experiment.Simulation.Field.Maize │ ├── Report: .Simulations.Experiment.Simulation.Field.Report │ ├── Soil: .Simulations.Experiment.Simulation.Field.Soil │ │ ├── Chemical: .Simulations.Experiment.Simulation.Field.Soil.Chemical │ │ ├── NH4: .Simulations.Experiment.Simulation.Field.Soil.NH4 │ │ ├── NO3: .Simulations.Experiment.Simulation.Field.Soil.NO3 │ │ ├── Organic: .Simulations.Experiment.Simulation.Field.Soil.Organic │ │ ├── Physical: .Simulations.Experiment.Simulation.Field.Soil.Physical │ │ │ └── MaizeSoil: .Simulations.Experiment.Simulation.Field.Soil.Physical.MaizeSoil │ │ ├── Urea: .Simulations.Experiment.Simulation.Field.Soil.Urea │ │ └── Water: .Simulations.Experiment.Simulation.Field.Soil.Water │ ├── Sow using a variable rule: .Simulations.Experiment.Simulation.Field.Sow using a variable rule │ └── SurfaceOrganicMatter: .Simulations.Experiment.Simulation.Field.SurfaceOrganicMatter ├── Graph: .Simulations.Experiment.Simulation.Graph │ └── Series: .Simulations.Experiment.Simulation.Graph.Series ├── MicroClimate: .Simulations.Experiment.Simulation.MicroClimate ├── SoilArbitrator: .Simulations.Experiment.Simulation.SoilArbitrator ├── Summary: .Simulations.Experiment.Simulation.Summary └── Weather: .Simulations.Experiment.Simulation.WeatherSee also
Add a new factor to the experiment from an APSIM-style script specification.
Parameters
- specificationstr
An APSIM script-like expression that defines the parameter variation, e.g.
"[Organic].Carbon[1] = 1.2, 1.8"or"[Sow using a variable rule].Script.Population = 6, 10".- factor_namestr, optional
A unique name for the factor. If not provided, a name is auto-generated from the target variable in
specification(typically the last token).- **kwargs
Optional metadata or configuration (currently unused).
Raises
- ValueError
If a script-based specification references a non-existent or unlinked manager script.
Side Effects
Inserts the factor into the appropriate parent node (
PermutationorFactors).If a factor at the same index already exists, it is safely deleted before inserting the new one.
Notes
All methods from
ApsimModelremain available on this class. You can still inspect, run, and visualize results.Examples
Initialize an experiment:
from apsimNGpy.core.experimentmanager import ExperimentManager # initialize the model experiment = ExperimentManager('Maize', out_path='my_experiment.apsimx') # initialize experiment with permutation crossing of factors experiment.init_experiment(permutation=True)
Inspect model components:
experiment.inspect_model('Models.Manager')
['.Simulations.Experiment.Simulation.Field.Sow using a variable rule', '.Simulations.Experiment.Simulation.Field.Fertilise at sowing', '.Simulations.Experiment.Simulation.Field.Harvest']
experiment.inspect_model('Models.Factorial.Experiment')
['.Simulations.Experiment']
1) Add a factor associated with a manager script
experiment.add_factor( specification='[Sow using a variable rule].Script.Population = 6, 10', factor_name='Population' )
2) Add a factor associated with a soil node (e.g., initial soil organic carbon)
experiment.add_factor( specification='[Organic].Carbon[1] = 1.2, 1.8', factor_name='initial_carbon' )
Check how many factors have been added:
experiment.n_factors # 2
Inspect factors:
experiment.inspect_model('Models.Factorial.Factor')
['.Simulations.Experiment.Factors.Permutation.Nitrogen', '.Simulations.Experiment.Factors.Permutation.initial_carbon']
Get factor names only:
experiment.inspect_model('Models.Factorial.Factor', fullpath=False)
['Nitrogen', 'initial_carbon']
Run the model and summarize results:
experiment.run() df = experiment.results df.groupby(['Population', 'initial_carbon'])['Yield'].mean()
Population initial_carbon 10 1.2 6287.538183 1.8 6225.861601 6 1.2 5636.529504 1.8 5608.971306 Name: Yield, dtype: float64Save the experiment (same as
ApsimModel):experiment.save()
See also
save().Common Pitfalls
1) Adding the same specification with only a different
factor_nameexperiment.add_factor( specification='[Organic].Carbon[1] = 1.2, 1.8', factor_name='initial_carbon' ) experiment.add_factor( specification='[Organic].Carbon[1] = 1.2, 1.8', factor_name='carbon' )
By default, specifications are evaluated on their arguments, so the example above creates two identical factors—usually not desired.
experiment.save() experiment.inspect_model('Models.Factorial.Factor')
['.Simulations.Experiment.Factors.Permutation.initial_carbon', '.Simulations.Experiment.Factors.Permutation.carbon']
2) Invalid specification path to target parameters
Common causes include referencing models not present in the script, adding quotes around numeric levels, or inserting stray spaces in paths.
Invalid (extra quotes):
experiment.add_factor( specification='[Organic].Carbon[1] = "1.2, 1.8"', factor_name='initial_carbon' )
Correct:
experiment.add_factor( specification='[Organic].Carbon[1] = 1.2, 1.8', factor_name='initial_carbon' )
Invalid (extra space in path):
experiment.add_factor( specification='[Organic]. Carbon[1] = 1.2, 1.8', factor_name='initial_carbon' )
Correct:
experiment.add_factor( specification='[Organic].Carbon[1] = 1.2, 1.8', factor_name='initial_carbon' )
- property n_factors
- Returns:
int: The total number of active factor specifications currently added to the experiment.
- finalize(self)
” Finalizes the experiment setup by re-creating the internal APSIM factor nodes from specs.
This method is designed as a guard against unintended modifications and ensures that all factor definitions are fully resolved and written before saving.
- Side Effects:
Clears existing children from the parent factor node. Re-creates and attaches each factor as a new node. Triggers model saving.
- evaluate_simulated_output(self, ref_data: pandas.core.frame.DataFrame, table, ref_data_col, target_col, index_col, expr=None) (inherited)
Evaluate APSIM-simulated output against a reference (observed) dataset.
This method compares observed data (
ref_data) with simulated predictions obtained either from a provided DataFrame or from a table name that is used to extract simulation output throughget_simulated_output(). The comparison is performed throughfinal_evalfromapsimNGpy.optimizer.problems.back_end, which computes common evaluation metrics (e.g., RMSE, RRMSE, WIA, CCC, bias), depending on the implementation offinal_eval.Added in v0.39.12.21+
Parameters
- ref_datapandas.DataFrame
The reference or observed dataset against which predictions will be evaluated. Must contain at least the column specified by
ref_data_coland the index column.- tablestr or pandas.DataFrame
- Either:
A string referring to an APSIM output table name. In this case, simulated output is retrieved using :meth:`~apsimNGpy.core.apsim.ApsimModel.get_simulated_output`(table).
A DataFrame containing simulated predictions directly.
Any other type will raise a
TypeError.- ref_data_colstr
Column name in
ref_datacontaining the observed values.- target_colstr
Column name in the simulated dataset indicating the predicted values to be compared against the observations.
- index_colstr
Column used to join observed and simulated data (e.g., date, sample number, simulation ID). Both datasets must contain this column.
- exprcallable or str, optional
An optional transformation or expression to apply before comparison. Can be a lambda function, a string expression, or
None. Default isNone.
Returns
- dict or pandas.DataFrame
The output of
final_eval, typically containing evaluation metrics such as RMSE, RRMSE, WIA, CCC, ME, and bias.
Raises
- TypeError
If
tableis neither a string nor a pandas DataFrame.
Notes
This method streamlines comparison between observed and simulated APSIM outputs during model calibration or performance assessment. It allows the user to directly pass simulation tables or retrieve them automatically by name, ensuring a consistent evaluation workflow. Examples ——– .. code-block:: python
from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel from apsimNGpy.tests.unittests.test_factory import obs model = ApsimModel(‘Maize’) # need to add column year to act as common index with observed data model.add_report_variable(variable_spec=’[Clock].Today.Year as year’, report_name=’Report’) model.evaluate_simulated_output(ref_data=obs, table=’Report’, index_col=[‘year’],
target_col=’Yield’, ref_data_col=’observed’)
Model Evaluation Metrics ---------------------------------------- RMSE : 0.0003 MAE : 0.0003 MSE : 0.0000 RRMSE : 0.0000 bias : -0.0001 ME : 1.0000 WIA : 1.0000 R2 : 1.0000 CCC : 1.0000 SLOPE : 1.0000
Added in version v0.39.12.21+.
Set parameters for the given model by passing a dictionary or keyword arguments.
Parameters
- paramsdict, optional
A dictionary mapping APSIM parameter names to their corresponding values. If
paramsisNone, thenkwargsis expected, following the same signature asedit_model_by_path().- **kwargs :
Additional keyword arguments equivalent to entries in
params. These are interpreted according to the same signature asedit_model_by_path().
Returns
- selfApsimModel
Returns the same instance for method chaining.
Raises
- TypeError if any of the above arguments does not resolve to a dictionary. Other errors maybe raised gracefully
by
edit_model_by_path().
Notes
This flexible design allows users to supply parameters either as standard keyword arguments or as dictionary objects. The dictionary-based approach is particularly useful when working with JSON-compatible data structures, as commonly required during large-scale model optimization, calibration, or parameter sensitivity analysis workflows. In such cases, parameter sets can be programmatically generated, serialized, and reused without manual modification of code.
- get_soil_from_web(self, simulation_name: Union[str, tuple, NoneType] = None, *, lonlat: Optional[System.Tuple[Double, Double]] = None, soil_series: Optional[str] = None, thickness_sequence: Optional[Sequence[float]] = 'auto', thickness_value: int = None, max_depth: Optional[int] = 2400, n_layers: int = 10, thinnest_layer: int = 100, thickness_growth_rate: float = 1.5, edit_sections: Optional[Sequence[str]] = None, attach_missing_sections: bool = True, additional_plants: tuple = None, adjust_dul: bool = True) (inherited)
Download SSURGO-derived soil for a given location and populate the APSIM NG soil sections in the current model.
This method updates the target Simulation(s) in-place by attaching a Soil node (if missing) and writing section properties from the downloaded profile.
Parameters
- simulationstr | sequence[str] | None, default None
Target simulation name(s). If
None, all simulations are updated.- lonlattuple[float, float] | None
Location for SSURGO download, as
(lon, lat)in decimal degrees (e.g.,(-93.045, 42.012)).- soil_seriesstr | None, optional
Optional component/series filter. If
None, the dominant series by area is used. If a non-existent series is supplied, an error is raised.- thickness_sequencesequence[float] | str | None, default “auto”
Explicit layer thicknesses (mm). If
"auto", thicknesses are generated from the layer controls (e.g., number of layers, growth rate, thinnest layer, andmax_depth). IfNone, you must providethickness_valueandmax_depthto construct a uniform sequence.- thickness_valueint | None, optional
Uniform thickness (mm) for all layers. Ignored if
thickness_sequenceis provided; used only whenthickness_sequenceisNone.- max_depthint, default 2400
Maximum soil depth (mm) to cover with the thickness sequence.
- edit_sectionssequence[str], optional
Sections to edit. Default:
("physical", "organic", "chemical", "water", "water_balance", "solutes", "soil_crop", "meta_info"). Note: if sections are edited with differing layer counts, APSIM may error at run time.- attach_missing_sectionsbool, default True
If
True, create and attach missing section nodes before editing.- additional_plantssequence[str] | None, optional
Plant names for which to create/populate
SoilCropentries (e.g., to set KL/XF).- adjust_dulbool, optional
If
True, adjust layer values whereSATexceedsDULto prevent APSIM runtime errors.
Returns
- self
The same instance, to allow method chaining.
Raises
- ValueError
thickness_sequenceprovided with any non-positive value(s).thickness_sequenceisNoneandthickness_valueisNone.Units mismatch or inconsistency between
thickness_valueandmax_depth.
Notes
Assumes soil sections live under a Soil node; when
attach_missing_sections=Truea Soil node is created if missing.Uses the optimized SoilManager routines (vectorized assignments / .NET double[] marshaling).
- Side effects (in place on the APSIM model):
Creates/attaches Soil when needed.
Creates/updates child sections (
Physical,Organic,Chemical,Water,WaterBalance,SoilCrop) as listed inedit_sections.Overwrites section properties (e.g., layer arrays such as
Depth,BD,LL15,DUL,SAT; solutes; crop KL/XF) with downloaded values.Add SoilCrop children for any names in
additional_plants.Performs network I/O to retrieve SSURGO tables when
lonlatis provided.Emits log messages (warnings/info) when attaching nodes, resolving thickness controls, or skipping missing columns.
Caches the computed soil profile in the helper during execution; the in-memory APSIM tree remains modified after return.
Does not write files; call
save()on the model if you want to persist changes.The existing soil-profile structure is completed override by the newly generated soil profile. So, variables like soil thickness, number of soil layers, etc. might be different from the old one.
- adjust_dul(self, simulations: Union[tuple, list] = None) (inherited)
This method checks whether the soil
SATis above or belowDULand decreasesDULvalues accordinglyNeed to call this method everytime
SATis changed, orDULis changed accordingly.
simulations: str, name of the simulation where we want to adjust DUL and SAT according.returns:model the object for method chaining
- replace_downloaded_soils(self, soil_tables: Union[dict, list], simulation_names: Union[tuple, list], **kwargs) (inherited)
- @deprecated and will be removed in the future versions
Updates soil parameters and configurations for downloaded soil data in simulation models.
This method adjusts soil physical and organic parameters based on provided soil tables and applies these adjustments to specified simulation models.
Parameters:
soil_tables(list): A list containing soil data tables. Expected to contain: see the naming convention in the for APSIM - [0]: DataFrame with physical soil parameters. - [1]: DataFrame with organic soil parameters. - [2]: DataFrame with crop-specific soil parameters. - simulation_names (list of str): Names or identifiers for the simulations to be updated.sReturns: - self: Returns an instance of the class for
chainingmethods.This method directly modifies the simulation instances found by
find_simulationsmethod calls, updating physical and organic soil properties, as well as crop-specific parameters like lower limit (LL), drain upper limit (DUL), saturation (SAT), bulk density (BD), hydraulic conductivity at saturation (KS), and more based on the provided soil tables.
->> key-word argument
set_sw_con: Boolean, set the drainage coefficient for each layeradJust_kl:: Bollean, adjust, kl based on productivity indexCultvarName: cultivar name which is in the sowing module for adjusting the ruetillage: specify whether you will be carried to adjust some physical parameters- read_apsimx_data(self, table=None) (inherited)
Read APSIM NG datastore for the current model. Raises FileNotFoundError if the model was initialized from default models because those need to be executed first to generate a database.
The rationale for this method is that you can just access the results from the previous session without running it if the database is in the same location as the apsimx file.
Since apsimNGpy clones the apsimx file, the original file is kept with attribute name
_model, that is what is being used to access the datasettable: (str) name of the database table to read if none of all tables are returned
Returns: pandas.DataFrame
KeyError: if table is not found in the database
- property simulations(inherited)
Retrieve simulation nodes in the APSIMx
Model.Core.Simulationsobject.We search all-Models.Core.Simulation in the scope of Model.Core.Simulations. Please note the difference Simulations is the whole json object Simulation is the child with the field zones, crops, soils and managers.
Any structure of apsimx file can be handled.
Note
The simulations are c# referenced objects, and their manipulation maybe for advanced users only.
- property simulation_names(inherited)
@deprecated will be removed in future releases. Please use inspect_model function instead.
retrieves the name of the simulations in the APSIMx file @return: list of simulation names
- property tables_list(inherited)
quick property returns available database report tables name
- property managers_scripts_list(inherited)
quick property returns available database manager script names
- property simulations_list(inherited)
quick property for returning a list of available simulation names @return:
- restart_model(self, model_info=None) (inherited)
Reinitialize the APSIM model instance after edits or management updates.
Parameters
- model_infocollections.NamedTuple, optional
A named tuple returned by
load_apsim_modelfrom themodel_loadermodule. Contains references to the APSIM model, datastore, and file path. If not provided, the method reinitializes the model using the existingself.model_infoobject.
Notes
This method is essential when the model needs to be reloaded after modifying management scripts or saving an edited APSIM file.
It may be invoked automatically by internal methods such as
save_edited_file,save, andupdate_mgt.Reinitializing ensures that all APSIM NG components and datastore references are refreshed and consistent with the modified file.
Returns
- selfobject
Returns the updated ApsimModel instance.
- save(self, file_name: 'Union[str, Path, None]' = None, reload=True) (inherited)
Saves the current APSIM NG model (
Simulations) to disk and refresh runtime state.This method writes the model to a file, using a version-aware strategy:
After writing, the model is recompiled via
recompile(self)()and the in-memory instance is refreshed usingrestart_model(), ensuring the object graph reflects the just-saved state. This is now only impozed if the user specifiedrelaod = True.Parameters
- file_namestr or pathlib.Path, optional
Output path for the saved model file. If omitted (
None), the method uses the instance’s existingpath. The resolved path is also written back to instancepathattribute for consistency if reload is True.- reload: bool Optional default is True
resets the reference path to the one provided after serializing to disk. This implies that the instance
pathwill be the providedfile_name
Returns
- Self
The same model/manager instance to support method chaining.
Raises
- OSError
If the file cannot be written due to I/O errors, permissions, or invalid path.
- AttributeError
If required attributes (e.g.,
self.Simulations) or methods are missing.- Exception
Any exception propagated by
save_model_to_file(),recompile(), orrestart_model().
Side Effects
Sets
self.pathto the resolved output path (string).Writes the model file to disk (overwrites if it exists).
If reload is True (default), recompiles the model and restarts the in-memory instance.
Notes
Path normalization: The path is stringified via
str(file_name)just in case it is a pathlib object.Reload semantics: Post-save recompilation and restart ensure any code generation or cached reflection is refreshed to match the serialized model.
Examples
- check the current path before saving the model
>>> from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel >>> from pathlib import Path >>> model = ApsimModel("Maize", out_path='saved_maize.apsimx') >>> model.path scratch\saved_maize.apsimx
- Save to a new path and continue working with the refreshed instance
>>> model.save(file_name='out_maize.apsimx', reload=True) # check the path >>> model.path 'out_maize.apsimx' # possible to run again the refreshed model. >>> model.run()
- Save to a new path without refreshing the instance path
>>> model = ApsimModel("Maize", out_path='saved_maize.apsimx') >>> model.save(file_name='out_maize.apsimx', reload=False) # check the current reference path for the model. >>> model.path 'scratch\saved_maize.apsimx' # When reload is False, the original referenced path remains as shown above
As shown above, everything is saved in the scratch folder; if the path is not abolutely provided, e.g., a relative path. If the path is not provided as shown below, the reference path is the current path for the isntance model.
>>> model = ApsimModel("Maize", out_path='saved_maize.apsimx') >>> model.path 'scratch\saved_maize.apsimx' # save the model without providing the path. >>> model.save()# uses the default, in this case the defaul path is the existing path >>> model.path 'scratch\saved_maize.apsimx'
In the above case, both reload =
FalseorTrue, will produce the same reference path for the live instance class.- property results(inherited)
Legacy method for retrieving simulation results.
This method is implemented as a
propertyto enable lazy loading—results are only loaded into memory when explicitly accessed. This design helps optimizememoryusage, especially forlargesimulations.It must be called only after invoking
run(). If accessed before the simulation is run, it will raise an error.Notes
The
run()method should be called with a validreport nameor a list of report names.If
report_namesis not provided (i.e.,None), the system will inspect the model and automatically detect all available report components. These reports will then be used to collect the data.If multiple report names are used, their corresponding data tables will be concatenated along the rows.
Returns
- pd.DataFrame
A DataFrame containing the simulation output results.
Examples
>>> from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel # create an instance of ApsimModel class >>> model = ApsimModel("Maize", out_path="my_maize_model.apsimx") # run the simulation >>> model.run() # get the results >>> df = model.results # do something with the results e.g. get the mean of numeric columns >>> df.mean(numeric_only=True) Out[12]: CheckpointID 1.000000 SimulationID 1.000000 Maize.AboveGround.Wt 1225.099950 Maize.AboveGround.N 12.381196 Yield 5636.529504 Maize.Grain.Wt 563.652950 Maize.Grain.Size 0.284941 Maize.Grain.NumberFunction 1986.770519 Maize.Grain.Total.Wt 563.652950 Maize.Grain.N 7.459296 Maize.Total.Wt 1340.837427
If there are more than one database tables or
reportsas called in APSIM, results are concatenated along the axis 0, implying along rows. The example below mimics this scenario.>>> model.add_db_table( ... variable_spec=['[Clock].Today.Year as year', ... 'sum([Soil].Nutrient.TotalC)/1000 from 01-jan to [clock].Today as soc'], ... rename='soc' ... ) # inspect the reports >>> model.inspect_model('Models.Report', fullpath=False) ['Report', 'soc'] >>> model.run() >>> model.results CheckpointID SimulationID Zone ... source_table year soc 0 1 1 Field ... Report NaN NaN 1 1 1 Field ... Report NaN NaN 2 1 1 Field ... Report NaN NaN 3 1 1 Field ... Report NaN NaN 4 1 1 Field ... Report NaN NaN 5 1 1 Field ... Report NaN NaN 6 1 1 Field ... Report NaN NaN 7 1 1 Field ... Report NaN NaN 8 1 1 Field ... Report NaN NaN 9 1 1 Field ... Report NaN NaN 10 1 1 Field ... soc 1990.0 77.831512 11 1 1 Field ... soc 1991.0 78.501766 12 1 1 Field ... soc 1992.0 78.916339 13 1 1 Field ... soc 1993.0 78.707094 14 1 1 Field ... soc 1994.0 78.191686 15 1 1 Field ... soc 1995.0 78.573085 16 1 1 Field ... soc 1996.0 78.724598 17 1 1 Field ... soc 1997.0 79.043935 18 1 1 Field ... soc 1998.0 78.343111 19 1 1 Field ... soc 1999.0 78.872767 20 1 1 Field ... soc 2000.0 79.916413 [21 rows x 17 columns]
By default all the tables are returned and the column
source_tabletells us the source table for each row. Sinceresultsis a property attribute, which does not take in any argument, we can only decide this when calling therunmethod as shown below.>>> model.run(report_name='soc') >>> model.results CheckpointID SimulationID Zone year soc source_table 0 1 1 Field 1990.0 77.831512 soc 1 1 1 Field 1991.0 78.501766 soc 2 1 1 Field 1992.0 78.916339 soc 3 1 1 Field 1993.0 78.707094 soc 4 1 1 Field 1994.0 78.191686 soc 5 1 1 Field 1995.0 78.573085 soc 6 1 1 Field 1996.0 78.724598 soc 7 1 1 Field 1997.0 79.043935 soc 8 1 1 Field 1998.0 78.343111 soc 9 1 1 Field 1999.0 78.872767 soc 10 1 1 Field 2000.0 79.916413 soc
The above example has dataset only from one database table specified at run time.
See also
Related API:
get_simulated_output().- get_simulated_output(self, report_names: 'Union[str, list]', axis=0, **kwargs)
Reads report data from CSV files generated by the simulation. More Advanced table-merging arguments will be introduced soon.
Parameters:
- report_names: (str, iterable)
Name or list names of report tables to read. These should match the report names in the simulation output.
- axis: int, Optional. Default to 0
concatenation axis numbers for multiple reports or database tables. if axis is 0, source_table column is populated to show source of the data for each row
Returns:
pd.DataFrameConcatenated DataFrame containing the data from the specified reports.
Raises:
- ValueError
If any of the requested report names are not found in the available tables.
- RuntimeError
If the simulation has not been
runsuccessfully before attempting to read data.
Examples
>>> from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel >>> model = ApsimModel(model='Maize') # replace with your path to the apsim template model >>> model.run() # if we are going to use get_simulated_output, no need to provide the report name in ``run()`` method >>> df = model.get_simulated_output(report_names="Report") SimulationName SimulationID CheckpointID ... Maize.Total.Wt Yield Zone 0 Simulation 1 1 ... 1728.427 8469.616 Field 1 Simulation 1 1 ... 920.854 4668.505 Field 2 Simulation 1 1 ... 204.118 555.047 Field 3 Simulation 1 1 ... 869.180 3504.000 Field 4 Simulation 1 1 ... 1665.475 7820.075 Field 5 Simulation 1 1 ... 2124.740 8823.517 Field 6 Simulation 1 1 ... 1235.469 3587.101 Field 7 Simulation 1 1 ... 951.808 2939.152 Field 8 Simulation 1 1 ... 1986.968 8379.435 Field 9 Simulation 1 1 ... 1689.966 7370.301 Field [10 rows x 16 columns]
This method also handles more than one reports as shown below.
>>> model.add_db_table( ... variable_spec=[ ... '[Clock].Today.Year as year', ... 'sum([Soil].Nutrient.TotalC)/1000 from 01-jan to [clock].Today as soc' ... ], ... rename='soc' ... ) # inspect the reports >>> model.inspect_model('Models.Report', fullpath=False) ['Report', 'soc'] >>> model.run() >>> model.get_simulated_output(["soc", "Report"], axis=0) CheckpointID SimulationID ... Maize.Grain.N Maize.Total.Wt 0 1 1 ... NaN NaN 1 1 1 ... NaN NaN 2 1 1 ... NaN NaN 3 1 1 ... NaN NaN 4 1 1 ... NaN NaN 5 1 1 ... NaN NaN 6 1 1 ... NaN NaN 7 1 1 ... NaN NaN 8 1 1 ... NaN NaN 9 1 1 ... NaN NaN 10 1 1 ... NaN NaN 11 1 1 ... 11.178291 1728.427114 12 1 1 ... 6.226327 922.393712 13 1 1 ... 0.752357 204.108770 14 1 1 ... 4.886844 869.242545 15 1 1 ... 10.463854 1665.483701 16 1 1 ... 11.253916 2124.739830 17 1 1 ... 5.044417 1261.674967 18 1 1 ... 3.955080 951.303260 19 1 1 ... 11.080878 1987.106980 20 1 1 ... 9.751001 1693.893386 [21 rows x 17 columns]
>>> model.get_simulated_output(['soc', 'Report'], axis=1) CheckpointID SimulationID ... Maize.Grain.N Maize.Total.Wt 0 1 1 ... 11.178291 1728.427114 1 1 1 ... 6.226327 922.393712 2 1 1 ... 0.752357 204.108770 3 1 1 ... 4.886844 869.242545 4 1 1 ... 10.463854 1665.483701 5 1 1 ... 11.253916 2124.739830 6 1 1 ... 5.044417 1261.674967 7 1 1 ... 3.955080 951.303260 8 1 1 ... 11.080878 1987.106980 9 1 1 ... 9.751001 1693.893386 10 1 1 ... NaN NaN [11 rows x 19 columns]
See also
Related API:
results.- run(self, report_name: 'Union[tuple, list, str]' = None, simulations: 'Union[tuple, list]' = None, clean_up: 'bool' = True, verbose: 'bool' = False, timeout: 'int' = 800, cpu_count: 'int' = -1, **kwargs)
- Run APSIM model simulations to write the results either to SQLite database or csv file. Does not collect the
simulated output into memory. Please see related APIs:
resultsandget_simulated_output().
Parameters
- report_name: Union[tuple, list, str], optional
Defaults to APSIM default Report Name if not specified. - If iterable, all report tables are read and aggregated into one DataFrame.
- simulations: Union[tuple, list], optional
List of simulation names to run. If None, runs all simulations.
- clean_up: bool, optional
If True, removes the existing database before running.
- verbose: bool, optional
If True, enables verbose output for debugging. The method continues with debugging info anyway if the run was unsuccessful
- timeout: int, default is 800 seconds
Enforces a timeout and returns a CompletedProcess-like object.
- cpu_count: int, Optional default is -1, referring to all threads
This parameter is useful when the number of simulations are more than 1, below that performance differences are minimal added in 0.39.11.21+
- kwargs: **dict
Additional keyword arguments, e.g., to_csv=True, use this flag to correct results from a csv file directly stored at the location of the running apsimx file.
Warning:
In my experience with Models.exe, CSV outputs are not always overwritten; after edits, stale results can persist. Proceed with caution.
Returns
Instance of the respective model class e.g., ApsimModel, ExperimentManager.
RuntimeErrorRaised if the
APSIMrun is unsuccessful. Common causes includemissing meteorological files, mismatched simulationstartdates withweatherdata, or otherconfiguration issues.
Example:
Instantiate an
apsimNGpy.core.apsim.ApsimModelobject and run:from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel model = ApsimModel(model= 'Maize')# replace with your path to the apsim template model model.run(report_name = "Report") # check if the run was successful model.ran_ok 'True'
Note
Updates the
ran_okflag toTrueif no error was encountered.See also
Related APIs:
resultsandget_simulated_output().- rename_model(self, model_type, *, old_name, new_name) (inherited)
Renames a model within the APSIM simulation tree.
This method searches for a model of the specified type and current name, then updates its name to the new one provided. After renaming, it saves the updated simulation file to enforce the changes.
- model_typestr
The type of the model to rename (e.g., “Manager”, “Clock”, etc.).
- old_namestr
The current name of the model to be renamed.
- new_namestr
The new name to assign to the model.
- selfobject
Returns the modified object to allow for method chaining.
- ValueError
If the model of the specified type and name is not found.
Tip
This method uses
get_or_check_modelwith action=’get’ to locate the model, and then updates the model’sNameattribute. The model is serialized using thesave()immediately after to apply and enfoce the change.>>> from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel >>> model = ApsimModel(model = 'Maize', out_path='my_maize.apsimx') >>> model.rename_model(model_type="Models.Core.Simulation", old_name ='Simulation', new_name='my_simulation') # check if it has been successfully renamed >>> model.inspect_model(model_type='Models.Core.Simulation', fullpath = False) ['my_simulation'] # The alternative is to use model.inspect_file to see your changes >>> model.inspect_file()
└── Models.Core.Simulations: .Simulations ├── Models.Storage.DataStore: .Simulations.DataStore ├── Models.Core.Folder: .Simulations.Replacements │ └── Models.PMF.Plant: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize │ └── Models.Core.Folder: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Atrium │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.CG4141 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Dekalb_XL82 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.GH_5009 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.GH_5019WX │ ├── Models.Core.Folder: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_100 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_103 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_105 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_108 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_110 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_112 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_115 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_120 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_130 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_80 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_90 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_95 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_100 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_103 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_105 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_108 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_110 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_112 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_115 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_120 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_130 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_80 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_90 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_95 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.HY_110 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.LY_110 │ │ └── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.P1197 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Hycorn_40 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Hycorn_53 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Katumani │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Laila │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Makueni │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Melkassa │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.NSCM_41 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_3153 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_33M54 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_34K77 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_38H20 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_39G12 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_39V43 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.malawi_local │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh12 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh16 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh17 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh18 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh19 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.r201 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.r215 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc401 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc501 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc601 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc623 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc625 │ └── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.sr52 └── Models.Core.Simulation: .Simulations.Simulation ├── Models.Clock: .Simulations.Simulation.Clock ├── Models.Core.Zone: .Simulations.Simulation.Field │ ├── Models.Manager: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Fertilise at sowing │ ├── Models.Fertiliser: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Fertiliser │ ├── Models.Manager: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Harvest │ ├── Models.PMF.Plant: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize │ │ └── Models.Core.Folder: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Atrium │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.CG4141 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Dekalb_XL82 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.GH_5009 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.GH_5019WX │ │ ├── Models.Core.Folder: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_100 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_103 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_105 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_108 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_110 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_112 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_115 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_120 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_130 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_80 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_90 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_95 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_100 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_103 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_105 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_108 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_110 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_112 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_115 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_120 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_130 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_80 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_90 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_95 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.HY_110 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.LY_110 │ │ │ └── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.P1197 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Hycorn_40 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Hycorn_53 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Katumani │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Laila │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Makueni │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Melkassa │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.NSCM_41 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_3153 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_33M54 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_34K77 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_38H20 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_39G12 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_39V43 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.malawi_local │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh12 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh16 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh17 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh18 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh19 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.r201 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.r215 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc401 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc501 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc601 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc623 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc625 │ │ └── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.sr52 │ ├── Models.Report: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Report │ ├── Models.Soils.Soil: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Chemical: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Chemical │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Solute: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.NH4 │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Solute: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.NO3 │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Organic: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Organic │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Physical: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Physical │ │ │ └── Models.Soils.SoilCrop: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Physical.MaizeSoil │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Solute: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Urea │ │ └── Models.Soils.Water: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Water │ ├── Models.Manager: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Sow using a variable rule │ └── Models.Surface.SurfaceOrganicMatter: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.SurfaceOrganicMatter ├── Models.Graph: .Simulations.Simulation.Graph │ └── Models.Series: .Simulations.Simulation.Graph.Series ├── Models.MicroClimate: .Simulations.Simulation.MicroClimate ├── Models.Soils.Arbitrator.SoilArbitrator: .Simulations.Simulation.SoilArbitrator ├── Models.Summary: .Simulations.Simulation.Summary └── Models.Climate.Weather: .Simulations.Simulation.WeatherSee also
Related APIs:
add_model(),clone_model(), andmove_model().- clone_model(self, model_type, model_name, adoptive_parent_type, rename=None, adoptive_parent_name=None) (inherited)
Clone an existing
modeland move it to a specified parent within the simulation structure. The function modifies the simulation structure by adding the cloned model to the designated parent.This function is useful when a model instance needs to be duplicated and repositioned in the
APSIMsimulation hierarchy without manually redefining its structure.Parameters:
- model_type: Models
The type of the model to be cloned, e.g.,
Models.SimulationorModels.Clock.- model_name: str
The unique identification name of the model instance to be cloned, e.g.,
"clock1".- adoptive_parent_type: Models
The type of the new parent model where the cloned model will be placed.
- rename: str, optional
The new name for the cloned model. If not provided, the clone will be renamed using the original name with a
_clonesuffix.- adoptive_parent_name: str, optional
The name of the parent model where the cloned model should be moved. If not provided, the model will be placed under the default parent of the specified type.
- in_place: bool, optional
If
True, the cloned model remains in the same location but is duplicated. Defaults toFalse.
Returns:
None
Example:
Create a cloned version of
"clock1"and place it under"Simulation"with the new name"new_clock:>>> from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel >>> model = ApsimModel('Maize', out_path='my_maize.apsimx') >>> model.clone_model(model_type='Models.Core.Simulation', model_name="Simulation", ... rename="Sim2", adoptive_parent_type = 'Models.Core.Simulations', ... adoptive_parent_name='Simulations') >>> model.inspect_file() └── Simulations: .Simulations ├── DataStore: .Simulations.DataStore ├── Sim2: .Simulations.Sim2 │ ├── Clock: .Simulations.Sim2.Clock │ ├── Field: .Simulations.Sim2.Field │ │ ├── Fertilise at sowing: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Fertilise at sowing │ │ ├── Fertiliser: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Fertiliser │ │ ├── Harvest: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Harvest │ │ ├── Maize: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Maize │ │ ├── Report: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Report │ │ ├── Soil: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Soil │ │ │ ├── Chemical: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Soil.Chemical │ │ │ ├── NH4: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Soil.NH4 │ │ │ ├── NO3: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Soil.NO3 │ │ │ ├── Organic: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Soil.Organic │ │ │ ├── Physical: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Soil.Physical │ │ │ │ └── MaizeSoil: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Soil.Physical.MaizeSoil │ │ │ ├── Urea: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Soil.Urea │ │ │ └── Water: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Soil.Water │ │ ├── Sow using a variable rule: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Sow using a variable rule │ │ ├── SurfaceOrganicMatter: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.SurfaceOrganicMatter │ │ └── soc_table: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.soc_table │ ├── Graph: .Simulations.Sim2.Graph │ │ └── Series: .Simulations.Sim2.Graph.Series │ ├── MicroClimate: .Simulations.Sim2.MicroClimate │ ├── SoilArbitrator: .Simulations.Sim2.SoilArbitrator │ ├── Summary: .Simulations.Sim2.Summary │ └── Weather: .Simulations.Sim2.Weather └── Simulation: .Simulations.Simulation ├── Clock: .Simulations.Simulation.Clock ├── Field: .Simulations.Simulation.Field │ ├── Fertilise at sowing: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Fertilise at sowing │ ├── Fertiliser: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Fertiliser │ ├── Harvest: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Harvest │ ├── Maize: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize │ ├── Report: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Report │ ├── Soil: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil │ │ ├── Chemical: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Chemical │ │ ├── NH4: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.NH4 │ │ ├── NO3: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.NO3 │ │ ├── Organic: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Organic │ │ ├── Physical: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Physical │ │ │ └── MaizeSoil: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Physical.MaizeSoil │ │ ├── Urea: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Urea │ │ └── Water: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Water │ ├── Sow using a variable rule: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Sow using a variable rule │ ├── SurfaceOrganicMatter: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.SurfaceOrganicMatter │ └── soc_table: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.soc_table ├── Graph: .Simulations.Simulation.Graph │ └── Series: .Simulations.Simulation.Graph.Series ├── MicroClimate: .Simulations.Simulation.MicroClimate ├── SoilArbitrator: .Simulations.Simulation.SoilArbitrator ├── Summary: .Simulations.Simulation.Summary └── Weather: .Simulations.Simulation.Weather
See also
Related APIs:
add_model()andmove_model().- static find_model(model_name: 'str') (inherited)
Find a model from the Models namespace and return its path.
Parameters:
- model_name: (str)
The name of the model to find.
- model_namespace: (object, optional):
The root namespace (defaults to Models).
- path: (str, optional)
The accumulated path to the model.
- Returns:
str: The full path to the model if found, otherwise None.
Example:
>>> from apsimNGpy import core # doctest: >>> model =core.apsim.ApsimModel(model = "Maize", out_path ='my_maize.apsimx') >>> model.find_model("Weather") 'Models.Climate.Weather' >>> model.find_model("Clock") 'Models.Clock'
- add_model(self, model_type, adoptive_parent, rename=None, adoptive_parent_name=None, verbose=False, source='Models', source_model_name=None, override=True, **kwargs) (inherited)
Adds a model to the Models Simulations namespace.
Some models are restricted to specific parent models, meaning they can only be added to compatible models. For example, a Clock model cannot be added to a Soil model.
Parameters:
- model_type: (str or Models object)
The type of model to add, e.g.,
Models.Clockor just"Clock". if the APSIM Models namespace is exposed to the current script, then model_class can be Models.Clock without strings quotes- rename (str):
The new name for the model.
- adoptive_parent: (Models object)
The target parent where the model will be added or moved e.g
Models.ClockorClockas string all are valid- adoptive_parent_name: (Models object, optional)
Specifies the parent name for precise location. e.g.,
Models.Core.SimulationorSimulationsall are valid- source: Models, str, CoreModel, ApsimModel object: defaults to Models namespace.
The source can be an existing Models or string name to point to one of the default model examples, which we can extract the model from
- override: bool, optional defaults to
True. When
True(recommended), it deletes any model with the same name and type at the suggested parent location before adding the new model ifFalseand proposed model to be added exists at the parent location;APSIMautomatically generates a new name for the newly added model. This is not recommended.- Returns:
None:
Modelsare modified in place, so models retains the same reference.Caution
Added models from
Models namespaceare initially empty. Additional configuration is required to set parameters. For example, after adding a Clock module, you must set the start and end dates.Example
>>> from apsimNGpy import core >>> from apsimNGpy.core.core import Models >>> model = core.apsim.ApsimModel("Maize") >>> model.remove_model(Models.Clock) # first delete the model >>> model.add_model(Models.Clock, adoptive_parent=Models.Core.Simulation, rename='Clock_replaced', verbose=False)
>>> model.add_model(model_class=Models.Core.Simulation, adoptive_parent=Models.Core.Simulations, rename='Iowa')
>>> model.preview_simulation()
>>> model.add_model( ... Models.Core.Simulation, ... adoptive_parent='Simulations', ... rename='soybean_replaced', ... source='Soybean') # basically adding another simulation from soybean to the maize simulation
See also
Related APIs:
clone_model()andmove_model().- detect_model_type(self, model_instance: 'Union[str, Models]') (inherited)
Detects the model type from a given APSIM model instance or path string.
- edit_model_by_path(self, path: 'str', **kwargs) (inherited)
Edit a model component located by an APSIM path, dispatching to type-specific editors.
This method resolves a node under
instance.Simulationsusing an APSIM path, then edits that node by delegating to an editor based on the node’s runtime type. It supports common APSIM NG components (e.g., Weather, Manager, Cultivar, Clock, Soil subcomponents, Report, SurfaceOrganicMatter). Unsupported types raiseNotImplementedError.Parameters
- pathstr
APSIM path to a target node under
self.Simulations(e.g., ‘.Simulations.Simulations.Weather’ or a similar canonical path).
kwargs
Additional keyword arguments specific to the model type. Atleast one key word argument is required. These vary by component:
- Models.Climate.Weather:
weather_file(str): Path to the weather.metfile.- Models.Clock:
Date properties such as
StartandEndin ISO format (e.g., ‘2021-01-01’).- Models.Manager:
Variables to update in the Manager script using
update_mgt_by_path.- Soils.Physical | Soils.Chemical | Soils.Organic | Soils.Water:
Variables to replace using
replace_soils_values_by_path.Valid
parametersare shown below;Soil Model Type
Supported key word arguments
Physical
AirDry, BD, DUL, DULmm, Depth, DepthMidPoints, KS, LL15, LL15mm, PAWC, PAWCmm, SAT, SATmm, SW, SWmm, Thickness, ThicknessCumulative
Organic
CNR, Carbon, Depth, FBiom, FInert, FOM, Nitrogen, SoilCNRatio, Thickness
Chemical
Depth, PH, Thickness
- Models.Report:
- report_name (str):
Name of the report model (optional depending on structure).
- variable_spec` (list[str] or str):
Variables to include in the report.
- set_event_names` (list[str], optional):
Events that trigger the report.
- Models.PMF.Cultivar:
- commands (str):
APSIM path to the cultivar parameter to update.
- values: (Any)
Value to assign.
- cultivar_manager: (str)
Name of the Manager script managing the cultivar, which must contain the
CultivarNameparameter. Required to propagate updated cultivar values, as APSIM treats cultivars as read-only.
Warning
- ValueError
If the model instance is not found, required kwargs are missing, or
kwargsis empty.- NotImplementedError
If the logic for the specified
model_classis not implemented.
Examples
Edit a Manager script parameter:
model.edit_model_by_path( ".Simulations.Simulation.Field.Sow using a variable rule", verbose=True, Population=10)
Point a Weather component to a new
.metfile:model.edit_model_by_path( path=".Simulations.Simulation.Weather", FileName="data/weather/Ames_2020.met")
Change Clock dates:
model.edit_model_by_path( ".Simulations.Simulation.Clock", StartDate="2020-01-01", EndDate="2020-12-31")
Update soil water properties at a specific path:
model.edit_model_by_path( ".Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Physical", LL15="[0.26, 0.18, 0.10, 0.12]")
Apply cultivar edits:
model.edit_model_by_path( ".Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh18", sowed=True, **{"Phenology.EmergencePhase.Photo-period": "Short"} )
See also
Related API:
edit_model().- add_base_replacements(self) (inherited)
Add base replacements with all available models of type Plants and then start from there to add more @return: self
- edit_model(self, model_type: 'str', model_name: 'str', simulations: 'Union[str, list]' = 'all', exclude=None, verbose=False, **kwargs) (inherited)
Modify various APSIM model components by specifying the model type and name across given simulations.
Tip
Editing APSIM models in apsimNGpy does not require placing the target model inside a Replacements folder or node. However, when modifying cultivar parameters, it can be helpful to include a Replacements folder containing the relevant plant definition hosting that cultivar. In many cases, apsimNGpy will handle this automatically.
Selective Editing
Selective editing allows you to apply modifications only to certain simulations. This is not possible when the same model instance is shared through a common Replacements folder. For reliable selective editing, each simulation should ideally reference a uniquely named model. However, even when model names are not unique, apsimNGpy still enables targeted editing through two mechanisms:
Exclusion strategy You can explicitly exclude simulations to which the edits should not be applied.
Specification strategy You can explicitly specify which simulations should have their models edited or replaced with new parameters.
Parameters
- model_type: str, required
Type of the model component to modify (e.g., ‘Clock’, ‘Manager’, ‘Soils.Physical’, etc.).
- simulations: Union[str, list], optional
A simulation name or list of simulation names in which to search. Defaults to all simulations in the model.
- model_name: str, required
Name of the model instance to modify.
- verbose: bool, optional
print the status of the editing activities
- exclude: Union[str, None, Iterable[str]], optional,default is None
Added in ‘V0.39.10.20’+. It is used to specify which simulation should be skipped during the editing process, in case there are more than simulations
kwargs
Additional keyword arguments specific to the model type. Atleast one key word argument is required. These vary by component:
- Models.Climate.Weather:
weather_file(str): Path to the weather.metfile.- Models.Clock:
Date properties such as
StartandEndin ISO format (e.g., ‘2021-01-01’).- Models.Manager:
Variables to update in the Manager script using
update_mgt_by_path.- Soils.Physical | Soils.Chemical | Soils.Organic | Soils.Water:
Variables to replace using
replace_soils_values_by_path.Valid
parametersare shown below;Soil Model Type
Supported key word arguments
Physical
AirDry, BD, DUL, DULmm, Depth, DepthMidPoints, KS, LL15, LL15mm, PAWC, PAWCmm, SAT, SATmm, SW, SWmm, Thickness, ThicknessCumulative
Organic
CNR, Carbon, Depth, FBiom, FInert, FOM, Nitrogen, SoilCNRatio, Thickness
Chemical
Depth, PH, Thickness
- Models.Report:
- report_name (str):
Name of the report model (optional depending on structure).
- variable_spec` (list[str] or str):
Variables to include in the report.
- set_event_names` (list[str], optional):
Events that trigger the report.
- Models.PMF.Cultivar:
- commands (str):
APSIM path to the cultivar parameter to update.
- values: (Any)
Value to assign.
- cultivar_manager: (str)
Name of the Manager script managing the cultivar, which must contain the
CultivarNameparameter. Required to propagate updated cultivar values, as APSIM treats cultivars as read-only.
Warning
- ValueError
If the model instance is not found, required kwargs are missing, or
kwargsis empty.- NotImplementedError
If the logic for the specified
model_classis not implemented.
Examples:
from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel model = ApsimModel(model='Maize')
Example of how to edit a cultivar model:
model.edit_model(model_type='Cultivar', simulations='Simulation', commands='[Phenology].Juvenile.Target.FixedValue', values=256, model_name='B_110', new_cultivar_name='B_110_edited', cultivar_manager='Sow using a variable rule')
Edit a soil organic matter module:
model.edit_model( model_type='Organic', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Organic', Carbon=1.23)
Edit multiple soil layers:
model.edit_model( model_type='Organic', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Organic', Carbon=[1.23, 1.0])
Example of how to edit solute models:
model.edit_model( model_type='Solute', simulations='Simulation', model_name='NH4', InitialValues=0.2) model.edit_model( model_class='Solute', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Urea', InitialValues=0.002)
Edit a manager script:
model.edit_model( model_type='Manager', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Sow using a variable rule', population=8.4)
Edit surface organic matter parameters:
model.edit_model( model_type='SurfaceOrganicMatter', simulations='Simulation', model_name='SurfaceOrganicMatter', InitialResidueMass=2500) model.edit_model( model_type='SurfaceOrganicMatter', simulations='Simulation', model_name='SurfaceOrganicMatter', InitialCNR=85)
Edit Clock start and end dates:
model.edit_model( model_type='Clock', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Clock', Start='2021-01-01', End='2021-01-12')
Edit report _variables:
model.edit_model( model_type='Report', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Report', variable_spec='[Maize].AboveGround.Wt as abw')
Multiple report _variables:
model.edit_model( model_type='Report', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Report', variable_spec=[ '[Maize].AboveGround.Wt as abw', '[Maize].Grain.Total.Wt as grain_weight'])
the best way to edit cultivar with minimal error is to use a dict of commands as follows.
params = { "[Leaf].Photosynthesis.RUE.FixedValue": 1.8984705340394, "[Phenology].GrainFilling.Target.FixedValue": 710, "[Grain].MaximumGrainsPerCob.FixedValue": 810, "[Phenology].FloweringToGrainFilling.Target.FixedValue": 215, "[Phenology].MaturityToHarvestRipe.Target.FixedValue": 100, "[Maize].Grain.MaximumPotentialGrainSize.FixedValue": 0.867411373063701, "[Grain].MaximumNConc.InitialPhase.InitialNconc.FixedValue": 0.05, '[Maize].Root.SpecificRootLength.FixedValue': 135, '[Maize].Root.RootFrontVelocity.PotentialRootFrontVelocity.PreFlowering.RootFrontVelocity.FixedValue': 22, '[Rachis].DMDemands.Structural.DMDemandFunction.MaximumOrganWt.FixedValue': 36
}
- model.edit_model_by_path(model_type=’Models.PMF.Cultivar, model_name=’Dekalb_XL82’,
commands=params, cultivar_manager=’Sow using a variable rule, parameter_name=’CultivarName’ )
See also
Related API:
edit_model_by_path().- static inspect_settable_attributes(model_type) (inherited)
Inspect and return all settable attributes for a given APSIM model type.
This method identifies which attributes of a model can be modified by the user. APSIM model classes typically expose writable parameters through setter methods following the naming convention
set_<AttributeName>(). This function extracts all such attributes and returns them in a clean, user-friendly list.Added in v0.39.12.21
Parameters
- model_typetype or str
The APSIM model class or the registered model name. This value is validated and resolved to a concrete APSIM model class via
validate_model_obj().
Returns
- list of str
A list of attribute names that can be set on the specified model. These correspond to all public APSIM parameters for which a
set_<AttributeName>method exists. Theset_prefix is removed for clarity, so the list contains clean parameter names.
Notes
This method does not set or modify any attributes—its purpose is diagnostic and introspective.
Useful for error reporting, documentation, and informing users which parameters are valid inputs for
edit_model()or related methods.
Examples
from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel sm = ApsimModel('Maize') sm.inspect_settable_attributes(model_type='Models.Surface.SurfaceOrganicMatter')
['Canopies', 'Children', 'Enabled', 'InitialCNR', 'InitialCPR', 'InitialResidueMass', 'InitialResidueName', 'InitialResidueType', 'InitialStandingFraction', 'IsHidden', 'Name', 'Node', 'Parent', 'ReadOnly', 'ResourceName', 'Structure']
sm.inspect_settable_attributes(Models.WaterModel.WaterBalance)
['CN2Bare', 'CNCov', 'CNRed', 'CatchmentArea', 'Children', 'Depth', 'DiffusConst', 'DiffusSlope', 'DischargeWidth', 'Enabled', 'Eo', 'IsHidden', 'KLAT', 'Name', 'Node', 'PSIDul', 'Parent', 'PoreInteractionIndex', 'PotentialInfiltration', 'PrecipitationInterception', 'ReadOnly', 'ResourceName', 'Runon', 'SW', 'SWCON', 'Salb', 'Structure', 'SummerCona', 'SummerDate', 'SummerU', 'Thickness', 'Water', 'WaterTable', 'WinterCona', 'WinterDate', 'WinterU']
Added in version 0.39.12.21.
- find_model_in_replacements(self, model_type, model_name) (inherited)
checks whether the model to be edited is in the replacement, there is no point to contnue editing from individual simulations
- add_report_variable(self, variable_spec: 'Union[list, str, tuple]', report_name: 'str' = None, set_event_names: 'Union[str, list]' = None, simulations=None) (inherited)
This adds a report variable to the end of other _variables, if you want to change the whole report use change_report
Parameters
- variable_spec: str, required.
list of text commands for the report _variables e.g., ‘[Clock].Today as Date’
- param report_name: str, optional.
Name of the report variable if not specified, the first accessed report object will be altered
- set_event_names: list or str, optional.
A list of APSIM events that trigger the recording of _variables. Defaults to [‘[Clock].EndOfYear’] if not provided.
Returns
returns instance of apsimNGpy.core.core.apsim.ApsimModel or apsimNGpy.core.core.apsim.CoreModel
Raise
raises an
ValueErrorif a report is not foundExamples
>>> from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel >>> model = ApsimModel('Maize') >>> model.add_report_variable(variable_spec = '[Clock].Today as Date', report_name = 'Report') # isnepct the report >>> model.inspect_model_parameters(model_type='Models.Report', model_name='Report') {'EventNames': ['[Maize].Harvesting'], 'VariableNames': ['[Clock].Today', '[Maize].Phenology.CurrentStageName', '[Maize].AboveGround.Wt', '[Maize].AboveGround.N', '[Maize].Grain.Total.Wt*10 as Yield', '[Maize].Grain.Wt', '[Maize].Grain.Size', '[Maize].Grain.NumberFunction', '[Maize].Grain.Total.Wt', '[Maize].Grain.N', '[Maize].Total.Wt', '[Clock].Today as Date']} The new report variable is appended at the end of the existing ones
See also
Related APIs:
remove_report_variable()andadd_db_table().- remove_report_variable(self, variable_spec: 'Union[list, tuple, str]', report_name: 'str | None' = None) (inherited)
Remove one or more variable expressions from an APSIM Report component.
Parameters
- variable_specstr | list[str] | tuple[str, …]
Variable expression(s) to remove, e.g.
"[Clock].Today"or"[Clock].Today as Date". You may pass a single string or a list/tuple. Matching is done by exact text after whitespace normalization (consecutive spaces collapsed), so minor spacing differences are tolerated.- report_namestr, optional
Name of the Report component to modify. If
None, the default resolver (self._get_report) is used to locate the target report.
Returns
- list[str]
The updated list of variable expressions remaining in the report (in original order, without duplicates).
Notes
Variables not present are ignored (no error raised).
Order is preserved; duplicates are removed.
The model is saved at the end of this call.
Examples
>>> model= CoreModel('Maize') >>> model.add_report_variable(variable_spec='[Clock].Today as Date', report_name='Report') >>> model.inspect_model_parameters('Models.Report', 'Report')['VariableNames'] ['[Clock].Today', '[Maize].Phenology.CurrentStageName', '[Maize].AboveGround.Wt', '[Maize].AboveGround.N', '[Maize].Grain.Total.Wt*10 as Yield', '[Maize].Grain.Wt', '[Maize].Grain.Size', '[Maize].Grain.NumberFunction', '[Maize].Grain.Total.Wt', '[Maize].Grain.N', '[Maize].Total.Wt', '[Clock].Today as Date'] >>> model.remove_report_variable(variable_spec='[Clock].Today as Date', report_name='Report') >>> model.inspect_model_parameters('Models.Report', 'Report')['VariableNames'] ['[Clock].Today', '[Maize].Phenology.CurrentStageName', '[Maize].AboveGround.Wt', '[Maize].AboveGround.N', '[Maize].Grain.Total.Wt*10 as Yield', '[Maize].Grain.Wt', '[Maize].Grain.Size', '[Maize].Grain.NumberFunction', '[Maize].Grain.Total.Wt', '[Maize].Grain.N', '[Maize].Total.Wt']
See also
Related APIs:
add_report_variable()andadd_db_table().- remove_model(self, model_type: 'Models', model_name) (inherited)
Removes a model from the APSIM Models.Simulations namespace.
- model_type: Models
The type of the model to remove (e.g.,
Models.Clock). This parameter is required.- model_name: str, optional
The name of the specific model instance to remove (e.g.,
"Clock"). If not provided, all models of the specified type may be removed.
Returns:
None
Example:
from apsimNGpy import core from apsimNGpy.core.core import Models model = core.base_data.load_default_simulations(crop = 'Maize') model.remove_model(Models.Clock) #deletes the clock node model.remove_model(Models.Climate.Weather) #deletes the weather node
See also
Related APIs:
clone_model()andadd_model().- move_model(self, model_type: 'Models', new_parent_type: 'Models', model_name: 'str' = None, new_parent_name: 'str' = None, verbose: 'bool' = False, simulations: 'Union[str, list]' = None) (inherited)
Args:
- model_type: Models
type of model tied to Models Namespace
- new_parent_type: Models.
New model parent type (Models)
- model_name: str
Name of the model e.g., Clock, or Clock2, whatever name that was given to the model
- new_parent_name``: str
The new parent names =Field2, this field is optional but important if you have nested simulations
Returns:
returns instance of apsimNGpy.core.core.apsim.ApsimModel or apsimNGpy.core.core.apsim.CoreModel
- replicate_file(self, k: 'int', path: 'os.PathLike' = None, suffix: 'str' = 'replica') (inherited)
Replicates a file
ktimes. Parameters ———- path:str default is NoneIf specified, the copies will be placed in that dir_path with incremented filenames. If no path is specified, copies are created in the same dir_path as the original file, also with incremented filenames.
- k int:
The number of copies to create.
- suffix: str, optional
a suffix to attach with the copies. Default to “replicate”
Returns:
A generator(str) is returned.
- get_crop_replacement(self, Crop) (inherited)
- param Crop:
crop to get the replacement
- return:
System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerable APSIM plant object
- inspect_model_parameters(self, model_type: 'Union[Models, str]', model_name: 'str', simulations: 'Union[str, list]' = <UserOptionMissing>, parameters: 'Union[list, set, tuple, str]' = 'all', exclude: 'list | set | tuple | str' = None, **kwargs) (inherited)
Inspect the input parameters of a specific
APSIMmodel type instance within selected simulations.This method consolidates functionality previously spread across
examine_management_info,read_cultivar_params, and other inspectors, allowing a unified interface for querying parameters of interest across a wide range of APSIM models.Parameters
- model_type: str required
The name of the model class to inspect (e.g., ‘Clock’, ‘Manager’, ‘Physical’, ‘Chemical’, ‘Water’, ‘Solute’). Shorthand names are accepted (e.g., ‘Clock’, ‘Weather’) as well as fully qualified names (e.g., ‘Models.Clock’, ‘Models.Climate.Weather’).
- simulations: Union[str, list]
A single simulation name or a list of simulation names within the APSIM context to inspect.
- model_name: str
The name of the specific model instance within each simulation. For example, if
model_class='Solute',model_namemight be ‘NH4’, ‘Urea’, or another solute name.- parameters: Union[str, set, list, tuple], optional
A specific parameter or a collection of parameters to inspect. Defaults to
'all', in which case all accessible attributes are returned. For layered models like Solute, valid parameters includeDepth,InitialValues,SoluteBD,Thickness, etc.- exclude: Union[str, list, tuple], optional
used to exclude a few simulations and include only the rest of the simulations Added in v0.39.10.20+
- kwargs:
Reserved for future compatibility; currently unused.
Returns
Union[dict, list, pd.DataFrame, Any] The format depends on the model type as shown below:
- Weather:
file path(s) as string(s)
- Clock:
dictionary with start and end datetime objects (or a single datetime if only one is requested).
- Manager:
dictionary of script parameters.
- Soil-related:
pandas DataFrame of layered values.
- Report:
A dictionary with
VariableNamesandEventNames.
Cultivar: dictionary of parameter strings.
Raises
ValueErrorIf the specified model or simulation is not found or arguments are invalid.
NotImplementedErrorIf the model type is unsupported by the current interface.
Requirements
APSIM Next Generation Python bindings (
apsimNGpy)Python 3.10+
Examples:
from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel model_instance = ApsimModel('Maize')
Inspect full soil
Organicprofile:model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Organic', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Organic') CNR Carbon Depth FBiom ... FOM Nitrogen SoilCNRatio Thickness 0 12.0 1.20 0-150 0.04 ... 347.129032 0.100 12.0 150.0 1 12.0 0.96 150-300 0.02 ... 270.344362 0.080 12.0 150.0 2 12.0 0.60 300-600 0.02 ... 163.972144 0.050 12.0 300.0 3 12.0 0.30 600-900 0.02 ... 99.454133 0.025 12.0 300.0 4 12.0 0.18 900-1200 0.01 ... 60.321981 0.015 12.0 300.0 5 12.0 0.12 1200-1500 0.01 ... 36.587131 0.010 12.0 300.0 6 12.0 0.12 1500-1800 0.01 ... 22.191217 0.010 12.0 300.0 [7 rows x 9 columns]
Inspect soil
Physicalprofile:model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Physical', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Physical') AirDry BD DUL ... SWmm Thickness ThicknessCumulative 0 0.130250 1.010565 0.521000 ... 78.150033 150.0 150.0 1 0.198689 1.071456 0.496723 ... 74.508522 150.0 300.0 2 0.280000 1.093939 0.488438 ... 146.531282 300.0 600.0 3 0.280000 1.158613 0.480297 ... 144.089091 300.0 900.0 4 0.280000 1.173012 0.471584 ... 141.475079 300.0 1200.0 5 0.280000 1.162873 0.457071 ... 137.121171 300.0 1500.0 6 0.280000 1.187495 0.452332 ... 135.699528 300.0 1800.0 [7 rows x 17 columns]
Inspect soil
Chemicalprofile:model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Chemical', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Chemical') Depth PH Thickness 0 0-150 8.0 150.0 1 150-300 8.0 150.0 2 300-600 8.0 300.0 3 600-900 8.0 300.0 4 900-1200 8.0 300.0 5 1200-1500 8.0 300.0 6 1500-1800 8.0 300.0
Inspect one or more specific parameters:
model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Organic', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Organic', parameters='Carbon') Carbon 0 1.20 1 0.96 2 0.60 3 0.30 4 0.18 5 0.12 6 0.12
Inspect more than one specific properties:
model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Organic', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Organic', parameters=['Carbon', 'CNR']) Carbon CNR 0 1.20 12.0 1 0.96 12.0 2 0.60 12.0 3 0.30 12.0 4 0.18 12.0 5 0.12 12.0 6 0.12 12.0
Inspect Report module attributes:
model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Report', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Report') {'EventNames': ['[Maize].Harvesting'], 'VariableNames': ['[Clock].Today', '[Maize].Phenology.CurrentStageName', '[Maize].AboveGround.Wt', '[Maize].AboveGround.N', '[Maize].Grain.Total.Wt*10 as Yield', '[Maize].Grain.Wt', '[Maize].Grain.Size', '[Maize].Grain.NumberFunction', '[Maize].Grain.Total.Wt', '[Maize].Grain.N', '[Maize].Total.Wt']}
Specify only EventNames:
model_instance.inspect_model_parameters(‘Report’, simulations=’Simulation’, model_name=’Report’, parameters=’EventNames’) {‘EventNames’: [‘[Maize].Harvesting’]}
Inspect a weather file path:
model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Weather', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Weather') '%root%/Examples/WeatherFiles/AU_Dalby.met'
Inspect manager script parameters:
model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Manager', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Sow using a variable rule') {'Crop': 'Maize', 'StartDate': '1-nov', 'EndDate': '10-jan', 'MinESW': '100.0', 'MinRain': '25.0', 'RainDays': '7', 'CultivarName': 'Dekalb_XL82', 'SowingDepth': '30.0', 'RowSpacing': '750.0', 'Population': '10'}
Inspect manager script by specifying one or more parameters:
model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Manager', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Sow using a variable rule', parameters='Population') {'Population': '10'}
Inspect cultivar parameters:
model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Cultivar', simulations='Simulation', model_name='B_110') # lists all path specifications for B_110 parameters abd their values model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Cultivar', simulations='Simulation', model_name='B_110', parameters='[Phenology].Juvenile.Target.FixedValue') {'[Phenology].Juvenile.Target.FixedValue': '210'}
Inspect surface organic matter module:
model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Models.Surface.SurfaceOrganicMatter', simulations='Simulation', model_name='SurfaceOrganicMatter') {'NH4': 0.0, 'InitialResidueMass': 500.0, 'StandingWt': 0.0, 'Cover': 0.0, 'LabileP': 0.0, 'LyingWt': 0.0, 'InitialCNR': 100.0, 'P': 0.0, 'InitialCPR': 0.0, 'SurfOM': <System.Collections.Generic.List[SurfOrganicMatterType] object at 0x000001DABDBB58C0>, 'C': 0.0, 'N': 0.0, 'NO3': 0.0}
Inspect a few parameters as needed:
model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Models.Surface.SurfaceOrganicMatter', simulations='Simulation', ... model_name='SurfaceOrganicMatter', parameters={'InitialCNR', 'InitialResidueMass'}) {'InitialCNR': 100.0, 'InitialResidueMass': 500.0}
Inspect a clock:
model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Clock', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Clock') {'End': datetime.datetime(2000, 12, 31, 0, 0), 'Start': datetime.datetime(1990, 1, 1, 0, 0)}
Inspect a few Clock parameters as needed:
model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Clock', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Clock', parameters='End') datetime.datetime(2000, 12, 31, 0, 0)
Access specific components of the datetime object e.g., year, month, day, hour, minute:
model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Clock', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Clock', parameters='Start').year # gets the start year only 1990
Inspect solute models:
model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Solute', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Urea') Depth InitialValues SoluteBD Thickness 0 0-150 0.0 1.010565 150.0 1 150-300 0.0 1.071456 150.0 2 300-600 0.0 1.093939 300.0 3 600-900 0.0 1.158613 300.0 4 900-1200 0.0 1.173012 300.0 5 1200-1500 0.0 1.162873 300.0 6 1500-1800 0.0 1.187495 300.0 model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Solute', simulations='Simulation', model_name='NH4', parameters='InitialValues') InitialValues 0 0.1 1 0.1 2 0.1 3 0.1 4 0.1 5 0.1 6 0.1
See also
Related API:
inspect_model_parameters_by_path()- inspect_model_parameters_by_path(self, path, *, parameters: 'Union[list, set, tuple, str]' = None) (inherited)
Inspect and extract parameters from a model component specified by its path.
Parameters:
- path: str required
The path relative to the Models.Core.Simulations Node
- parameters: Union[str, set, list, tuple], optional
A specific parameter or a collection of parameters to inspect. Defaults to
'all', in which case all accessible attributes are returned. For layered models like Solute, valid parameters includeDepth,InitialValues,SoluteBD,Thickness, etc.- kwargs:
Reserved for future compatibility; currently unused.
Returns
Union[dict, list, pd.DataFrame, Any] The format depends on the model type as shown below:
- Weather:
file path(s) as string(s)
- Clock:
dictionary with start and end datetime objects (or a single datetime if only one is requested).
- Manager:
dictionary of script parameters.
- Soil-related:
pandas DataFrame of layered values.
- Report:
A dictionary with
VariableNamesandEventNames.
Cultivar: dictionary of parameter strings.
Raises
ValueErrorIf the specified model or simulation is not found or arguments are invalid.
NotImplementedErrorIf the model type is unsupported by the current interface.
Requirements
APSIM Next Generation Python bindings (
apsimNGpy)Python 3.10+
See also
Related API:
inspect_model_parameters()Others:inspect_model(),inspect_file()- edit_cultivar(self, *, CultivarName: 'str', commands: 'str', values: 'Any', **kwargs) (inherited)
@deprecated Edits the parameters of a given cultivar. we don’t need a simulation name for this unless if you are defining it in the manager section, if that it is the case, see update_mgt.
- Requires:
required a replacement for the crops
Args:
CultivarName (str, required): Name of the cultivar (e.g., ‘laila’).
variable_spec (str, required): A strings representing the parameter paths to be edited.
Returns: instance of the class CoreModel or ApsimModel
Example:
('[Grain].MaximumGrainsPerCob.FixedValue', '[Phenology].GrainFilling.Target.FixedValue') - values: values for each command (e.g., (721, 760)).
- update_cultivar(self, *, parameters: 'dict', simulations: 'Union[list, tuple]' = None, clear=False, **kwargs) (inherited)
Update cultivar parameters
- parameters: (dict, required)
dictionary of cultivar parameters to update.
- simulationsstr optional
List or tuples of simulation names to update if
Noneupdate all simulations.- clear (bool, optional)
If
Trueremove all existing parameters, by defaultFalse.
- recompile_edited_model(self, out_path: 'os.PathLike') (inherited)
Args:
out_path: os.PathLike object this method is called to convert the simulation object from ConverterReturnType to model like objectreturn:self- update_mgt_by_path(self, *, path: 'str', fmt='.', **kwargs) (inherited)
Parameters
- path: str
A complete node path to the script manager e.g. ‘.Simulations.Simulation.Field.Sow using a variable rule’
- fmt: str
seperator for formatting the path e.g., “.”. Other characters can be used with caution, e.g., / and clearly declared in fmt argument. If you want to use the forward slash, it will be ‘/Simulations/Simulation/Field/Sow using a variable rule’, fmt = ‘/’
- **kwargs:
Corresponding keyword arguments representing the paramters in the script manager and their values. Values is what you want to change to; Example here
Population=8.2, values should be entered with their corresponding data types e.g., int, float, bool,str etc.
Returns:
Instance of apsimNgpy.core.ApsimModel or apsimNgpy.core.experimentmanager.ExperimentManager
- replace_model_from(self, model, model_type: 'str', model_name: 'str' = None, target_model_name: 'str' = None, simulations: 'str' = None) (inherited)
@deprecated and will be removed function has not been maintained for a long time, use it at your own risk
Replace a model, e.g., a soil model with another soil model from another APSIM model. The method assumes that the model to replace is already loaded in the current model and the same class as a source model. e.g., a soil node to soil node, clock node to clock node, et.c
Parameters:
model: Path to the APSIM model file or a CoreModel instance.
- model_type: (str):
Class name (as string) of the model to replace (e.g., “Soil”).
- model_name: (str, optional)
Name of the model instance to copy from the source model. If not provided, the first match is used.
- target_model_name: (str, optional)
Specific simulation name to target for replacement. Only used when replacing Simulation-level objects.
- simulations (str, optional):
Simulation(s) to operate on. If None, applies to all.
- Returns:
self: To allow method chaining.
- Raises:
ValueError: Ifmodel_classis “Simulations” which is not allowed for replacement.
- update_mgt(self, *, management: 'Union[dict, tuple]', simulations: '[list, tuple]' = <UserOptionMissing>, out: '[Path, str]' = None, reload: 'bool' = True, **kwargs) (inherited)
Update management settings in the model. This method handles one management parameter at a time.
Parameters
- management: dict or tuple
A dictionary or tuple of management parameters to update. The dictionary should have ‘Name’ as the key for the management script’s name and corresponding values to update. Lists are not allowed as they are mutable and may cause issues with parallel processing. If a tuple is provided, it should be in the form (param_name, param_value).
- simulations: list of str, optional
List of simulation names to update. If
None, updates all simulations. This is not recommended for large numbers of simulations as it may result in a high computational load.- out: str or pathlike, optional
Path to save the edited model. If
None, uses the default output path specified inself.out_pathorself.model_info.path. No need to callsave_edited_fileafter updating, as this method handles saving.
Returns
Returns the instance of the respective model class for method chaining.
..note:
Ensure that the `management` parameter is provided in the correct format to avoid errors. - This method does not perform `validation` on the provided `management` dictionary beyond checking for key existence. - If the specified management script or parameters do not exist, they will be ignored.
- preview_simulation(self, watch=False) (inherited)
Open the current simulation in the APSIM Next Gen GUI.
This first saves the in-memory simulation to
out_pathand then launches the APSIM Next Gen GUI (viaget_apsim_bin_path()) so you can inspect the model tree and make quick edits side by side.Parameters
- watchbool, default False
If True, Python will listen for GUI edits and sync them back into the model instance in (near) real time. This feature is experimental.
Returns
- None
This function performs a side effect (opening the GUI) and does not return a value.
Raises
- FileNotFoundError
If the file does not exist after
save().- RuntimeError
If the APSIM Next Gen executable cannot be located or the GUI fails to start.
Tip
The file opened in the GUI is a saved copy of this Python object. Changes made in the GUI are not propagated back to the
ApsimModelinstance unless you setwatch=True. Otherwise, to continue working in Python with GUI edits, save the file in APSIM and re-load it, for example:ApsimModel("gui_edited_file_path.apsimx")
Examples
1. Preview only
from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel model = ApsimModel("Maize", out_path="test_.apsimx") model.preview_simulation()

2. Preview and edit simultaneously
After opening the APSIMX file in the GUI via the watching mode (
watch=True), you can modify any parameters using GUI interface. The Example given below involved changing parameters such as Plant population (/m²), Cultivar to be sown, and Row spacing (mm) in the Sow using a variable rule script and finally, checked whether the changes were successful by inspecting the model.model.preview_simulation(watch=True)

Example console output when
watch=True:2025-10-24 13:05:08,480 - INFO - Watching for GUI edits... Save in APSIM to sync back. 2025-10-24 13:05:08,490 - INFO - Press Ctrl+C in this cell to stop. APSIM GUI saved. Syncing model... 2025-10-24 13:05:24,112 - INFO - Watching terminated successfully.
Tip
When
watch=True, follow the console instructions. One critical step is that you must pressCtrl+Cto stop watching.Checking if changes were successfully propagated back
model.inspect_model_parameters("Models.Manager", "Sow using a variable rule")
{'Crop': '[Maize]', 'StartDate': '1-nov', 'EndDate': '10-jan', 'MinESW': '100', 'MinRain': '25', 'RainDays': '7', 'CultivarName': 'B_95', 'SowingDepth': '25', 'RowSpacing': '700', 'Population': '4'}Tip
Depending on your environment, you may need to close the GUI window to continue or follow the prompts shown after termination.
- replace_met_file(self, *, weather_file: 'Union[Path, str]', simulations=<UserOptionMissing>, exclude: 'set | str | tuple | list' = None, **kwargs) (inherited)
Deprecated since version 0.**x**: This helper will be removed in a future release. Prefer newer weather configuration utilities or set the
FileNameproperty on weather nodes directly.Replace the
FileNameof everyModels.Climate.Weathernode under one or more simulations so they point to a new.metfile.This method traverses the APSIM NG model tree under each selected simulation and updates the weather component(s) in-place. Version-aware traversal is used:
If
APSIM_VERSION_NO > BASE_RELEASE_NOorAPSIM_VERSION_NO == GITHUB_RELEASE_NO: useModelTools.find_all_in_scope()to findModels.Climate.Weathernodes.Otherwise: fall back to
sim.FindAllDescendants[Models.Climate.Weather]().
Parameters
- weather_fileUnion[pathlib.Path, str]
Path to the
.metfile. May be absolute or relative to the current working directory. The path must exist at call time; otherwise aFileNotFoundErroris raised.- simulationsAny, optional
Simulation selector forwarded to
find_simulations(). If left asMissingOption(default) (or if your implementation acceptsNone), all simulations yielded byfind_simulations()are updated. Acceptable types depend on yourfind_simulations()contract (e.g., iterable of names, single name, or sentinel).- exclude: (str, tuple, list), optional
used to eliminate a given simulation from getting updated Added in 0.39.10.20+
- **kwargs
Ignored. Reserved for backward compatibility and future extensions.
Returns
- Self
The current model/manager instance to support method chaining.
Raises
- FileNotFoundError
If
weather_filedoes not exist.- Exception
Any exception raised by
find_simulations()or underlying APSIM traversal utilities is propagated unchanged.
Side Effects
Mutates the model by setting
met.FileName = os.path.realpath(weather_file)for each matchedModels.Climate.Weathernode.Notes
No-op safety: If a simulation has no Weather nodes, that simulation is silently skipped.
Path normalization: The stored path is the canonical real path (
os.path.realpath).Thread/process safety: This operation mutates in-memory model state and is not inherently thread-safe. Coordinate external synchronization if calling concurrently.
Examples
Update all simulations to use a local
Ames.met:model.replace_met_file(weather_file="data/weather/Ames.met")
Update only selected simulations:
model.replace_met_file( weather_file=Path("~/wx/Boone.met").expanduser(), simulations=("Sim_A", "Sim_B") )
See Also
find_simulations : Resolve and yield simulation objects by name/selector. ModelTools.find_all_in_scope : Scope-aware traversal utility. Models.Climate.Weather : APSIM NG weather component.
- get_weather_from_file(self, weather_file, simulations=None)
Point targeted APSIM Weather nodes to a local
.metfile.The function name mirrors the semantics of
get_weather_from_webbut sources the weather from disk. If the provided path lacks the.metsuffix, it is appended. The file must exist on disk.Parameters
- weather_file: str | Path
Path (absolute or relative) to a
.metfile. If the suffix is missing,.metis appended. AFileNotFoundErroris raised if the final path does not exist. The path is resolved to an absolute path to avoid ambiguity.- simulations: None | str | Iterable[str], optional
Which simulations to update: -
None(default): update all Weather nodes found underSimulations. -stror iterable of names: only update Weather nodes within the namedsimulation(s). A
ValueErroris raised if a requested simulation has no Weather nodes.
Returns
Instance of the model for method chaining
Raises
- FileNotFoundError
If the resolved
.metfile does not exist.- ValueError
If any requested simulation exists but contains no Weather nodes.
Side Effects
Sets
w.FileNamefor each targetedModels.Climate.Weathernode to the resolved path ofweather_file. The file is not copied; only the path inside the APSIM document is changed.Notes
APSIM resolves relative paths relative to the
.apsimxfile. Using an absolute path (the default here) reduces surprises across working directories.Replacement folders that contain Weather nodes are also updated when
simulationsisNone(i.e., “update everything in scope”).
Examples
Update all Weather nodes:
from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel model = ApsimModel("Maize") model.get_weather_from_file("data/ames_2020.met")
Update only two simulations (suffix added automatically):
model.get_weather_from_file("data/ames_2020", simulations=("Simulation",))
See also
Related APIs:
edit_model()andedit_model_by_path().- get_weather_from_web(self, lonlat: 'tuple', start: 'int', end: 'int', simulations=<UserOptionMissing>, source='nasa', filename=None) (inherited)
Replaces the weather (met) file in the model using weather data fetched from an online source. Internally, calls get_weather_from_file after downloading the weather
Parameters:
- lonlat: tuple
A tuple containing the longitude and latitude coordinates.
- start: int
Start date for the weather data retrieval.
- end: int
End date for the weather data retrieval.
- simulations: str | list[str] default is all or None list of simulations or a singular simulation
name, where to place the weather data, defaults to None, implying
allthe available simulations- source: str default is ‘nasa’
Source of the weather data.
- filename: str default is generated using the base name of the apsimx file in use, and the start and
end years Name of the file to save the retrieved data. If None, a default name is generated.
- Returns:
model object with the corresponding file replaced with the fetched weather data.
Examples
>>> from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel >>> model = ApsimModel(model= "Maize") >>> model.get_weather_from_web(lonlat = (-93.885490, 42.060650), start = 1990, end = 2001)
Changing weather data with non-matching start and end dates in the simulation will lead to RuntimeErrors. To avoid this, first check the start and end date before proceeding as follows:
>>> dt = model.inspect_model_parameters(model_class='Clock', model_name='Clock', simulations='Simulation') >>> start, end = dt['Start'].year, dt['End'].year # output: 1990, 2000
- change_report(self, *, command: 'str', report_name='Report', simulations=None, set_DayAfterLastOutput=None, **kwargs) (inherited)
Set APSIM report _variables for specified simulations.
This function allows you to set the variable names for an APSIM report in one or more simulations.
Parameters
- command: str
The new report string that contains variable names.
- report_name: str
The name of the APSIM report to update defaults to Report.
- simulations: list of str, optional
A list of simulation names to update. If
None, the function will update the report for all simulations.
Returns
None
- extract_soil_physical(self, simulations: '[tuple, list]' = None) (inherited)
Find physical soil
Parameters
simulation, optionalSimulation name, if
Noneuse the first simulation.
Returns
APSIM Models.Soils.Physical object
- extract_any_soil_physical(self, parameter, simulations: '[list, tuple]' = <UserOptionMissing>) (inherited)
Extracts soil physical parameters in the simulation
- Args::
parameter(_string_): string e.g. DUL, SATsimulations(string, optional): Targeted simulation name. Defaults to None.
- inspect_model(self, model_type: 'Union[str, Models]', fullpath=True, **kwargs) (inherited)
Inspect the model types and returns the model paths or names.
When is it needed?
useful if you want to identify the paths or name of the model for further editing the model e.g., with the
in edit_modelmethod.Parameters
- model_classtype | str
The APSIM model type to search for. You may pass either a class (e.g., Models.Clock, Models.Manager) or a string. Strings can be short names (e.g., “Clock”, “Manager”) or fully qualified (e.g., “Models.Core.Simulation”, “Models.Climate.Weather”, “Models.Core.IPlant”). Please see from The list of classes or model types from the Models Namespace below. Red represents the modules, and this method
will throw an error if only a module is supplied. The list constitutes the classes or model types under each module
- Models:
Models.Clock
Models.Fertiliser
Models.Irrigation
Models.Manager
Models.Memo
Models.MicroClimate
Models.Operations
Models.Report
Models.Summary
- Models.Climate:
Models.Climate.Weather
- Models.Core:
Models.Core.Folder
Models.Core.Simulation
Models.Core.Simulations
Models.Core.Zone
- Models.Factorial:
Models.Factorial.Experiment
Models.Factorial.Factors
Models.Factorial.Permutation
- Models.PMF:
Models.PMF.Cultivar
Models.PMF.Plant
- Models.Soils:
Models.Soils.Arbitrator.SoilArbitrator
Models.Soils.CERESSoilTemperature
Models.Soils.Chemical
Models.Soils.Nutrients.Nutrient
Models.Soils.Organic
Models.Soils.Physical
Models.Soils.Sample
Models.Soils.Soil
Models.Soils.SoilCrop
Models.Soils.Solute
Models.Soils.Water
- Models.Storage:
Models.Storage.DataStore
- Models.Surface:
Models.Surface.SurfaceOrganicMatter
- Models.WaterModel:
Models.WaterModel.WaterBalance
- fullpathbool, optional (default: False)
If False, return the model name only. If True, return the model’s full path relative to the Simulations root.
Returns
- list[str]
A list of model names or full paths, depending on
fullpath.
Examples:
from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel from apsimNGpy.core.core import Models
load default
maizemodule:model = ApsimModel('Maize')
Find the path to all the manager scripts in the simulation:
model.inspect_model(Models.Manager, fullpath=True) [.Simulations.Simulation.Field.Sow using a variable rule', '.Simulations.Simulation.Field.Fertilise at sowing', '.Simulations.Simulation.Field.Harvest']
Inspect the full path of the Clock Model:
model.inspect_model(Models.Clock) # gets the path to the Clock models ['.Simulations.Simulation.Clock']
Inspect the full path to the crop plants in the simulation:
model.inspect_model(Models.Core.IPlant) # gets the path to the crop model ['.Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize']
Or use the full string path as follows:
model.inspect_model(Models.Core.IPlant, fullpath=False) # gets you the name of the crop Models ['Maize']
Get the full path to the fertilizer model:
model.inspect_model(Models.Fertiliser, fullpath=True) ['.Simulations.Simulation.Field.Fertiliser']
The models from APSIM Models namespace are abstracted to use strings. All you need is to specify the name or the full path to the model enclosed in a stirng as follows:
model.inspect_model('Clock') # get the path to the clock model ['.Simulations.Simulation.Clock']
Alternatively, you can do the following:
model.inspect_model('Models.Clock') ['.Simulations.Simulation.Clock']
Repeat inspection of the plant model while using a
string:model.inspect_model('IPlant') ['.Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize']
Inspect using the full model namespace path:
model.inspect_model('Models.Core.IPlant')
What about the weather model?:
model.inspect_model('Weather') # inspects the weather module ['.Simulations.Simulation.Weather']
Alternative:
# or inspect using full model namespace path model.inspect_model('Models.Climate.Weather') ['.Simulations.Simulation.Weather']
Try finding the path to the cultivar model:
model.inspect_model('Cultivar', fullpath=False) # list all available cultivar names ['Hycorn_53', 'Pioneer_33M54', 'Pioneer_38H20','Pioneer_34K77', 'Pioneer_39V43','Atrium', 'Laila', 'GH_5019WX']
# we can get only the names of the cultivar models using the full string path:
model.inspect_model('Models.PMF.Cultivar', fullpath = False) ['Hycorn_53','Pioneer_33M54', 'Pioneer_38H20','Pioneer_34K77', 'Pioneer_39V43','Atrium', 'Laila', 'GH_5019WX']
Tip
- Models can be inspected either by importing the Models namespace or by using string paths. The most reliable
approach is to provide the full model path—either as a string or as the
Modelsobject.- However, remembering full paths can be tedious, so allowing partial model names or references can significantly
save time during development and exploration.
Note
You do not need to import
Modelsif you pass a string; both short and fully qualified names are supported.“Full path” is the APSIM tree path relative to the Simulations node (be mindful of the difference between Simulations (root) and an individual Simulation).
See also
Related APIs:
inspect_file(),inspect_model_parameters(),inspect_model_parameters_by_path()- property configs(inherited)
records activities or modifications to the model including changes to the file
- replace_soils_values_by_path(self, node_path: 'str', indices: 'list' = None, **kwargs) (inherited)
set the new values of the specified soil object by path. only layers parameters are supported.
Unfortunately, it handles one soil child at a time e.g.,
Physicalat a goParameters:
- node_path: (str, required):
complete path to the soil child of the Simulations e.g.,Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Organic. Use`copy path to node function in the GUI to get the real path of the soil node.
- indices: (list, optional)
defaults to none but could be the position of the replacement values for arrays
- **kwargs: (key word arguments)
This carries the parameter and the values e.g., BD = 1.23 or BD = [1.23, 1.75] if the child is
Physical, orCarbonif the child isOrganicraises: `ValueError if none of the key word arguments, representing the paramters are specified
- returns:
Instance of the model object
Example:
from apsimNGpy.core.base_data import load_default_simulations model = load_default_simulations(crop ='Maize', simulations_object=False) # initiate model. model = CoreModel(model) # ``replace`` with your intended file path model.replace_soils_values_by_path(node_path='.Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Organic', indices=[0], Carbon =1.3) sv= model.get_soil_values_by_path('.Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Organic', 'Carbon') output # {'Carbon': [1.3, 0.96, 0.6, 0.3, 0.18, 0.12, 0.12]}
- replace_soil_property_values(self, *, parameter: 'str', param_values: 'list', soil_child: 'str', simulations: 'list' = <UserOptionMissing>, indices: 'list' = None, crop=None, **kwargs) (inherited)
Replaces values in any soil property array. The soil property array.
parameter: str: parameter name e.g., NO3, ‘BD’param_values: list or tuple: values of the specified soil property name to replacesoil_child: str: sub child of the soil component e.g., organic, physical etc.simulations: list: list of simulations to where the child is found ifnot found, all current simulations will receive the new values, thus defaults to None
indices: list. Positions in the array which will be replaced. Please note that unlike C#, python satrt counting from 0crop(str, optional): string for soil water replacement. Default is None- clean_up(self, db=True, verbose=False, csv=True) (inherited)
Clears the file cloned the datastore and associated csv files are not deleted if db is set to False defaults to True.
- Returns:
>>None: This method does not return a value.
Caution
Please proceed with caution, we assume that if you want to clear the model objects, then you don’t need them, but by making copy compulsory, then, we are clearing the edited files
- create_experiment(self, permutation: 'bool' = True, base_name: 'str' = None, **kwargs) (inherited)
@deprecated and will be removed in future versions for this class.
Initialize an
ExperimentManagerinstance, adding the necessary models and factors.Args:
kwargs: Additional parameters for CoreModel.permutation(bool). If True, the experiment uses a permutation node to run unique combinations of the specified factors for the simulation. For example, if planting population and nitrogen fertilizers are provided, each combination of planting population level and fertilizer amount is run as an individual treatment.base_name(str, optional): The name of the base simulation to be moved into the experiment setup. if notprovided, it is expected to be Simulation as the default.
Warning
base_nameis optional but the experiment may not be created if there are more than one base simulations. Therefore, an error is likely.- refresh_model(self) (inherited)
for methods that will alter the simulation objects and need refreshing the second time we call @return: self for method chaining
- add_fac(self, model_type, parameter, model_name, values, factor_name=None) (inherited)
Add a factor to the initiated experiment. This should replace add_factor. which has less abstractionn @param model_type: model_class from APSIM Models namespace @param parameter: name of the parameter to fill e.g CNR @param model_name: name of the model @param values: values of the parameter, could be an iterable for case of categorical variables or a string e.g, ‘0 to 100 step 10 same as [0, 10, 20, 30, …]. @param factor_name: name to identify the factor in question @return:
- set_continuous_factor(self, factor_path, lower_bound, upper_bound, interval, factor_name=None) (inherited)
Wraps around
add_factorto add a continuous factor, just for clarity- Args:
factor_path: (str): The path of the factor definition relative to its child node,e.g.,
"[Fertilise at sowing].Script.Amount".
factor_name: (str): The name of the factor.lower_bound: (int or float): The lower bound of the factor.upper_bound: (int or float): The upper bound of the factor.interval: (int or float): The distance between the factor levels.Returns:ApsimModelorCoreModel: An instance ofapsimNGpy.core.core.apsim.ApsimModelorCoreModel.
Example:
from apsimNGpy.core import base_data apsim = base_data.load_default_simulations(crop='Maize') apsim.create_experiment(permutation=False) apsim.set_continuous_factor(factor_path = "[Fertilise at sowing].Script.Amount", lower_bound=100, upper_bound=300, interval=10)
- set_categorical_factor(self, factor_path: 'str', categories: 'Union[list, tuple]', factor_name: 'str' = None) (inherited)
wraps around
add_factor()to add a continuous factor, just for clarity.factor_path: (str, required): path of the factor definition relative to its child node “[Fertilise at sowing].Script.Amount”factor_name: (str) name of the factor.categories: (tuple, list, required): multiple values of a factorreturns:ApsimModelorCoreModel: An instance ofapsimNGpy.core.core.apsim.ApsimModelorCoreModel.
Example:
from apsimNGpy.core import base_data apsim = base_data.load_default_simulations(crop='Maize') apsim.create_experiment(permutation=False) apsim.set_continuous_factor(factor_path = "[Fertilise at sowing].Script.Amount", lower_bound=100, upper_bound=300, interval=10)
- add_crop_replacements(self, _crop: 'str') (inherited)
Adds a replacement folder as a child of the simulations.
Useful when you intend to edit cultivar parameters.
- Args:
_crop(str): Name of the crop to be added to the replacement folder.Returns:ApsimModel: An instance of
apsimNGpy.core.core.apsim.ApsimModelorCoreModel.
Raises:ValueError: If the specified crop is not found.
- get_model_paths(self, cultivar=False)
Select out a few model types to use for building the APSIM file inspections
- inspect_file(self, *, cultivar=False, console=True, **kwargs) (inherited)
Inspects the file by traversing the entire simulation tree, using
inspect_model()under the hoodThis method is important in inspecting the
whole fileand also getting thescripts paths.Parameters
- cultivar: (bool)
To include cultivar paths.
- console: (bool)
Prints to the console if True
Examples
from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel model = ApsimModel('Maize') model.inspect_file(cultivar=False)
# output
└── Models.Core.Simulations: .Simulations ├── Models.Storage.DataStore: .Simulations.DataStore ├── Models.Core.Folder: .Simulations.Replacements │ └── Models.PMF.Plant: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize └── Models.Core.Simulation: .Simulations.Simulation ├── Models.Clock: .Simulations.Simulation.Clock ├── Models.Core.Zone: .Simulations.Simulation.Field │ ├── Models.Manager: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Fertilise at sowing │ ├── Models.Fertiliser: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Fertiliser │ ├── Models.Manager: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Harvest │ ├── Models.PMF.Plant: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize │ ├── Models.Report: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Report │ ├── Models.Soils.Soil: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Chemical: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Chemical │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Solute: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.NH4 │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Solute: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.NO3 │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Organic: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Organic │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Physical: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Physical │ │ │ └── Models.Soils.SoilCrop: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Physical.MaizeSoil │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Solute: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Urea │ │ └── Models.Soils.Water: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Water │ ├── Models.Manager: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Sow using a variable rule │ └── Models.Surface.SurfaceOrganicMatter: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.SurfaceOrganicMatter ├── Models.Graph: .Simulations.Simulation.Graph │ └── Models.Series: .Simulations.Simulation.Graph.Series ├── Models.MicroClimate: .Simulations.Simulation.MicroClimate ├── Models.Soils.Arbitrator.SoilArbitrator: .Simulations.Simulation.SoilArbitrator ├── Models.Summary: .Simulations.Simulation.Summary └── Models.Climate.Weather: .Simulations.Simulation.WeatherTurn cultivar paths on as follows:
model.inspect_file(cultivar=True)
# output
└── Models.Core.Simulations: .Simulations ├── Models.Storage.DataStore: .Simulations.DataStore ├── Models.Core.Folder: .Simulations.Replacements │ └── Models.PMF.Plant: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize │ └── Models.Core.Folder: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Atrium │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.CG4141 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Dekalb_XL82 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.GH_5009 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.GH_5019WX │ ├── Models.Core.Folder: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_100 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_103 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_105 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_108 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_110 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_112 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_115 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_120 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_130 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_80 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_90 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_95 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_100 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_103 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_105 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_108 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_110 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_112 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_115 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_120 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_130 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_80 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_90 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_95 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.HY_110 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.LY_110 │ │ └── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.P1197 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Hycorn_40 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Hycorn_53 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Katumani │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Laila │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Makueni │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Melkassa │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.NSCM_41 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_3153 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_33M54 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_34K77 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_38H20 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_39G12 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_39V43 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.malawi_local │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh12 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh16 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh17 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh18 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh19 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.r201 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.r215 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc401 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc501 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc601 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc623 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc625 │ └── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.sr52 └── Models.Core.Simulation: .Simulations.Simulation ├── Models.Clock: .Simulations.Simulation.Clock ├── Models.Core.Zone: .Simulations.Simulation.Field │ ├── Models.Manager: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Fertilise at sowing │ ├── Models.Fertiliser: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Fertiliser │ ├── Models.Manager: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Harvest │ ├── Models.PMF.Plant: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize │ │ └── Models.Core.Folder: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Atrium │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.CG4141 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Dekalb_XL82 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.GH_5009 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.GH_5019WX │ │ ├── Models.Core.Folder: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_100 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_103 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_105 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_108 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_110 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_112 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_115 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_120 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_130 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_80 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_90 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_95 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_100 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_103 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_105 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_108 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_110 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_112 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_115 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_120 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_130 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_80 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_90 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_95 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.HY_110 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.LY_110 │ │ │ └── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.P1197 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Hycorn_40 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Hycorn_53 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Katumani │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Laila │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Makueni │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Melkassa │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.NSCM_41 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_3153 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_33M54 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_34K77 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_38H20 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_39G12 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_39V43 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.malawi_local │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh12 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh16 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh17 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh18 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh19 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.r201 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.r215 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc401 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc501 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc601 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc623 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc625 │ │ └── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.sr52 │ ├── Models.Report: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Report │ ├── Models.Soils.Soil: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Chemical: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Chemical │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Solute: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.NH4 │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Solute: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.NO3 │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Organic: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Organic │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Physical: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Physical │ │ │ └── Models.Soils.SoilCrop: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Physical.MaizeSoil │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Solute: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Urea │ │ └── Models.Soils.Water: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Water │ ├── Models.Manager: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Sow using a variable rule │ └── Models.Surface.SurfaceOrganicMatter: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.SurfaceOrganicMatter ├── Models.Graph: .Simulations.Simulation.Graph │ └── Models.Series: .Simulations.Simulation.Graph.Series ├── Models.MicroClimate: .Simulations.Simulation.MicroClimate ├── Models.Soils.Arbitrator.SoilArbitrator: .Simulations.Simulation.SoilArbitrator ├── Models.Summary: .Simulations.Simulation.Summary └── Models.Climate.Weather: .Simulations.Simulation.WeatherSee also
Related APIs:
inspect_model(),inspect_model_parameters()
- summarize_numeric(self, data_table: 'Union[str, tuple, list]' = None, columns: 'list' = None, percentiles=(0.25, 0.5, 0.75), round=2)
Summarize numeric columns in a simulated pandas DataFrame. Useful when you want to quickly look at the simulated data
Parameters:
data_table (list, tuple, str): The names of the data table attached to the simulations. defaults to all data tables.
specific (list) columns to summarize.
percentiles (tuple): Optional percentiles to include in the summary.
round (int): number of decimal places for rounding off.
Returns:
pd.DataFrame: A summary DataFrame with statistics for each numeric column.
- add_db_table(self, variable_spec: 'list' = None, set_event_names: 'list' = None, rename: 'str' = None, simulation_name: 'Union[str, list, tuple]' = <UserOptionMissing>) (inherited)
Adds a new database table, which
APSIMcallsReport(Models.Report) to theSimulationunder a Simulation Zone.This is different from
add_report_variablein that it creates a new, named report table that collects data based on a given list of _variables and events. actuParameters:
- variable_spec: (list or str)
A list of APSIM variable paths to include in the report table. If a string is passed, it will be converted to a list.
- set_event_names: (list or str, optional):
- A list of APSIM events that trigger the recording of _variables.
Defaults to [‘[Clock].EndOfYear’] if not provided. other examples include ‘[Clock].StartOfYear’, ‘[Clock].EndOfsimulation’, ‘[crop_name].Harvesting’ etc.
rename: (str): The name of the report table to be added. Defaults to ‘my_table’.
- simulation_name: (str,tuple, or list, Optional)
if specified, the name of the simulation will be searched and will become the parent candidate for the report table. If it is none, all Simulations in the file will be updated with the new db_table
Raises:
ValueError: If no variable_spec is provided.RuntimeError: If no Zone is found in the current simulation scope.Examples:
from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel model = ApsimModel('Maize') model.add_db_table(variable_spec=['[Clock].Today', '[Soil].Nutrient.TotalC[1]/1000 as SOC1'], rename='report2') model.add_db_table(variable_spec=['[Clock].Today', '[Soil].Nutrient.TotalC[1]/1000 as SOC1', '[Maize].Grain.Total.Wt*10 as Yield'], rename='report2', set_event_names=['[Maize].Harvesting','[Clock].EndOfYear' ])
See also
Related APIs:
remove_report_variables()andadd_report_variables().- plot_mva(self, table: pandas.core.frame.DataFrame, time_col: Hashable, response: Hashable, *, expression: str = None, window: int = 5, min_period: int = 1, grouping: Hashable | collections.abc.Sequence[Hashable] | NoneType = None, preserve_start: bool = True, kind: str = 'line', estimator='mean', plot_raw: bool = False, raw_alpha: float = 0.35, raw_linewidth: float = 1.0, auto_datetime: bool = False, ylabel: str | None = None, return_data: bool = False, **kwargs)
Plot a centered moving-average (MVA) of a response using
seaborn.relplot.Enhancements over a direct
relplotcall: - Computes and plots a smoothed series viaapsimNGpy.stats.data_insights.mva(). - Supports multi-column grouping; will auto-construct a composite hue if needed. - Optional overlay of the raw (unsmoothed) series for comparison. - Stable (mergesort) time ordering.Parameters
- tablepandas.DataFrame or str
Data source or table name; if
None, use :pyattr:`results`.- time_colhashable
Time (x-axis) column.
- responsehashable
Response (y) column to smooth.
- expression: str default is None
simple mathematical expression to create new columns from existing columns
- windowint, default=5
MVA window size.
- min_periodint, default=1
Minimum periods for the rolling mean.
- groupinghashable or sequence of hashable, optional
One or more grouping columns.
- preserve_startbool, default=True
Preserve initial values when centering.
- kind{“line”,”scatter”}, default=”line”
Passed to
sns.relplot.- estimatorstr or None, default=”mean”
Passed to
sns.relplot(set toNoneto plot raw observations).- plot_rawbool, default=False
Overlay the raw series on each facet.
- raw_alphafloat, default=0.35
Alpha for the raw overlay.
- raw_linewidthfloat, default=1.0
Line width for the raw overlay.
- auto_datetimebool, default=False
Attempt to convert
time_colto datetime.- ylabelstr, optional
Custom y-axis label; default is generated from window/response.
- return_databool, default=False
If
True, return(FacetGrid, smoothed_df).
Returns
- seaborn.FacetGrid
The relplot grid, or
(grid, smoothed_df)ifreturn_data=True.
Notes
This function calls
seaborn.relplot()and accepts its keyword arguments via**kwargs. See link below for details:https://seaborn.pydata.org/generated/seaborn/relplot.html
- boxplot(self, column, *, table=None, expression: str = None, by=None, figsize=(10, 8), grid=False, **kwargs) (inherited)
Plot a boxplot from simulation results using
pandas.DataFrame.boxplot.Parameters
- columnstr
Column to plot.
- tablestr or pandas.DataFrame, optional
Table name or DataFrame; if omitted, use :pyattr:`results`.
- bystr, optional
Grouping column.
figsize : tuple, default=(10, 8) grid : bool, default=False **kwargs
Forwarded to
pandas.DataFrame.boxplot().Returns
matplotlib.axes.Axes
See also
Related APIs:
cat_plot().- distribution(self, x, *, table=None, expression: str = None, **kwargs) (inherited)
Plot a uni-variate distribution/histogram using
seaborn.histplot().Parameters
- xstr
Numeric column to plot.
- tablestr or pandas.DataFrame, optional
Table name or DataFrame; if omitted, use :pyattr:`results`.
- expression: str default is None
simple mathematical expression to create new columns from existing columns
- **kwargs
Forwarded to
seaborn.histplot().
Raises
- ValueError
If
xis a string-typed column.
Notes
This function calls
seaborn.histplot()and accepts its keyword arguments via**kwargs. See link below for details:https://seaborn.pydata.org/generated/seaborn/histplot.html
- series_plot(self, table=None, expression: str = None, *, x: str = None, y: Union[str, list] = None, hue=None, size=None, style=None, units=None, weights=None, palette=None, hue_order=None, hue_norm=None, sizes=None, size_order=None, size_norm=None, dashes=True, markers=None, style_order=None, estimator='mean', errorbar=('ci', 95), n_boot=1000, seed=None, orient='x', sort=True, err_style='band', err_kws=None, legend='auto', ci='deprecated', ax=None, **kwargs) (inherited)
Just a wrapper for seaborn.lineplot that supports multiple y columns that could be provided as a list
- tablestr | [str] |None | None| pandas.DataFrame, optional. Default is None
If the table names are provided, results are collected from the simulated data, using that table names. If None, results will be all the table names inside concatenated along the axis 0 (not recommended).
- expression: str default is None
simple mathematical expression to create new columns from existing columns
If
yis a list of columns, the data are melted into long form and
the different series are colored by variable name.
- **Kwargs
Additional keyword args and all other arguments are for Seaborn.lineplot. See the reference below for all the kwargs.
reference; https://seaborn.pydata.org/generated/seaborn.lineplot.html
Examples
>>> model.series_plot(x='Year', y='Yield', table='Report') >>> model.series_plot(x='Year', y=['SOC1', 'SOC2'], table='Report')
Examples:
>>> from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel >>> model = ApsimModel(model= 'Maize') # run the results >>> model.run(report_names='Report') >>>model.series_plot(x='Maize.Grain.Size', y='Yield', table='Report') >>>model.render_plot(show=True, ylabel = 'Maize yield', xlabel ='Maize grain size')
Plot two variables:
>>>model.series_plot(x=’Yield’, y=[‘Maize.Grain.N’, ‘Maize.Grain.Size’], table= ‘Report’)
Notes
This function calls
seaborn.lineplot()and accepts its keyword arguments via**kwargs. See link below for detailed explanations:https://seaborn.pydata.org/generated/seaborn/lineplot.html
See also
Related APIs:
plot_mva().- scatter_plot(self, table=None, expression: str = None, *, x=None, y=None, hue=None, size=None, style=None, palette=None, hue_order=None, hue_norm=None, sizes=None, size_order=None, size_norm=None, markers=True, style_order=None, legend='auto', ax=None, **kwargs) (inherited)
Scatter plot using
seaborn.scatterplot()with flexible aesthetic mappings.Parameters
- tablestr | [str] |None | None| pandas.DataFrame, optional. Default is None
If the table names are provided, results are collected from the simulated data, using that table names. If None, results will be all the table names inside concatenated along the axis 0 (not recommended).
- x, y, hue, size, style, palette, hue_order, hue_norm, sizes, size_order, size_norm, markers, style_order, legend, ax
Passed through to
seaborn.scatterplot().- expression: str default is None
simple mathematical expression to create new columns from existing columns
- ** Kwargs
Additional keyword args for Seaborn.
See the reference below for all the kwargs. reference; https://seaborn.pydata.org/generated/seaborn.scatterplot.html
- cat_plot(self, table=None, expression=None, *, x=None, y=None, hue=None, row=None, col=None, kind='strip', estimator='mean', errorbar=('ci', 95), n_boot=1000, seed=None, units=None, weights=None, order=None, hue_order=None, row_order=None, col_order=None, col_wrap=None, height=5, aspect=1, log_scale=None, native_scale=False, formatter=None, orient=None, color=None, palette=None, hue_norm=None, legend='auto', legend_out=True, sharex=True, sharey=True, margin_titles=False, facet_kws=None, **kwargs) (inherited)
Categorical plot wrapper over
seaborn.catplot().
Parameters
table : str or pandas.DataFrame, optional
- expression: str default is None
simple mathematical expression to create new columns from existing columns
x, y, hue, row, col, kind, estimator, errorbar, n_boot, seed, units, weights, order, hue_order, row_order, col_order, col_wrap, height, aspect, log_scale, native_scale, formatter, orient, color, palette, hue_norm, legend, legend_out, sharex, sharey, margin_titles, facet_kws
Passed through to
seaborn.catplot().- **kwargs
Additional keyword args for Seaborn.
Returns
seaborn.axisgrid.FacetGrid
reference https://seaborn.pydata.org/generated/seaborn.catplot.html
Related APIs:
distribution().- reg_plot(self, table=None, expression=None, **kwargs) (inherited)
Wrapper around seaborn.lmplot. V 0.39.10.19+
Kwargs passed to seaborn.lmplot
- xstr or None, optional
Name of column in
datato plot on the x-axis.- ystr or None, optional
Name of column in
datato plot on the y-axis.- huestr or None, optional
Grouping variable that will produce elements with different colors.
- colstr or None, optional
Variable that defines columns of the facet grid.
- rowstr or None, optional
Variable that defines rows of the facet grid.
- palettestr, list, dict, or None, optional
Color palette for different
huelevels.- col_wrapint or None, optional
Wrap the column facets after this many columns.
- heightfloat, default=5
Height (in inches) of each facet.
- aspectfloat, default=1
Aspect ratio of each facet, so width = aspect * height.
- markersstr or list, default=’o’
Marker(s) used for the scatter plot points.
- sharexbool or None, optional
If True, share x-axis limits across facets.
- shareybool or None, optional
If True, share y-axis limits across facets.
- hue_orderlist or None, optional
Order to plot the levels of
hue.- col_orderlist or None, optional
Order to plot the levels of
col.- row_orderlist or None, optional
Order to plot the levels of
row.- legendbool, default=True
If True, add a legend for the
huevariable.- legend_outbool or None, optional
If True, place the legend outside the grid.
- x_estimatorcallable or None, optional
Function to compute a central tendency of
yfor each uniquex(e.g.np.mean). Plot points at that value instead of raw data.- x_binsint or None, optional
Bin the
xvariable into discrete bins before plotting.- x_ci‘ci’, ‘sd’, float, or None, default=’ci’
Size/definition of the confidence band around the estimator in
x_estimator.- scatterbool, default=True
If True, draw the scatter points.
- fit_regbool, default=True
If True, fit and plot a regression line.
- ciint or None, default=95
Size of the bootstrap confidence interval for the regression estimate.
- n_bootint, default=1000
Number of bootstrap samples to compute
ci.- unitsstr or None, optional
Column in
dataidentifying sampling units. Used for clustered bootstrap.- seedint, RandomState, or None, optional
Random seed for reproducible bootstrapping.
- orderint, default=1
Polynomial order of the regression (1 = linear).
- logisticbool, default=False
If True, fit a logistic regression.
- lowessbool, default=False
If True, fit a locally weighted regression (LOWESS).
- robustbool, default=False
If True, use a robust regression estimator.
- logxbool, default=False
If True, estimate the model in log10(x) space.
- x_partialstr, list of str, or None, optional
Columns in
datato regress out ofxbefore plotting.- y_partialstr, list of str, or None, optional
Columns in
datato regress out ofybefore plotting.- truncatebool, default=True
If True, limit the regression line to the data range.
- x_jitterfloat or None, optional
Amount of horizontal jitter to add to scatter points.
- y_jitterfloat or None, optional
Amount of vertical jitter to add to scatter points.
- scatter_kwsdict or None, optional
Additional keyword args passed to the scatter plot (e.g. alpha, s).
- line_kwsdict or None, optional
Additional keyword args passed to the regression line plot.
- facet_kwsdict or None, optional
Additional keyword args passed to seaborn.FacetGrid.
See Also
- seaborn.lmplotHigh-level interface for plotting linear models with faceting.
Tutorial: https://seaborn.pydata.org/tutorial/regression.html#regression-tutorial
- relplot(self, table=None, **kwargs) (inherited)
Plots a relation plot
apsimNGpy.core.mult_cores
Functions
- apsimNGpy.core.mult_cores.is_my_iterable(value)
Check if a value is an iterable, but not a string.
- apsimNGpy.core.mult_cores.simulation_exists(db_path: str, table_name: str, simulation_id: int) bool
Check if a simulation_id exists in the specified table.
- Args:
db_path (str): Path to the SQLite database file. table_name (str): Name of the table to query. simulation_id (int): ID of the simulation to check.
- Returns:
bool: True if exists, False otherwise.
Classes
- class apsimNGpy.core.mult_cores.MultiCoreManager
MultiCoreManager(db_path: Union[str, pathlib.Path, NoneType] = (None,), agg_func: Optional[str] = None, ran_ok: bool = False, incomplete_jobs: list = <factory>)
List of Public Attributes:
List of Public Methods
- __init__(self, db_path: Union[str, pathlib.Path, NoneType] = (None, ), agg_func: Optional[str] = None, ran_ok: bool = False, incomplete_jobs: list = <factory>) None
Initialize self. See help(type(self)) for accurate signature.
- tag
Default:
'multi-core'- default_db
Default:
'manager_datastorage.db'- insert_data(self, results, table)
Insert results into the specified table results: (Pd.DataFrame, dict) The results that will be inserted into the table table: str (name of the table to insert)
See also
- property tables
Summarizes all the tables that have been created from the simulations
- run_parallel(self, model)
This is the worker for each simulation.
The function performs two things; runs the simulation and then inserts the simulated data into a specified database.
- param model:
str, dict, or Path object related .apsimx json file
returns None
- get_simulated_output(self, axis=0)
Get simulated output from the API
- param axis:
if axis =0, concatenation is along the
rowsand if it is 1 concatenation is along thecolumns
- property results
property methods for getting simulated output
- clear_db(self)
Clears the database before any simulations.
First attempt a complete
deletionof the database if that fails, existing tables are all deleted- clear_scratch(self)
clears the scratch directory where apsim files are cloned before being loaded. should be called after all simulations are completed
- clean_up_data(self)
Clears the data associated with each job. Please call this method after run_all_jobs is complete
- save_tosql(self, db_name: str | pathlib.Path, *, table_name: str = 'aggregated_tables', if_exists: Literal['fail', 'replace', 'append'] = 'fail') None
Write simulation results to an SQLite database table.
This method writes
self.results(a pandas DataFrame) to the given SQLite database. It is designed to be robust in workflows where some simulations may fail: any successfully simulated rows present inself.resultsare still saved. This is useful when an ephemeral/temporary database was used during simulation, and you need a durable copy.Parameters
- db_namestr | pathlib.Path
Target database file. If a name without extension is provided, a
.dbsuffix is appended. If a relative path is given, it resolves against the current working directory.- table_namestr, optional
Name of the destination table. Defaults to
"Report".- if_exists: {“fail”, “replace”, “append”}, optional.
Write mode passed through to pandas: -
"fail": raise if the table already exists. -"replace": drop the table, create a new one, then insert. -"append": insert rows into existing table (default). (defaults to fail if table exists, more secure for the users to knowwhat they are doing)
Raises
- ValueError
If
self.resultsis missing or empty.- TypeError
If
self.resultsis not a pandas DataFrame.- RuntimeError
If the underlying database writes fails.
Notes
Ensure that
self.resultscontain only the rows you intend to persist with. If you maintain a separate collection of failed/incomplete jobs, they should not be included inself.results.This method does not mutate
self.results.
Examples
>>> mgr.results.head() sim_id yield n2o 0 1 10.2 0.8 >>> mgr.save("outputs/simulations.db")
See also
- save_tocsv(self, path_or_buf, **kwargs)
Persist simulation results to a SQLite database table.
This method writes
self.results(a pandas DataFrame) to the given csv file. It is designed to be robust in workflows where some simulations may fail: any successfully simulated rows present inself.resultsare still saved. This is useful when an ephemeral/temporary database was used during simulation and you need a durable copy.
Write object to a comma-separated values (csv) file.
Parameters
- path_or_bufstr, path object, file-like object, or None, default None
String, path object (implementing os.PathLike[str]), or file-like object implementing a write() function. If None, the result is returned as a string. If a non-binary file object is passed, it should be opened with
newline='', disabling universal newlines. If a binary file object is passed,modemight need to contain a'b'.- sepstr, default ‘,’
String of length 1. Field delimiter for the output file.
- na_repstr, default ‘’
Missing data representation.
- float_formatstr, Callable, default None
Format string for floating point numbers. If a Callable is given, it takes precedence over other numeric formatting parameters, like decimal.
- columnssequence, optional
Columns to write.
- headerbool or list of str, default True
Write out the column names. If a list of strings is given it is assumed to be aliases for the column names.
- indexbool, default True
Write row names (index).
- index_labelstr or sequence, or False, default None
Column label for index column(s) if desired. If None is given, and
headerandindexare True, then the index names are used. A sequence should be given if the object uses MultiIndex. If False do not print fields for index names. Use index_label=False for easier importing in R.- mode{‘w’, ‘x’, ‘a’}, default ‘w’
Forwarded to either
open(mode=)orfsspec.open(mode=)to control the file opening. Typical values include:‘w’, truncate the file first.
‘x’, exclusive creation, failing if the file already exists.
‘a’, append to the end of file if it exists.
- encodingstr, optional
A string representing the encoding to use in the output file, defaults to ‘utf-8’.
encodingis not supported ifpath_or_bufis a non-binary file object.- compressionstr or dict, default ‘infer’
For on-the-fly compression of the output data. If ‘infer’ and ‘path_or_buf’ is path-like, then detect compression from the following extensions: ‘.gz’, ‘.bz2’, ‘.zip’, ‘.xz’, ‘.zst’, ‘.tar’, ‘.tar.gz’, ‘.tar.xz’ or ‘.tar.bz2’ (otherwise no compression). Set to
Nonefor no compression. Can also be a dict with key'method'set to one of {'zip','gzip','bz2','zstd','xz','tar'} and other key-value pairs are forwarded tozipfile.ZipFile,gzip.GzipFile,bz2.BZ2File,zstandard.ZstdCompressor,lzma.LZMAFileortarfile.TarFile, respectively. As an example, the following could be passed for faster compression and to create a reproducible gzip archive:compression={'method': 'gzip', 'compresslevel': 1, 'mtime': 1}.Added in version 1.5.0: Added support for
.tarfiles.May be a dict with key ‘method’ as compression mode and other entries as additional compression options if compression mode is ‘zip’.
Passing compression options as keys in dict is supported for compression modes ‘gzip’, ‘bz2’, ‘zstd’, and ‘zip’.
- quotingoptional constant from csv module
Defaults to csv.QUOTE_MINIMAL. If you have set a
float_formatthen floats are converted to strings and thus csv.QUOTE_NONNUMERIC will treat them as non-numeric.- quotecharstr, default ‘"’
String of length 1. Character used to quote fields.
- lineterminatorstr, optional
The newline character or character sequence to use in the output file. Defaults to
os.linesep, which depends on the OS in which this method is called (’\n’ for linux, ‘\r\n’ for Windows, i.e.).Changed in version 1.5.0: Previously was line_terminator, changed for consistency with read_csv and the standard library ‘csv’ module.
- chunksizeint or None
Rows to write at a time.
- date_formatstr, default None
Format string for datetime objects.
- doublequotebool, default True
Control quoting of
quotecharinside a field.- escapecharstr, default None
String of length 1. Character used to escape
sepandquotecharwhen appropriate.- decimalstr, default ‘.’
Character recognized as decimal separator. E.g. use ‘,’ for European data.
- errorsstr, default ‘strict’
Specifies how encoding and decoding errors are to be handled. See the errors argument for
open()for a full list of options.- storage_optionsdict, optional
Extra options that make sense for a particular storage connection, e.g. host, port, username, password, etc. For HTTP(S) URLs the key-value pairs are forwarded to
urllib.request.Requestas header options. For other URLs (e.g. starting with “s3://”, and “gcs://”) the key-value pairs are forwarded tofsspec.open. Please seefsspecandurllibfor more details, and for more examples on storage options refer here.
Returns
- None or str
If path_or_buf is None, returns the resulting csv format as a string. Otherwise returns None.
See Also
read_csv : Load a CSV file into a DataFrame. to_excel : Write DataFrame to an Excel file.
Examples
Create ‘out.csv’ containing ‘df’ without indices
>>> df = pd.DataFrame({'name': ['Raphael', 'Donatello'], ... 'mask': ['red', 'purple'], ... 'weapon': ['sai', 'bo staff']}) >>> df.to_csv('out.csv', index=False)
Create ‘out.zip’ containing ‘out.csv’
>>> df.to_csv(index=False) 'name,mask,weapon\nRaphael,red,sai\nDonatello,purple,bo staff\n' >>> compression_opts = dict(method='zip', ... archive_name='out.csv') >>> df.to_csv('out.zip', index=False, ... compression=compression_opts)
To write a csv file to a new folder or nested folder you will first need to create it using either Pathlib or os:
>>> from pathlib import Path >>> filepath = Path('folder/subfolder/out.csv') >>> filepath.parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True) >>> df.to_csv(filepath)
>>> import os >>> os.makedirs('folder/subfolder', exist_ok=True) >>> df.to_csv('folder/subfolder/out.csv')
- run_all_jobs(self, jobs, *, n_cores=17, threads=False, clear_db=True, **kwargs)
runs all provided jobs using
processesorthreadsspecifiedParameters
- threads: (bool) default is False
Threads or processes, recommended is to use processes
- jobs: (iterable[simulations paths]
jobs to run
- n_cores: (int)
number of cores to use
- clear_db: (bool)
For clearing the database existing data if any. Defaults is True
- kwargs:
- retry_rate: (int, optional)
how many times to retry jobs before giving up
- returns:
None
- rtype:
None
- agg_func
Default:
<member 'agg_func' of 'MultiCoreManager' objects>- db_path
Default:
<member 'db_path' of 'MultiCoreManager' objects>- incomplete_jobs
Default:
<member 'incomplete_jobs' of 'MultiCoreManager' objects>- ran_ok
Default:
<member 'ran_ok' of 'MultiCoreManager' objects>
apsimNGpy.core.pythonet_config
Module attributes
- apsimNGpy.core.pythonet_config.CI
Default value:
ConfigRuntimeInfo(clr_loaded=True, bin_path=WindowsPath('D:/My_BOX/Box/PhD thes…
Functions
- apsimNGpy.core.pythonet_config.get_apsim_file_reader(method: str = 'string')
Return an APSIM file reader callable based on the requested method.
This helper selects the appropriate APSIM NG
FileFormatimplementation, accounting for runtime changes in the file format (viais_file_format_modified()) and whether the managed type is available underModels.Core.ApsimFile.FileFormatorAPSIM.Core.FileFormat. It then returns the corresponding static method to read an APSIM file either from a string or from a file path.Parameters
- method: {“string”, “file”}, optional
Which reader to return: - “string” >>> returns
FileFormat.ReadFromString. - “file” >>> returnsFileFormat.ReadFromFile. Defaults to"string".
Returns
- Callable
A .NET static method (callable from Python) that performs the read: either
ReadFromString(text: str)orReadFromFile(path: str).
Raises
- NotImplementedError
If
methodis not one ofstringorfile.- AttributeError
If the underlying APSIM
FileFormattype does not expose the expected reader method (environment/binaries misconfigured).
Notes
When : func:
is_file_format_modifiedreturnsbool.If False, thenModels.Core.ApsimFile.FileFormatis unavailable, the function falls back toAPSIM.Core.FileFormat.The returned callable is a .NET method; typical usage is
reader = get_apsim_file_reader("file"); model = reader(path).
Examples
Read from a file path:
>>> reader = get_apsim_file_reader("file") >>> sims = reader("/path/to/model.apsimx")
Read from a string (APSXML/JSON depending on APSIM NG):
>>> text = "...apsimx content..." >>> reader = get_apsim_file_reader("string") >>> sims = reader(text)
- apsimNGpy.core.pythonet_config.get_apsim_version(bin_path: str | pathlib.Path = 'D:\\My_BOX\\Box\\PhD thesis\\Objective two\\morrow plots 20250821\\APSIM2025.8.7844.0\\bin', release_number: bool = False) str | None
Return the APSIM version string detected from the installed binaries.
The function initializes pythonnet for the given APSIM binaries path (via
load_pythonnet(bin_path)), then loadsModels.dlland reads its assembly version. By default, the returned string is prefixed with"APSIM"; setrelease_number=Trueto get the raw semantic version.Parameters
- bin_pathstr or pathlib.Path, optional
Filesystem path to the APSIM binaries directory that contains
Models.dll. Defaults toAPSIM_BIN_PATH.- release_numberbool, optional
If
True, returns only the assembly version (e.g.,"2024.6.123"). IfFalse(default), prefix with"APSIM"(e.g.,"APSIM 2024.6.123").
Returns
- str or None
The version string if detected successfully; otherwise
Nonewhen required system modules are unavailable (e.g., if the binaries path is not correctly configured).
Raises
- ApsimBinPathConfigError
If pythonnet/CLR is not initialized for the provided
bin_path(i.e., APSIM binaries path has not been set up).
Notes
This call requires a valid APSIM NG binaries folder and a loadable
Models.dllatbin_path/Models.dll.load_pythonnetmust succeed so that the CLR is available; otherwise the version cannot be queried.
Examples
>>> get_apsim_version("/opt/apsim/bin") 'APSIM2024.6.123' >>> get_apsim_version("/opt/apsim/bin", True) '2024.6.123'
See Also
load_pythonnet : Initialize pythonnet/CLR for APSIM binaries.
- apsimNGpy.core.pythonet_config.is_file_format_modified(bin_path: str | pathlib.Path | NoneType = None) bool
Checks if the APSIM.CORE.dll is present in the bin path. Normally, the new APSIM version has this dll file.
Parameters
- bin_path: Union[str, Path, None].
Default is the current bin_path for apsimNGpy, used only when bin_path is None.
- returns:
bool
- apsimNGpy.core.pythonet_config.load_pythonnet(bin_path: str | pathlib.Path = None)
A method for loading Python for .NET (pythonnet) and APSIM models from the binary path. It is also cached to avoid rerunning many times.
It initializes the Python for .NET (pythonnet) runtime and load APSIM models.
Loads the ‘coreclr’ runtime, and if not found, falls back to an alternate runtime. It also sets the APSIM binary path, adds the necessary references, and returns a reference to the loaded APSIM models.
Returns:
- ConfigRuntimeInfo:
an instance of ConfigRuntimeInfo with reference to the loaded APSIM models
Raises:
KeyError: If APSIM path is not found in the system environmental variable. ValueError: If the provided APSIM path is invalid.
Important
This function is called internally by apsimNGpy modules, but it is dependent on correct configuration of the bin path. Please edit the system environmental variable on your computer or set it using:
set_apsim_bin_path()
Classes
- class apsimNGpy.core.pythonet_config.ConfigRuntimeInfo
ConfigRuntimeInfo(clr_loaded: bool, bin_path: Union[pathlib.Path, str], file_format_modified: bool = True)
- __init__(self, clr_loaded: bool, bin_path: pathlib.Path | str, file_format_modified: bool = True) None
Initialize self. See help(type(self)) for accurate signature.
- file_format_modified
Default:
True
apsimNGpy.core.runner
Functions
- apsimNGpy.core.runner.build_apsim_command(dir_path: 'str', pattern: 'str', *, cpu_count: 'int' = -1, recursive: 'bool' = False, verbose: 'bool' = False, write_tocsv: 'bool' = False) 'List[str]'
Build the APSIM command-line invocation for all files in a directory matching a given pattern.
- apsimNGpy.core.runner.collect_csv_by_model_path(model_path) 'dict[Any, Any]'
Collects the data from the simulated model after run
- apsimNGpy.core.runner.collect_csv_from_dir(dir_path, pattern, recursive=False) 'pd.DataFrame'
Collects the csf=v files in a directory using a pattern, usually the pattern resembling the one of the simulations used to generate those csv files
dir_path: (str) path where to look for csv filesrecursive: (bool) whether to recursively search through the directory defaults to false:pattern:(str) pattern of the apsim files that produced the csv files through simulations- returns
a generator object with pandas data frames
Example:
mock_data = Path.home() / 'mock_data' # this a mock directory substitute accordingly df1= list(collect_csv_from_dir(mock_data, '*.apsimx', recursive=True)) # collects all csf file produced by apsimx recursively df2= list(collect_csv_from_dir(mock_data, '*.apsimx', recursive=False)) # collects all csf file produced by apsimx only in the specified directory directory
- apsimNGpy.core.runner.collect_db_from_dir(dir_path, pattern, recursive=False, tables=None, con=None) 'pd.DataFrame'
- Collects the data in a directory using a pattern, usually the pattern resembling the one of the simulations
used to generate those csv files
Parameters
- dir_path(str)
path where to look for csv files
- recursive(bool)
whether to recursively search through the directory defaults to false:
- pattern :(str)
pattern of the apsim files that produced the csv files through simulations
- con: database connection
database connection object to aggregate the date to from all the simulation
- returns
a dict generator object with pandas data frames as the values as the schemas as the keys, note the schemas are grouped according to their similarities on of data types
Example:
mock_data = Path.home() / 'mock_data' # this a mock directory substitute accordingly df1= list(collect_csv_from_dir(mock_data, '*.apsimx', recursive=True)) # collects all csf file produced by apsimx recursively df2= list(collect_csv_from_dir(mock_data, '*.apsimx', recursive=False)) # collects all csf file produced by apsimx only in the specified directory directory
- apsimNGpy.core.runner.dir_simulations_to_csv(dir_path: 'str | Path', pattern: 'str', *, verbose: 'bool' = False, recursive: 'bool' = False, cpu_count: 'int' = -1) 'Iterable[pd.DataFrame]'
Run APSIM for all files matching a pattern in a directory and load outputs from CSV files into memory.
APSIM is invoked with the
--csvflag, so reports are written to CSV files in the same directories as the input *.apsimx files. This function then callscollect_csv_from_dir()to return the results.Parameters
- dir_pathstr or Path
Path to the directory containing the simulation files.
- patternstr
File pattern to match simulation files (e.g.,
"*.apsimx").- verbosebool, optional
If True, log APSIM console output.
- recursivebool, optional
If True, search recursively through subdirectories.
- cpu_countint, optional
Number of threads to use for APSIM’s internal parallel processing.
- What this function does is that it makes it easy to retrieve the simulated files, returning a generator that
yields data frames
Returns
- Iterable[pd.DataFrame]
(commonly a generator or list of DataFrames, one per report file).
Raises
- RuntimeError
If the APSIM process fails.
- apsimNGpy.core.runner.dir_simulations_to_dfs(dir_path: 'str | Path', pattern: 'str', *, verbose: 'bool' = False, recursive: 'bool' = False, cpu_count: 'int' = -1, tables: 'Optional[List[str], str]' = None, axis: 'int' = 0, order_sensitive: 'bool' = False, add_keys: 'bool' = False, keys_prefix: 'str' = 'g') 'Dict[SchemaKey, pd.DataFrame]'
Run APSIM for all files matching a pattern in a directory, collect results from APSIM databases, and return grouped DataFrames based on schema.
Parameters
- dir_pathstr or Path
Path to the directory containing the simulation files.
- patternstr
File pattern to match simulation files (e.g.,
"*.apsimx").- verbosebool, optional
If True, log APSIM console output.
- recursivebool, optional
If True, search recursively through subdirectories.
- cpu_countint, optional
Number of threads to use for APSIM’s internal parallel processing.
- tableslist of str, optional
Subset of table names to collect from each APSIM database. If None, all tables are collected.
- axis{0, 1}, optional
Axis along which to concatenate grouped DataFrames.
- order_sensitivebool, optional
If True, column order is part of the schema definition when grouping.
- add_keysbool, optional
If True, add keys when concatenating grouped DataFrames.
- keys_prefixstr, optional
Prefix for keys used when concatenating grouped DataFrames.
- What this function does is that it makes it easy to retrieve the simulated files, returning a dict that
yields data frames
Returns
- dict
Mapping from schema signatures to concatenated DataFrames. Each key is a tuple of (column_name, dtype_str) pairs describing the schema. if all simulations are the same, the key
is going to be one, as keys and values are filtered according to data types similarities among data frames
Raises
- RuntimeError
If the APSIM process fails.
- apsimNGpy.core.runner.dir_simulations_to_sql(dir_path: 'str | Path', pattern: 'str', connection: 'Engine', *, verbose: 'bool' = False, recursive: 'bool' = False, cpu_count: 'int' = -1, tables: 'Optional[List[str], str]' = None, axis: 'int' = 0, order_sensitive: 'bool' = False, add_keys: 'bool' = False, keys_prefix: 'str' = 'g', base_table_prefix: 'str' = 'group', schema_table_name: 'str' = '_schemas') 'None'
Run APSIM, collect grouped results from databases, and write the grouped tables plus a schema metadata table into a SQL database via the provided database connection.
Parameters
- dir_pathstr or Path
Path to the directory containing the simulation files.
- patternstr
File pattern to match simulation files (e.g.,
"*.apsimx").- connectionsqlalchemy.engine.Engine
SQLAlchemy engine (or compatible) to write tables into.
- verbosebool, optional
If True, log APSIM console output.
- recursivebool, optional
If True, search recursively through subdirectories.
- cpu_countint, optional
Number of threads to use for APSIM’s internal parallel processing.
- tableslist of str, optional
Subset of table names to collect from each APSIM database. If None, all tables are collected.
- axis{0, 1}, optional
Axis along which to concatenate grouped DataFrames.
- order_sensitivebool, optional
If True, column order is part of the schema definition when grouping.
- add_keysbool, optional
If True, add keys when concatenating grouped DataFrames.
- keys_prefixstr, optional
Prefix for keys used when concatenating grouped DataFrames.
- base_table_prefixstr, optional
Prefix for the generated data table names in SQL.
- schema_table_namestr, optional
Name of the schema metadata table in SQL.
What this function does is that it makes it easy to aggregate the simulated files to an SQL database
Returns
None
Raises
- RuntimeError
If the APSIM process fails.
- apsimNGpy.core.runner.get_apsim_version(verbose: 'bool' = False)
Display version information of the apsim model currently in the apsimNGpy config environment.
verbose: (bool) Prints the version informationinstantlyExample:
apsim_version = get_apsim_version()
- apsimNGpy.core.runner.get_matching_files(dir_path: 'Union[str, Path]', pattern: 'str', recursive: 'bool' = False) 'List[Path]'
Search for files matching a given pattern in the specified directory.
- Args:
dir_path(Union[str, Path]): The directory path to search in.pattern(str): The filename pattern to match (e.g., “*.apsimx”).recursive(bool): If True, search recursively; otherwise, search only in the top-level directory.- Returns:
List[Path]: A
listof matching Path objects.- Raises:
``ValueError: `` If no matching files are found.
- apsimNGpy.core.runner.is_connection(obj)
Return True if obj looks like a DB connection.
- apsimNGpy.core.runner.run_dir_simulations(dir_path: 'str', pattern: 'str', *, cpu_count: 'int' = -1, recursive: 'bool' = False, verbose: 'bool' = False, write_tocsv: 'bool' = False) 'Popen[str]'
Execute APSIM simulations for all matching files in a directory and wait for completion.
This helper is responsible only for building the command, running it, logging output, and ensuring resources are cleaned up. It either completes successfully or raises an exception.
used by:
dir_simulations_to_dfs(),dir_simulations_to_sql(),dir_simulations_to_csv()Returns
- processsubprocess.Popen
The completed APSIM process object.
Raises
- RuntimeError
If APSIM returns a non-zero exit code.
- apsimNGpy.core.runner.run_model_externally(model: 'Union[Path, str]', *, apsim_exec: 'Optional[Union[Path, str]]' = WindowsPath('D:/My_BOX/Box/PhD thesis/Objective two/morrow plots 20250821/APSIM2025.8.7844.0/bin/Models.exe'), verbose: 'bool' = False, to_csv: 'bool' = False, timeout: 'int' = 600, cpu_count=-1, cwd: 'Optional[Union[Path, str]]' = None, env: 'Optional[Mapping[str, str]]' = None) 'subprocess.CompletedProcess[str]'
Run APSIM externally (cross-platform) with safe defaults.
Validates an executable and model path.
Captures stderr always; stdout only if verbose.
Uses UTF-8 decoding with error replacement.
Enforces a timeout and returns a CompletedProcess-like object.
Does NOT use shell, eliminating injection risk.
See also
Related API:
run_from_dir()
- apsimNGpy.core.runner.trial_run(self, report_name=None, simulations=None, clean=False, multithread=True, verbose=False, get_dict=False, **kwargs)
Run APSIM model simulations.
Parameters
- report_namestr or list of str, optional
Name(s) of report table(s) to retrieve. If not specified or missing in the database, the model still runs and results can be accessed later.
- simulationslist of str, optional
Names of simulations to run. If None, all simulations are executed.
- cleanbool, default False
If True, deletes the existing database file before running.
- multithreadbool, default True
If True, runs simulations using multiple threads.
- verbosebool, default False
If True, prints diagnostic messages (e.g., missing report names).
- get_dictbool, default False
If True, returns results as a dictionary {table_name: DataFrame}.
Returns
- resultsDataFrame or list or dict of DataFrames
Simulation output(s) from the specified report table(s).
See also
Related API:
run_model_externally()
- apsimNGpy.core.runner.upgrade_apsim_file(file: 'str', verbose: 'bool' = True)
Upgrade a file to the latest version of the .apsimx file format without running the file.
Parameters
file: file to be upgraded to the newest versionverbose: Write detailed messages to stdout when a conversion starts/finishes.returnThe latest version of the .apsimx file with the same name as the input file
Example:
from apsimNGpy.core.base_data import load_default_simulations filep =load_default_simulations(simulations_object= False)# this is just an example perhaps you need to pass a lower verion file because this one is extracted from thecurrent model as the excutor upgrade_file =upgrade_apsim_file(filep, verbose=False)
Classes
- class apsimNGpy.core.runner.RunError
Raised when the APSIM external run fails.
- with_traceback() (inherited)
Exception.with_traceback(tb) – set self.__traceback__ to tb and return self.
- add_note() (inherited)
Exception.add_note(note) – add a note to the exception
- args(inherited)
Default:
<attribute 'args' of 'BaseException' objects>
apsimNGpy.core.senstivitymanager
Classes
- class apsimNGpy.core.senstivitymanager.SensitivityManager
This class inherits methods and attributes from:
ApsimModelto manage APSIM Sensitivity Analysis in apsimNGpy You first need to initialize the class, define parameters and build the sensitivity analysis modelAdded in V0.39.12.21+
The flow of method for
SensitivityManagerclass is shown in the diagram below:PlotManager --> CoreModel --> ApsimModel --> SensitivityManager
PlotManager→ Produces visual outputs from model results (Not exposed in the API reference)CoreModel→ contains methods for running and manipulating models (Not exposed in the API reference)ApsimModel→ ExtendsCoremodelcapabilities with more functionalitiesSensitivityManager→ Manages and creates a new sensitivity experiment model from the suggested base.
List of Public Attributes:
default_intervalsdefault_jumpsis_recent_versionstr_model
List of Public Methods
- __init__(self, model, out_path=None)
Initialize self. See help(type(self)) for accurate signature.
- setup(self, agg_col_name: str, method: str = 'Morris', table_name: str = 'Report', base_simulation: str = None, num_paths=None, jumps=10, intervals=20)
Initialize the sensitivity analysis experiment structure within the APSIM file.
- agg_col_namestr
Name of the column in the database table used for aggregating values.
- methodstr, optional
Sensitivity method to use. Supported options are
'morris'and'sobol'. Default is'Morris'.- table_namestr, optional
Name of the table where sensitivity results will be stored.
- base_simulationstr, optional
Name of the base simulation to use for constructing the experiment. If
None, the first available simulation is used as the base.- num_pathsint, optional
Number of parameter paths for the Morris method. The Morris method generates multiple parameter trajectories across the N-dimensional parameter space. The number of paths should be sufficiently large to adequately explore the parameter space and capture variability in model responses. If
None, a default value is computed based on the number of decision variables.
- jumpsint, optional
Applicable only to the Morris method. Determines the number of discrete steps (also called “jumps”) each parameter is allowed to move within the defined sampling grid. A higher number of jumps increases the number of possible perturbation positions for a parameter and therefore results in a more detailed exploration of the input space. However, increasing the number of jumps also leads to more computational demand because the total number of model evaluations scales with jumps × paths × (k + 1), where k is the number of parameters. If omitted, a reasonable default based on the number of decision variables is used.
- intervalsint, optional
Applicable only to the Morris method. Specifies the number of levels into which the range of each parameter is discretized. The parameter space is divided into
intervalsequally spaced points, and the Morris trajectories (paths) move across these points to compute elementary effects. A larger number of intervals increases the resolution of the sensitivity analysis, allowing finer distinction between parameter influences, but also expands the computational cost. When not provided, a default value is chosen according to recommended Morris design practices.
If a Replacements folder is present, it is moved or retained under the
Simulationsnode as appropriate.A new sensitivity experiment (Morris or Sobol) is added under
Simulations.
Create and initialize a sensitivity experiment:
from apsimNGpy.core.senstivitymanager import SensitivityManager exp = SensitivityManager("Maize", out_path="dtb.apsimx")
Add sensitivity factors:
exp.add_sens_factor(name='cnr', path='Field.SurfaceOrganicMatter.InitialCNR', lower_bound=10, upper_bound=120) exp.add_sens_factor(name='cn2bare', path='Field.Soil.SoilWater.CN2Bare', lower_bound=70, upper_bound=100) exp.finalize(method='Morris', aggregation_column_name='Clock.Today') exp.run()
You can inspect the updated APSIM file structure using the
inspect_file()method, inherited fromApsimModel. This allows you to verify that a sensitivity analysis model has been added under theSimulationsnode:
exp.inspect_file()
- add_sens_factor(self, name, path, lower_bound, upper_bound, **kwargs)
Add a new factor to the experiment from an APSIM-style script specification.
Parameters
- namestr
A unique name for the factor.
- pathstr, optional
full node path specification
- lower_boundint, required
lower limit of the factor
- upper boundint required
Upper limit of the factor
- **kwargs
Optional metadata or configuration (currently unused).
Raises
- ValueError
If a script-based specification references a non-existent or unlinked manager script.
Side Effects
Inserts the factor into the appropriate parent node (
PermutationorFactors).If a factor at the same index already exists, it is safely deleted before inserting the new one.
Notes
All methods from
ApsimModelremain available on this class. You can still inspect, run, and visualize results.Examples
configure factors:
exp.add_sens_factor(name='cnr', path='Field.SurfaceOrganicMatter.InitialCNR', lower_bound=10, upper_bound=120) exp.add_sens_factor(name='cn2bare', path='Field.Soil.SoilWater.CN2Bare', lower_bound=70, upper_bound=100)
- property n_factors
- Returns:
int: The total number of active factor specifications currently added to the experiment.
Compute a reasonable default NumPaths for Morris sensitivity analysis.
Parameters
- kint
Number of decision variables.
Returns
- int
Recommended number of Morris paths.
- property statistics
Retrieve the sensitivity statistics produced by APSIM after running the sensitivity analysis.
This attribute reads the appropriate statistics table (Morris or Sobol) from the APSIM datastore once the sensitivity experiment has been executed using
run().Returns
- pandas.DataFrame
A DataFrame containing the sensitivity statistics computed by APSIM.
Raises
- RuntimeError
If the required statistics table is not present in the datastore. This typically occurs when the sensitivity analysis has not been run or the APSIM output has not yet been generated.
Notes
Ensure that the sensitivity analysis has completed successfully before calling this method.
- build_sense_model(self, method: str, aggregation_column_name, base_simulation: str = None, num_path: int = None, jumps: int = None, intervals: int = None)
To be released in V0.39.12.21
Finalize and build the sensitivity analysis experiment inside the APSIM file.
This method acts as a convenience wrapper around
setup(), providing a simplified interface for constructing the sensitivity experiment. It configures the sensitivity method (Morris or Sobol), assigns the aggregation column, selects or infers the base simulation, and applies the number of paths for Morris analyses. After configuration, the APSIM file is updated and a garbage collection call is issued to ensure clean C# object management.Parameters
- methodstr
Sensitivity analysis method to apply. Supported values are
'morris'and'sobol'.- aggregation_column_namestr
Name of the column in the data table used to aggregate values during sensitivity analysis.
- base_simulationstr, optional
Name of the base simulation for constructing the experiment. If
None, the first available simulation in the APSIM file is used.- num_pathint, optional
Number of parameter paths for the Morris method. If
None, a default is computed automatically based on the number of decision variables.- jumpsint, optional
Morris method only. Specifies the number of discrete step movements (
"jumps") allowed along each parameter dimension during the construction of a trajectory. Each Morris trajectory begins at a randomly selected point in the parameter space and perturbs one parameter at a time by a fixed step sizeΔ. Thejumpsvalue determines how many such perturbations can occur within each trajectory.Increasing
jumpsimproves the diversity of sampled elementary effects, especially in complex models with non-linear interactions. However, higher values also increase computational cost because the total number of model evaluations scales approximately as:\[N_{mathrm{sims}} = r , (k + 1)\]where
ris the number of paths andkis the number of parameters. Ifjumpsis not provided, a recommended default is chosen to balance computational efficiency with adequate exploration of the parameter space.- intervalsint, optional
Morris method only. Defines the number of discrete levels into which each parameter range is partitioned. The Morris method samples parameters on a
p-level grid, wherep = intervals. Each parameter range is divided intointervalsequally spaced points, and trajectories move across these grid points to compute elementary effects.A larger number of intervals increases the resolution of the sampling grid, enabling more detailed sensitivity insights and reducing discretization error. However, high values also increase computational overhead and may not necessarily improve screening quality. When omitted, a reasonable default is selected according to standard Morris design guidelines.
Side Effects
Modifies the APSIM file by inserting a sensitivity analysis experiment under the
Simulationsnode.Ensures proper .NET resource cleanup via an explicit garbage collection call.
- evaluate_simulated_output(self, ref_data: pandas.core.frame.DataFrame, table, ref_data_col, target_col, index_col, expr=None) (inherited)
Evaluate APSIM-simulated output against a reference (observed) dataset.
This method compares observed data (
ref_data) with simulated predictions obtained either from a provided DataFrame or from a table name that is used to extract simulation output throughget_simulated_output(). The comparison is performed throughfinal_evalfromapsimNGpy.optimizer.problems.back_end, which computes common evaluation metrics (e.g., RMSE, RRMSE, WIA, CCC, bias), depending on the implementation offinal_eval.Added in v0.39.12.21+
Parameters
- ref_datapandas.DataFrame
The reference or observed dataset against which predictions will be evaluated. Must contain at least the column specified by
ref_data_coland the index column.- tablestr or pandas.DataFrame
- Either:
A string referring to an APSIM output table name. In this case, simulated output is retrieved using :meth:`~apsimNGpy.core.apsim.ApsimModel.get_simulated_output`(table).
A DataFrame containing simulated predictions directly.
Any other type will raise a
TypeError.- ref_data_colstr
Column name in
ref_datacontaining the observed values.- target_colstr
Column name in the simulated dataset indicating the predicted values to be compared against the observations.
- index_colstr
Column used to join observed and simulated data (e.g., date, sample number, simulation ID). Both datasets must contain this column.
- exprcallable or str, optional
An optional transformation or expression to apply before comparison. Can be a lambda function, a string expression, or
None. Default isNone.
Returns
- dict or pandas.DataFrame
The output of
final_eval, typically containing evaluation metrics such as RMSE, RRMSE, WIA, CCC, ME, and bias.
Raises
- TypeError
If
tableis neither a string nor a pandas DataFrame.
Notes
This method streamlines comparison between observed and simulated APSIM outputs during model calibration or performance assessment. It allows the user to directly pass simulation tables or retrieve them automatically by name, ensuring a consistent evaluation workflow. Examples ——– .. code-block:: python
from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel from apsimNGpy.tests.unittests.test_factory import obs model = ApsimModel(‘Maize’) # need to add column year to act as common index with observed data model.add_report_variable(variable_spec=’[Clock].Today.Year as year’, report_name=’Report’) model.evaluate_simulated_output(ref_data=obs, table=’Report’, index_col=[‘year’],
target_col=’Yield’, ref_data_col=’observed’)
Model Evaluation Metrics ---------------------------------------- RMSE : 0.0003 MAE : 0.0003 MSE : 0.0000 RRMSE : 0.0000 bias : -0.0001 ME : 1.0000 WIA : 1.0000 R2 : 1.0000 CCC : 1.0000 SLOPE : 1.0000
Added in version v0.39.12.21+.
Set parameters for the given model by passing a dictionary or keyword arguments.
Parameters
- paramsdict, optional
A dictionary mapping APSIM parameter names to their corresponding values. If
paramsisNone, thenkwargsis expected, following the same signature asedit_model_by_path().- **kwargs :
Additional keyword arguments equivalent to entries in
params. These are interpreted according to the same signature asedit_model_by_path().
Returns
- selfApsimModel
Returns the same instance for method chaining.
Raises
- TypeError if any of the above arguments does not resolve to a dictionary. Other errors maybe raised gracefully
by
edit_model_by_path().
Notes
This flexible design allows users to supply parameters either as standard keyword arguments or as dictionary objects. The dictionary-based approach is particularly useful when working with JSON-compatible data structures, as commonly required during large-scale model optimization, calibration, or parameter sensitivity analysis workflows. In such cases, parameter sets can be programmatically generated, serialized, and reused without manual modification of code.
- get_soil_from_web(self, simulation_name: Union[str, tuple, NoneType] = None, *, lonlat: Optional[System.Tuple[Double, Double]] = None, soil_series: Optional[str] = None, thickness_sequence: Optional[Sequence[float]] = 'auto', thickness_value: int = None, max_depth: Optional[int] = 2400, n_layers: int = 10, thinnest_layer: int = 100, thickness_growth_rate: float = 1.5, edit_sections: Optional[Sequence[str]] = None, attach_missing_sections: bool = True, additional_plants: tuple = None, adjust_dul: bool = True) (inherited)
Download SSURGO-derived soil for a given location and populate the APSIM NG soil sections in the current model.
This method updates the target Simulation(s) in-place by attaching a Soil node (if missing) and writing section properties from the downloaded profile.
Parameters
- simulationstr | sequence[str] | None, default None
Target simulation name(s). If
None, all simulations are updated.- lonlattuple[float, float] | None
Location for SSURGO download, as
(lon, lat)in decimal degrees (e.g.,(-93.045, 42.012)).- soil_seriesstr | None, optional
Optional component/series filter. If
None, the dominant series by area is used. If a non-existent series is supplied, an error is raised.- thickness_sequencesequence[float] | str | None, default “auto”
Explicit layer thicknesses (mm). If
"auto", thicknesses are generated from the layer controls (e.g., number of layers, growth rate, thinnest layer, andmax_depth). IfNone, you must providethickness_valueandmax_depthto construct a uniform sequence.- thickness_valueint | None, optional
Uniform thickness (mm) for all layers. Ignored if
thickness_sequenceis provided; used only whenthickness_sequenceisNone.- max_depthint, default 2400
Maximum soil depth (mm) to cover with the thickness sequence.
- edit_sectionssequence[str], optional
Sections to edit. Default:
("physical", "organic", "chemical", "water", "water_balance", "solutes", "soil_crop", "meta_info"). Note: if sections are edited with differing layer counts, APSIM may error at run time.- attach_missing_sectionsbool, default True
If
True, create and attach missing section nodes before editing.- additional_plantssequence[str] | None, optional
Plant names for which to create/populate
SoilCropentries (e.g., to set KL/XF).- adjust_dulbool, optional
If
True, adjust layer values whereSATexceedsDULto prevent APSIM runtime errors.
Returns
- self
The same instance, to allow method chaining.
Raises
- ValueError
thickness_sequenceprovided with any non-positive value(s).thickness_sequenceisNoneandthickness_valueisNone.Units mismatch or inconsistency between
thickness_valueandmax_depth.
Notes
Assumes soil sections live under a Soil node; when
attach_missing_sections=Truea Soil node is created if missing.Uses the optimized SoilManager routines (vectorized assignments / .NET double[] marshaling).
- Side effects (in place on the APSIM model):
Creates/attaches Soil when needed.
Creates/updates child sections (
Physical,Organic,Chemical,Water,WaterBalance,SoilCrop) as listed inedit_sections.Overwrites section properties (e.g., layer arrays such as
Depth,BD,LL15,DUL,SAT; solutes; crop KL/XF) with downloaded values.Add SoilCrop children for any names in
additional_plants.Performs network I/O to retrieve SSURGO tables when
lonlatis provided.Emits log messages (warnings/info) when attaching nodes, resolving thickness controls, or skipping missing columns.
Caches the computed soil profile in the helper during execution; the in-memory APSIM tree remains modified after return.
Does not write files; call
save()on the model if you want to persist changes.The existing soil-profile structure is completed override by the newly generated soil profile. So, variables like soil thickness, number of soil layers, etc. might be different from the old one.
- adjust_dul(self, simulations: Union[tuple, list] = None) (inherited)
This method checks whether the soil
SATis above or belowDULand decreasesDULvalues accordinglyNeed to call this method everytime
SATis changed, orDULis changed accordingly.
simulations: str, name of the simulation where we want to adjust DUL and SAT according.returns:model the object for method chaining
- replace_downloaded_soils(self, soil_tables: Union[dict, list], simulation_names: Union[tuple, list], **kwargs) (inherited)
- @deprecated and will be removed in the future versions
Updates soil parameters and configurations for downloaded soil data in simulation models.
This method adjusts soil physical and organic parameters based on provided soil tables and applies these adjustments to specified simulation models.
Parameters:
soil_tables(list): A list containing soil data tables. Expected to contain: see the naming convention in the for APSIM - [0]: DataFrame with physical soil parameters. - [1]: DataFrame with organic soil parameters. - [2]: DataFrame with crop-specific soil parameters. - simulation_names (list of str): Names or identifiers for the simulations to be updated.sReturns: - self: Returns an instance of the class for
chainingmethods.This method directly modifies the simulation instances found by
find_simulationsmethod calls, updating physical and organic soil properties, as well as crop-specific parameters like lower limit (LL), drain upper limit (DUL), saturation (SAT), bulk density (BD), hydraulic conductivity at saturation (KS), and more based on the provided soil tables.
->> key-word argument
set_sw_con: Boolean, set the drainage coefficient for each layeradJust_kl:: Bollean, adjust, kl based on productivity indexCultvarName: cultivar name which is in the sowing module for adjusting the ruetillage: specify whether you will be carried to adjust some physical parameters- read_apsimx_data(self, table=None) (inherited)
Read APSIM NG datastore for the current model. Raises FileNotFoundError if the model was initialized from default models because those need to be executed first to generate a database.
The rationale for this method is that you can just access the results from the previous session without running it if the database is in the same location as the apsimx file.
Since apsimNGpy clones the apsimx file, the original file is kept with attribute name
_model, that is what is being used to access the datasettable: (str) name of the database table to read if none of all tables are returned
Returns: pandas.DataFrame
KeyError: if table is not found in the database
- property simulations(inherited)
Retrieve simulation nodes in the APSIMx
Model.Core.Simulationsobject.We search all-Models.Core.Simulation in the scope of Model.Core.Simulations. Please note the difference Simulations is the whole json object Simulation is the child with the field zones, crops, soils and managers.
Any structure of apsimx file can be handled.
Note
The simulations are c# referenced objects, and their manipulation maybe for advanced users only.
- property simulation_names(inherited)
@deprecated will be removed in future releases. Please use inspect_model function instead.
retrieves the name of the simulations in the APSIMx file @return: list of simulation names
- property tables_list(inherited)
quick property returns available database report tables name
- property managers_scripts_list(inherited)
quick property returns available database manager script names
- property simulations_list(inherited)
quick property for returning a list of available simulation names @return:
- restart_model(self, model_info=None) (inherited)
Reinitialize the APSIM model instance after edits or management updates.
Parameters
- model_infocollections.NamedTuple, optional
A named tuple returned by
load_apsim_modelfrom themodel_loadermodule. Contains references to the APSIM model, datastore, and file path. If not provided, the method reinitializes the model using the existingself.model_infoobject.
Notes
This method is essential when the model needs to be reloaded after modifying management scripts or saving an edited APSIM file.
It may be invoked automatically by internal methods such as
save_edited_file,save, andupdate_mgt.Reinitializing ensures that all APSIM NG components and datastore references are refreshed and consistent with the modified file.
Returns
- selfobject
Returns the updated ApsimModel instance.
- save(self, file_name: 'Union[str, Path, None]' = None, reload=True) (inherited)
Saves the current APSIM NG model (
Simulations) to disk and refresh runtime state.This method writes the model to a file, using a version-aware strategy:
After writing, the model is recompiled via
recompile(self)()and the in-memory instance is refreshed usingrestart_model(), ensuring the object graph reflects the just-saved state. This is now only impozed if the user specifiedrelaod = True.Parameters
- file_namestr or pathlib.Path, optional
Output path for the saved model file. If omitted (
None), the method uses the instance’s existingpath. The resolved path is also written back to instancepathattribute for consistency if reload is True.- reload: bool Optional default is True
resets the reference path to the one provided after serializing to disk. This implies that the instance
pathwill be the providedfile_name
Returns
- Self
The same model/manager instance to support method chaining.
Raises
- OSError
If the file cannot be written due to I/O errors, permissions, or invalid path.
- AttributeError
If required attributes (e.g.,
self.Simulations) or methods are missing.- Exception
Any exception propagated by
save_model_to_file(),recompile(), orrestart_model().
Side Effects
Sets
self.pathto the resolved output path (string).Writes the model file to disk (overwrites if it exists).
If reload is True (default), recompiles the model and restarts the in-memory instance.
Notes
Path normalization: The path is stringified via
str(file_name)just in case it is a pathlib object.Reload semantics: Post-save recompilation and restart ensure any code generation or cached reflection is refreshed to match the serialized model.
Examples
- check the current path before saving the model
>>> from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel >>> from pathlib import Path >>> model = ApsimModel("Maize", out_path='saved_maize.apsimx') >>> model.path scratch\saved_maize.apsimx
- Save to a new path and continue working with the refreshed instance
>>> model.save(file_name='out_maize.apsimx', reload=True) # check the path >>> model.path 'out_maize.apsimx' # possible to run again the refreshed model. >>> model.run()
- Save to a new path without refreshing the instance path
>>> model = ApsimModel("Maize", out_path='saved_maize.apsimx') >>> model.save(file_name='out_maize.apsimx', reload=False) # check the current reference path for the model. >>> model.path 'scratch\saved_maize.apsimx' # When reload is False, the original referenced path remains as shown above
As shown above, everything is saved in the scratch folder; if the path is not abolutely provided, e.g., a relative path. If the path is not provided as shown below, the reference path is the current path for the isntance model.
>>> model = ApsimModel("Maize", out_path='saved_maize.apsimx') >>> model.path 'scratch\saved_maize.apsimx' # save the model without providing the path. >>> model.save()# uses the default, in this case the defaul path is the existing path >>> model.path 'scratch\saved_maize.apsimx'
In the above case, both reload =
FalseorTrue, will produce the same reference path for the live instance class.- property results(inherited)
Legacy method for retrieving simulation results.
This method is implemented as a
propertyto enable lazy loading—results are only loaded into memory when explicitly accessed. This design helps optimizememoryusage, especially forlargesimulations.It must be called only after invoking
run(). If accessed before the simulation is run, it will raise an error.Notes
The
run()method should be called with a validreport nameor a list of report names.If
report_namesis not provided (i.e.,None), the system will inspect the model and automatically detect all available report components. These reports will then be used to collect the data.If multiple report names are used, their corresponding data tables will be concatenated along the rows.
Returns
- pd.DataFrame
A DataFrame containing the simulation output results.
Examples
>>> from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel # create an instance of ApsimModel class >>> model = ApsimModel("Maize", out_path="my_maize_model.apsimx") # run the simulation >>> model.run() # get the results >>> df = model.results # do something with the results e.g. get the mean of numeric columns >>> df.mean(numeric_only=True) Out[12]: CheckpointID 1.000000 SimulationID 1.000000 Maize.AboveGround.Wt 1225.099950 Maize.AboveGround.N 12.381196 Yield 5636.529504 Maize.Grain.Wt 563.652950 Maize.Grain.Size 0.284941 Maize.Grain.NumberFunction 1986.770519 Maize.Grain.Total.Wt 563.652950 Maize.Grain.N 7.459296 Maize.Total.Wt 1340.837427
If there are more than one database tables or
reportsas called in APSIM, results are concatenated along the axis 0, implying along rows. The example below mimics this scenario.>>> model.add_db_table( ... variable_spec=['[Clock].Today.Year as year', ... 'sum([Soil].Nutrient.TotalC)/1000 from 01-jan to [clock].Today as soc'], ... rename='soc' ... ) # inspect the reports >>> model.inspect_model('Models.Report', fullpath=False) ['Report', 'soc'] >>> model.run() >>> model.results CheckpointID SimulationID Zone ... source_table year soc 0 1 1 Field ... Report NaN NaN 1 1 1 Field ... Report NaN NaN 2 1 1 Field ... Report NaN NaN 3 1 1 Field ... Report NaN NaN 4 1 1 Field ... Report NaN NaN 5 1 1 Field ... Report NaN NaN 6 1 1 Field ... Report NaN NaN 7 1 1 Field ... Report NaN NaN 8 1 1 Field ... Report NaN NaN 9 1 1 Field ... Report NaN NaN 10 1 1 Field ... soc 1990.0 77.831512 11 1 1 Field ... soc 1991.0 78.501766 12 1 1 Field ... soc 1992.0 78.916339 13 1 1 Field ... soc 1993.0 78.707094 14 1 1 Field ... soc 1994.0 78.191686 15 1 1 Field ... soc 1995.0 78.573085 16 1 1 Field ... soc 1996.0 78.724598 17 1 1 Field ... soc 1997.0 79.043935 18 1 1 Field ... soc 1998.0 78.343111 19 1 1 Field ... soc 1999.0 78.872767 20 1 1 Field ... soc 2000.0 79.916413 [21 rows x 17 columns]
By default all the tables are returned and the column
source_tabletells us the source table for each row. Sinceresultsis a property attribute, which does not take in any argument, we can only decide this when calling therunmethod as shown below.>>> model.run(report_name='soc') >>> model.results CheckpointID SimulationID Zone year soc source_table 0 1 1 Field 1990.0 77.831512 soc 1 1 1 Field 1991.0 78.501766 soc 2 1 1 Field 1992.0 78.916339 soc 3 1 1 Field 1993.0 78.707094 soc 4 1 1 Field 1994.0 78.191686 soc 5 1 1 Field 1995.0 78.573085 soc 6 1 1 Field 1996.0 78.724598 soc 7 1 1 Field 1997.0 79.043935 soc 8 1 1 Field 1998.0 78.343111 soc 9 1 1 Field 1999.0 78.872767 soc 10 1 1 Field 2000.0 79.916413 soc
The above example has dataset only from one database table specified at run time.
See also
Related API:
get_simulated_output().- get_simulated_output(self, report_names: 'Union[str, list]', axis=0, **kwargs)
Reads report data from CSV files generated by the simulation. More Advanced table-merging arguments will be introduced soon.
Parameters:
- report_names: (str, iterable)
Name or list names of report tables to read. These should match the report names in the simulation output.
- axis: int, Optional. Default to 0
concatenation axis numbers for multiple reports or database tables. if axis is 0, source_table column is populated to show source of the data for each row
Returns:
pd.DataFrameConcatenated DataFrame containing the data from the specified reports.
Raises:
- ValueError
If any of the requested report names are not found in the available tables.
- RuntimeError
If the simulation has not been
runsuccessfully before attempting to read data.
Examples
>>> from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel >>> model = ApsimModel(model='Maize') # replace with your path to the apsim template model >>> model.run() # if we are going to use get_simulated_output, no need to provide the report name in ``run()`` method >>> df = model.get_simulated_output(report_names="Report") SimulationName SimulationID CheckpointID ... Maize.Total.Wt Yield Zone 0 Simulation 1 1 ... 1728.427 8469.616 Field 1 Simulation 1 1 ... 920.854 4668.505 Field 2 Simulation 1 1 ... 204.118 555.047 Field 3 Simulation 1 1 ... 869.180 3504.000 Field 4 Simulation 1 1 ... 1665.475 7820.075 Field 5 Simulation 1 1 ... 2124.740 8823.517 Field 6 Simulation 1 1 ... 1235.469 3587.101 Field 7 Simulation 1 1 ... 951.808 2939.152 Field 8 Simulation 1 1 ... 1986.968 8379.435 Field 9 Simulation 1 1 ... 1689.966 7370.301 Field [10 rows x 16 columns]
This method also handles more than one reports as shown below.
>>> model.add_db_table( ... variable_spec=[ ... '[Clock].Today.Year as year', ... 'sum([Soil].Nutrient.TotalC)/1000 from 01-jan to [clock].Today as soc' ... ], ... rename='soc' ... ) # inspect the reports >>> model.inspect_model('Models.Report', fullpath=False) ['Report', 'soc'] >>> model.run() >>> model.get_simulated_output(["soc", "Report"], axis=0) CheckpointID SimulationID ... Maize.Grain.N Maize.Total.Wt 0 1 1 ... NaN NaN 1 1 1 ... NaN NaN 2 1 1 ... NaN NaN 3 1 1 ... NaN NaN 4 1 1 ... NaN NaN 5 1 1 ... NaN NaN 6 1 1 ... NaN NaN 7 1 1 ... NaN NaN 8 1 1 ... NaN NaN 9 1 1 ... NaN NaN 10 1 1 ... NaN NaN 11 1 1 ... 11.178291 1728.427114 12 1 1 ... 6.226327 922.393712 13 1 1 ... 0.752357 204.108770 14 1 1 ... 4.886844 869.242545 15 1 1 ... 10.463854 1665.483701 16 1 1 ... 11.253916 2124.739830 17 1 1 ... 5.044417 1261.674967 18 1 1 ... 3.955080 951.303260 19 1 1 ... 11.080878 1987.106980 20 1 1 ... 9.751001 1693.893386 [21 rows x 17 columns]
>>> model.get_simulated_output(['soc', 'Report'], axis=1) CheckpointID SimulationID ... Maize.Grain.N Maize.Total.Wt 0 1 1 ... 11.178291 1728.427114 1 1 1 ... 6.226327 922.393712 2 1 1 ... 0.752357 204.108770 3 1 1 ... 4.886844 869.242545 4 1 1 ... 10.463854 1665.483701 5 1 1 ... 11.253916 2124.739830 6 1 1 ... 5.044417 1261.674967 7 1 1 ... 3.955080 951.303260 8 1 1 ... 11.080878 1987.106980 9 1 1 ... 9.751001 1693.893386 10 1 1 ... NaN NaN [11 rows x 19 columns]
See also
Related API:
results.- run(self, report_name: 'Union[tuple, list, str]' = None, simulations: 'Union[tuple, list]' = None, clean_up: 'bool' = True, verbose: 'bool' = False, timeout: 'int' = 800, cpu_count: 'int' = -1, **kwargs)
- Run APSIM model simulations to write the results either to SQLite database or csv file. Does not collect the
simulated output into memory. Please see related APIs:
resultsandget_simulated_output().
Parameters
- report_name: Union[tuple, list, str], optional
Defaults to APSIM default Report Name if not specified. - If iterable, all report tables are read and aggregated into one DataFrame.
- simulations: Union[tuple, list], optional
List of simulation names to run. If None, runs all simulations.
- clean_up: bool, optional
If True, removes the existing database before running.
- verbose: bool, optional
If True, enables verbose output for debugging. The method continues with debugging info anyway if the run was unsuccessful
- timeout: int, default is 800 seconds
Enforces a timeout and returns a CompletedProcess-like object.
- cpu_count: int, Optional default is -1, referring to all threads
This parameter is useful when the number of simulations are more than 1, below that performance differences are minimal added in 0.39.11.21+
- kwargs: **dict
Additional keyword arguments, e.g., to_csv=True, use this flag to correct results from a csv file directly stored at the location of the running apsimx file.
Warning:
In my experience with Models.exe, CSV outputs are not always overwritten; after edits, stale results can persist. Proceed with caution.
Returns
Instance of the respective model class e.g., ApsimModel, ExperimentManager.
RuntimeErrorRaised if the
APSIMrun is unsuccessful. Common causes includemissing meteorological files, mismatched simulationstartdates withweatherdata, or otherconfiguration issues.
Example:
Instantiate an
apsimNGpy.core.apsim.ApsimModelobject and run:from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel model = ApsimModel(model= 'Maize')# replace with your path to the apsim template model model.run(report_name = "Report") # check if the run was successful model.ran_ok 'True'
Note
Updates the
ran_okflag toTrueif no error was encountered.See also
Related APIs:
resultsandget_simulated_output().- rename_model(self, model_type, *, old_name, new_name) (inherited)
Renames a model within the APSIM simulation tree.
This method searches for a model of the specified type and current name, then updates its name to the new one provided. After renaming, it saves the updated simulation file to enforce the changes.
- model_typestr
The type of the model to rename (e.g., “Manager”, “Clock”, etc.).
- old_namestr
The current name of the model to be renamed.
- new_namestr
The new name to assign to the model.
- selfobject
Returns the modified object to allow for method chaining.
- ValueError
If the model of the specified type and name is not found.
Tip
This method uses
get_or_check_modelwith action=’get’ to locate the model, and then updates the model’sNameattribute. The model is serialized using thesave()immediately after to apply and enfoce the change.>>> from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel >>> model = ApsimModel(model = 'Maize', out_path='my_maize.apsimx') >>> model.rename_model(model_type="Models.Core.Simulation", old_name ='Simulation', new_name='my_simulation') # check if it has been successfully renamed >>> model.inspect_model(model_type='Models.Core.Simulation', fullpath = False) ['my_simulation'] # The alternative is to use model.inspect_file to see your changes >>> model.inspect_file()
└── Models.Core.Simulations: .Simulations ├── Models.Storage.DataStore: .Simulations.DataStore ├── Models.Core.Folder: .Simulations.Replacements │ └── Models.PMF.Plant: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize │ └── Models.Core.Folder: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Atrium │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.CG4141 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Dekalb_XL82 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.GH_5009 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.GH_5019WX │ ├── Models.Core.Folder: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_100 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_103 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_105 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_108 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_110 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_112 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_115 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_120 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_130 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_80 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_90 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_95 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_100 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_103 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_105 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_108 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_110 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_112 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_115 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_120 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_130 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_80 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_90 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_95 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.HY_110 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.LY_110 │ │ └── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.P1197 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Hycorn_40 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Hycorn_53 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Katumani │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Laila │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Makueni │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Melkassa │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.NSCM_41 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_3153 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_33M54 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_34K77 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_38H20 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_39G12 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_39V43 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.malawi_local │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh12 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh16 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh17 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh18 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh19 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.r201 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.r215 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc401 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc501 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc601 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc623 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc625 │ └── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.sr52 └── Models.Core.Simulation: .Simulations.Simulation ├── Models.Clock: .Simulations.Simulation.Clock ├── Models.Core.Zone: .Simulations.Simulation.Field │ ├── Models.Manager: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Fertilise at sowing │ ├── Models.Fertiliser: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Fertiliser │ ├── Models.Manager: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Harvest │ ├── Models.PMF.Plant: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize │ │ └── Models.Core.Folder: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Atrium │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.CG4141 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Dekalb_XL82 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.GH_5009 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.GH_5019WX │ │ ├── Models.Core.Folder: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_100 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_103 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_105 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_108 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_110 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_112 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_115 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_120 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_130 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_80 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_90 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_95 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_100 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_103 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_105 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_108 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_110 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_112 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_115 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_120 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_130 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_80 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_90 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_95 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.HY_110 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.LY_110 │ │ │ └── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.P1197 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Hycorn_40 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Hycorn_53 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Katumani │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Laila │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Makueni │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Melkassa │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.NSCM_41 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_3153 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_33M54 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_34K77 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_38H20 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_39G12 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_39V43 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.malawi_local │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh12 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh16 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh17 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh18 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh19 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.r201 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.r215 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc401 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc501 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc601 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc623 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc625 │ │ └── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.sr52 │ ├── Models.Report: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Report │ ├── Models.Soils.Soil: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Chemical: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Chemical │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Solute: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.NH4 │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Solute: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.NO3 │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Organic: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Organic │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Physical: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Physical │ │ │ └── Models.Soils.SoilCrop: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Physical.MaizeSoil │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Solute: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Urea │ │ └── Models.Soils.Water: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Water │ ├── Models.Manager: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Sow using a variable rule │ └── Models.Surface.SurfaceOrganicMatter: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.SurfaceOrganicMatter ├── Models.Graph: .Simulations.Simulation.Graph │ └── Models.Series: .Simulations.Simulation.Graph.Series ├── Models.MicroClimate: .Simulations.Simulation.MicroClimate ├── Models.Soils.Arbitrator.SoilArbitrator: .Simulations.Simulation.SoilArbitrator ├── Models.Summary: .Simulations.Simulation.Summary └── Models.Climate.Weather: .Simulations.Simulation.WeatherSee also
Related APIs:
add_model(),clone_model(), andmove_model().- clone_model(self, model_type, model_name, adoptive_parent_type, rename=None, adoptive_parent_name=None) (inherited)
Clone an existing
modeland move it to a specified parent within the simulation structure. The function modifies the simulation structure by adding the cloned model to the designated parent.This function is useful when a model instance needs to be duplicated and repositioned in the
APSIMsimulation hierarchy without manually redefining its structure.Parameters:
- model_type: Models
The type of the model to be cloned, e.g.,
Models.SimulationorModels.Clock.- model_name: str
The unique identification name of the model instance to be cloned, e.g.,
"clock1".- adoptive_parent_type: Models
The type of the new parent model where the cloned model will be placed.
- rename: str, optional
The new name for the cloned model. If not provided, the clone will be renamed using the original name with a
_clonesuffix.- adoptive_parent_name: str, optional
The name of the parent model where the cloned model should be moved. If not provided, the model will be placed under the default parent of the specified type.
- in_place: bool, optional
If
True, the cloned model remains in the same location but is duplicated. Defaults toFalse.
Returns:
None
Example:
Create a cloned version of
"clock1"and place it under"Simulation"with the new name"new_clock:>>> from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel >>> model = ApsimModel('Maize', out_path='my_maize.apsimx') >>> model.clone_model(model_type='Models.Core.Simulation', model_name="Simulation", ... rename="Sim2", adoptive_parent_type = 'Models.Core.Simulations', ... adoptive_parent_name='Simulations') >>> model.inspect_file() └── Simulations: .Simulations ├── DataStore: .Simulations.DataStore ├── Sim2: .Simulations.Sim2 │ ├── Clock: .Simulations.Sim2.Clock │ ├── Field: .Simulations.Sim2.Field │ │ ├── Fertilise at sowing: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Fertilise at sowing │ │ ├── Fertiliser: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Fertiliser │ │ ├── Harvest: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Harvest │ │ ├── Maize: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Maize │ │ ├── Report: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Report │ │ ├── Soil: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Soil │ │ │ ├── Chemical: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Soil.Chemical │ │ │ ├── NH4: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Soil.NH4 │ │ │ ├── NO3: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Soil.NO3 │ │ │ ├── Organic: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Soil.Organic │ │ │ ├── Physical: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Soil.Physical │ │ │ │ └── MaizeSoil: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Soil.Physical.MaizeSoil │ │ │ ├── Urea: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Soil.Urea │ │ │ └── Water: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Soil.Water │ │ ├── Sow using a variable rule: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.Sow using a variable rule │ │ ├── SurfaceOrganicMatter: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.SurfaceOrganicMatter │ │ └── soc_table: .Simulations.Sim2.Field.soc_table │ ├── Graph: .Simulations.Sim2.Graph │ │ └── Series: .Simulations.Sim2.Graph.Series │ ├── MicroClimate: .Simulations.Sim2.MicroClimate │ ├── SoilArbitrator: .Simulations.Sim2.SoilArbitrator │ ├── Summary: .Simulations.Sim2.Summary │ └── Weather: .Simulations.Sim2.Weather └── Simulation: .Simulations.Simulation ├── Clock: .Simulations.Simulation.Clock ├── Field: .Simulations.Simulation.Field │ ├── Fertilise at sowing: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Fertilise at sowing │ ├── Fertiliser: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Fertiliser │ ├── Harvest: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Harvest │ ├── Maize: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize │ ├── Report: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Report │ ├── Soil: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil │ │ ├── Chemical: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Chemical │ │ ├── NH4: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.NH4 │ │ ├── NO3: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.NO3 │ │ ├── Organic: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Organic │ │ ├── Physical: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Physical │ │ │ └── MaizeSoil: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Physical.MaizeSoil │ │ ├── Urea: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Urea │ │ └── Water: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Water │ ├── Sow using a variable rule: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Sow using a variable rule │ ├── SurfaceOrganicMatter: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.SurfaceOrganicMatter │ └── soc_table: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.soc_table ├── Graph: .Simulations.Simulation.Graph │ └── Series: .Simulations.Simulation.Graph.Series ├── MicroClimate: .Simulations.Simulation.MicroClimate ├── SoilArbitrator: .Simulations.Simulation.SoilArbitrator ├── Summary: .Simulations.Simulation.Summary └── Weather: .Simulations.Simulation.Weather
See also
Related APIs:
add_model()andmove_model().- static find_model(model_name: 'str') (inherited)
Find a model from the Models namespace and return its path.
Parameters:
- model_name: (str)
The name of the model to find.
- model_namespace: (object, optional):
The root namespace (defaults to Models).
- path: (str, optional)
The accumulated path to the model.
- Returns:
str: The full path to the model if found, otherwise None.
Example:
>>> from apsimNGpy import core # doctest: >>> model =core.apsim.ApsimModel(model = "Maize", out_path ='my_maize.apsimx') >>> model.find_model("Weather") 'Models.Climate.Weather' >>> model.find_model("Clock") 'Models.Clock'
- add_model(self, model_type, adoptive_parent, rename=None, adoptive_parent_name=None, verbose=False, source='Models', source_model_name=None, override=True, **kwargs) (inherited)
Adds a model to the Models Simulations namespace.
Some models are restricted to specific parent models, meaning they can only be added to compatible models. For example, a Clock model cannot be added to a Soil model.
Parameters:
- model_type: (str or Models object)
The type of model to add, e.g.,
Models.Clockor just"Clock". if the APSIM Models namespace is exposed to the current script, then model_class can be Models.Clock without strings quotes- rename (str):
The new name for the model.
- adoptive_parent: (Models object)
The target parent where the model will be added or moved e.g
Models.ClockorClockas string all are valid- adoptive_parent_name: (Models object, optional)
Specifies the parent name for precise location. e.g.,
Models.Core.SimulationorSimulationsall are valid- source: Models, str, CoreModel, ApsimModel object: defaults to Models namespace.
The source can be an existing Models or string name to point to one of the default model examples, which we can extract the model from
- override: bool, optional defaults to
True. When
True(recommended), it deletes any model with the same name and type at the suggested parent location before adding the new model ifFalseand proposed model to be added exists at the parent location;APSIMautomatically generates a new name for the newly added model. This is not recommended.- Returns:
None:
Modelsare modified in place, so models retains the same reference.Caution
Added models from
Models namespaceare initially empty. Additional configuration is required to set parameters. For example, after adding a Clock module, you must set the start and end dates.Example
>>> from apsimNGpy import core >>> from apsimNGpy.core.core import Models >>> model = core.apsim.ApsimModel("Maize") >>> model.remove_model(Models.Clock) # first delete the model >>> model.add_model(Models.Clock, adoptive_parent=Models.Core.Simulation, rename='Clock_replaced', verbose=False)
>>> model.add_model(model_class=Models.Core.Simulation, adoptive_parent=Models.Core.Simulations, rename='Iowa')
>>> model.preview_simulation()
>>> model.add_model( ... Models.Core.Simulation, ... adoptive_parent='Simulations', ... rename='soybean_replaced', ... source='Soybean') # basically adding another simulation from soybean to the maize simulation
See also
Related APIs:
clone_model()andmove_model().- detect_model_type(self, model_instance: 'Union[str, Models]') (inherited)
Detects the model type from a given APSIM model instance or path string.
- edit_model_by_path(self, path: 'str', **kwargs) (inherited)
Edit a model component located by an APSIM path, dispatching to type-specific editors.
This method resolves a node under
instance.Simulationsusing an APSIM path, then edits that node by delegating to an editor based on the node’s runtime type. It supports common APSIM NG components (e.g., Weather, Manager, Cultivar, Clock, Soil subcomponents, Report, SurfaceOrganicMatter). Unsupported types raiseNotImplementedError.Parameters
- pathstr
APSIM path to a target node under
self.Simulations(e.g., ‘.Simulations.Simulations.Weather’ or a similar canonical path).
kwargs
Additional keyword arguments specific to the model type. Atleast one key word argument is required. These vary by component:
- Models.Climate.Weather:
weather_file(str): Path to the weather.metfile.- Models.Clock:
Date properties such as
StartandEndin ISO format (e.g., ‘2021-01-01’).- Models.Manager:
Variables to update in the Manager script using
update_mgt_by_path.- Soils.Physical | Soils.Chemical | Soils.Organic | Soils.Water:
Variables to replace using
replace_soils_values_by_path.Valid
parametersare shown below;Soil Model Type
Supported key word arguments
Physical
AirDry, BD, DUL, DULmm, Depth, DepthMidPoints, KS, LL15, LL15mm, PAWC, PAWCmm, SAT, SATmm, SW, SWmm, Thickness, ThicknessCumulative
Organic
CNR, Carbon, Depth, FBiom, FInert, FOM, Nitrogen, SoilCNRatio, Thickness
Chemical
Depth, PH, Thickness
- Models.Report:
- report_name (str):
Name of the report model (optional depending on structure).
- variable_spec` (list[str] or str):
Variables to include in the report.
- set_event_names` (list[str], optional):
Events that trigger the report.
- Models.PMF.Cultivar:
- commands (str):
APSIM path to the cultivar parameter to update.
- values: (Any)
Value to assign.
- cultivar_manager: (str)
Name of the Manager script managing the cultivar, which must contain the
CultivarNameparameter. Required to propagate updated cultivar values, as APSIM treats cultivars as read-only.
Warning
- ValueError
If the model instance is not found, required kwargs are missing, or
kwargsis empty.- NotImplementedError
If the logic for the specified
model_classis not implemented.
Examples
Edit a Manager script parameter:
model.edit_model_by_path( ".Simulations.Simulation.Field.Sow using a variable rule", verbose=True, Population=10)
Point a Weather component to a new
.metfile:model.edit_model_by_path( path=".Simulations.Simulation.Weather", FileName="data/weather/Ames_2020.met")
Change Clock dates:
model.edit_model_by_path( ".Simulations.Simulation.Clock", StartDate="2020-01-01", EndDate="2020-12-31")
Update soil water properties at a specific path:
model.edit_model_by_path( ".Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Physical", LL15="[0.26, 0.18, 0.10, 0.12]")
Apply cultivar edits:
model.edit_model_by_path( ".Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh18", sowed=True, **{"Phenology.EmergencePhase.Photo-period": "Short"} )
See also
Related API:
edit_model().- add_base_replacements(self) (inherited)
Add base replacements with all available models of type Plants and then start from there to add more @return: self
- edit_model(self, model_type: 'str', model_name: 'str', simulations: 'Union[str, list]' = 'all', exclude=None, verbose=False, **kwargs) (inherited)
Modify various APSIM model components by specifying the model type and name across given simulations.
Tip
Editing APSIM models in apsimNGpy does not require placing the target model inside a Replacements folder or node. However, when modifying cultivar parameters, it can be helpful to include a Replacements folder containing the relevant plant definition hosting that cultivar. In many cases, apsimNGpy will handle this automatically.
Selective Editing
Selective editing allows you to apply modifications only to certain simulations. This is not possible when the same model instance is shared through a common Replacements folder. For reliable selective editing, each simulation should ideally reference a uniquely named model. However, even when model names are not unique, apsimNGpy still enables targeted editing through two mechanisms:
Exclusion strategy You can explicitly exclude simulations to which the edits should not be applied.
Specification strategy You can explicitly specify which simulations should have their models edited or replaced with new parameters.
Parameters
- model_type: str, required
Type of the model component to modify (e.g., ‘Clock’, ‘Manager’, ‘Soils.Physical’, etc.).
- simulations: Union[str, list], optional
A simulation name or list of simulation names in which to search. Defaults to all simulations in the model.
- model_name: str, required
Name of the model instance to modify.
- verbose: bool, optional
print the status of the editing activities
- exclude: Union[str, None, Iterable[str]], optional,default is None
Added in ‘V0.39.10.20’+. It is used to specify which simulation should be skipped during the editing process, in case there are more than simulations
kwargs
Additional keyword arguments specific to the model type. Atleast one key word argument is required. These vary by component:
- Models.Climate.Weather:
weather_file(str): Path to the weather.metfile.- Models.Clock:
Date properties such as
StartandEndin ISO format (e.g., ‘2021-01-01’).- Models.Manager:
Variables to update in the Manager script using
update_mgt_by_path.- Soils.Physical | Soils.Chemical | Soils.Organic | Soils.Water:
Variables to replace using
replace_soils_values_by_path.Valid
parametersare shown below;Soil Model Type
Supported key word arguments
Physical
AirDry, BD, DUL, DULmm, Depth, DepthMidPoints, KS, LL15, LL15mm, PAWC, PAWCmm, SAT, SATmm, SW, SWmm, Thickness, ThicknessCumulative
Organic
CNR, Carbon, Depth, FBiom, FInert, FOM, Nitrogen, SoilCNRatio, Thickness
Chemical
Depth, PH, Thickness
- Models.Report:
- report_name (str):
Name of the report model (optional depending on structure).
- variable_spec` (list[str] or str):
Variables to include in the report.
- set_event_names` (list[str], optional):
Events that trigger the report.
- Models.PMF.Cultivar:
- commands (str):
APSIM path to the cultivar parameter to update.
- values: (Any)
Value to assign.
- cultivar_manager: (str)
Name of the Manager script managing the cultivar, which must contain the
CultivarNameparameter. Required to propagate updated cultivar values, as APSIM treats cultivars as read-only.
Warning
- ValueError
If the model instance is not found, required kwargs are missing, or
kwargsis empty.- NotImplementedError
If the logic for the specified
model_classis not implemented.
Examples:
from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel model = ApsimModel(model='Maize')
Example of how to edit a cultivar model:
model.edit_model(model_type='Cultivar', simulations='Simulation', commands='[Phenology].Juvenile.Target.FixedValue', values=256, model_name='B_110', new_cultivar_name='B_110_edited', cultivar_manager='Sow using a variable rule')
Edit a soil organic matter module:
model.edit_model( model_type='Organic', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Organic', Carbon=1.23)
Edit multiple soil layers:
model.edit_model( model_type='Organic', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Organic', Carbon=[1.23, 1.0])
Example of how to edit solute models:
model.edit_model( model_type='Solute', simulations='Simulation', model_name='NH4', InitialValues=0.2) model.edit_model( model_class='Solute', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Urea', InitialValues=0.002)
Edit a manager script:
model.edit_model( model_type='Manager', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Sow using a variable rule', population=8.4)
Edit surface organic matter parameters:
model.edit_model( model_type='SurfaceOrganicMatter', simulations='Simulation', model_name='SurfaceOrganicMatter', InitialResidueMass=2500) model.edit_model( model_type='SurfaceOrganicMatter', simulations='Simulation', model_name='SurfaceOrganicMatter', InitialCNR=85)
Edit Clock start and end dates:
model.edit_model( model_type='Clock', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Clock', Start='2021-01-01', End='2021-01-12')
Edit report _variables:
model.edit_model( model_type='Report', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Report', variable_spec='[Maize].AboveGround.Wt as abw')
Multiple report _variables:
model.edit_model( model_type='Report', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Report', variable_spec=[ '[Maize].AboveGround.Wt as abw', '[Maize].Grain.Total.Wt as grain_weight'])
the best way to edit cultivar with minimal error is to use a dict of commands as follows.
params = { "[Leaf].Photosynthesis.RUE.FixedValue": 1.8984705340394, "[Phenology].GrainFilling.Target.FixedValue": 710, "[Grain].MaximumGrainsPerCob.FixedValue": 810, "[Phenology].FloweringToGrainFilling.Target.FixedValue": 215, "[Phenology].MaturityToHarvestRipe.Target.FixedValue": 100, "[Maize].Grain.MaximumPotentialGrainSize.FixedValue": 0.867411373063701, "[Grain].MaximumNConc.InitialPhase.InitialNconc.FixedValue": 0.05, '[Maize].Root.SpecificRootLength.FixedValue': 135, '[Maize].Root.RootFrontVelocity.PotentialRootFrontVelocity.PreFlowering.RootFrontVelocity.FixedValue': 22, '[Rachis].DMDemands.Structural.DMDemandFunction.MaximumOrganWt.FixedValue': 36
}
- model.edit_model_by_path(model_type=’Models.PMF.Cultivar, model_name=’Dekalb_XL82’,
commands=params, cultivar_manager=’Sow using a variable rule, parameter_name=’CultivarName’ )
See also
Related API:
edit_model_by_path().- static inspect_settable_attributes(model_type) (inherited)
Inspect and return all settable attributes for a given APSIM model type.
This method identifies which attributes of a model can be modified by the user. APSIM model classes typically expose writable parameters through setter methods following the naming convention
set_<AttributeName>(). This function extracts all such attributes and returns them in a clean, user-friendly list.Added in v0.39.12.21
Parameters
- model_typetype or str
The APSIM model class or the registered model name. This value is validated and resolved to a concrete APSIM model class via
validate_model_obj().
Returns
- list of str
A list of attribute names that can be set on the specified model. These correspond to all public APSIM parameters for which a
set_<AttributeName>method exists. Theset_prefix is removed for clarity, so the list contains clean parameter names.
Notes
This method does not set or modify any attributes—its purpose is diagnostic and introspective.
Useful for error reporting, documentation, and informing users which parameters are valid inputs for
edit_model()or related methods.
Examples
from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel sm = ApsimModel('Maize') sm.inspect_settable_attributes(model_type='Models.Surface.SurfaceOrganicMatter')
['Canopies', 'Children', 'Enabled', 'InitialCNR', 'InitialCPR', 'InitialResidueMass', 'InitialResidueName', 'InitialResidueType', 'InitialStandingFraction', 'IsHidden', 'Name', 'Node', 'Parent', 'ReadOnly', 'ResourceName', 'Structure']
sm.inspect_settable_attributes(Models.WaterModel.WaterBalance)
['CN2Bare', 'CNCov', 'CNRed', 'CatchmentArea', 'Children', 'Depth', 'DiffusConst', 'DiffusSlope', 'DischargeWidth', 'Enabled', 'Eo', 'IsHidden', 'KLAT', 'Name', 'Node', 'PSIDul', 'Parent', 'PoreInteractionIndex', 'PotentialInfiltration', 'PrecipitationInterception', 'ReadOnly', 'ResourceName', 'Runon', 'SW', 'SWCON', 'Salb', 'Structure', 'SummerCona', 'SummerDate', 'SummerU', 'Thickness', 'Water', 'WaterTable', 'WinterCona', 'WinterDate', 'WinterU']
Added in version 0.39.12.21.
- find_model_in_replacements(self, model_type, model_name) (inherited)
checks whether the model to be edited is in the replacement, there is no point to contnue editing from individual simulations
- add_report_variable(self, variable_spec: 'Union[list, str, tuple]', report_name: 'str' = None, set_event_names: 'Union[str, list]' = None, simulations=None) (inherited)
This adds a report variable to the end of other _variables, if you want to change the whole report use change_report
Parameters
- variable_spec: str, required.
list of text commands for the report _variables e.g., ‘[Clock].Today as Date’
- param report_name: str, optional.
Name of the report variable if not specified, the first accessed report object will be altered
- set_event_names: list or str, optional.
A list of APSIM events that trigger the recording of _variables. Defaults to [‘[Clock].EndOfYear’] if not provided.
Returns
returns instance of apsimNGpy.core.core.apsim.ApsimModel or apsimNGpy.core.core.apsim.CoreModel
Raise
raises an
ValueErrorif a report is not foundExamples
>>> from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel >>> model = ApsimModel('Maize') >>> model.add_report_variable(variable_spec = '[Clock].Today as Date', report_name = 'Report') # isnepct the report >>> model.inspect_model_parameters(model_type='Models.Report', model_name='Report') {'EventNames': ['[Maize].Harvesting'], 'VariableNames': ['[Clock].Today', '[Maize].Phenology.CurrentStageName', '[Maize].AboveGround.Wt', '[Maize].AboveGround.N', '[Maize].Grain.Total.Wt*10 as Yield', '[Maize].Grain.Wt', '[Maize].Grain.Size', '[Maize].Grain.NumberFunction', '[Maize].Grain.Total.Wt', '[Maize].Grain.N', '[Maize].Total.Wt', '[Clock].Today as Date']} The new report variable is appended at the end of the existing ones
See also
Related APIs:
remove_report_variable()andadd_db_table().- remove_report_variable(self, variable_spec: 'Union[list, tuple, str]', report_name: 'str | None' = None) (inherited)
Remove one or more variable expressions from an APSIM Report component.
Parameters
- variable_specstr | list[str] | tuple[str, …]
Variable expression(s) to remove, e.g.
"[Clock].Today"or"[Clock].Today as Date". You may pass a single string or a list/tuple. Matching is done by exact text after whitespace normalization (consecutive spaces collapsed), so minor spacing differences are tolerated.- report_namestr, optional
Name of the Report component to modify. If
None, the default resolver (self._get_report) is used to locate the target report.
Returns
- list[str]
The updated list of variable expressions remaining in the report (in original order, without duplicates).
Notes
Variables not present are ignored (no error raised).
Order is preserved; duplicates are removed.
The model is saved at the end of this call.
Examples
>>> model= CoreModel('Maize') >>> model.add_report_variable(variable_spec='[Clock].Today as Date', report_name='Report') >>> model.inspect_model_parameters('Models.Report', 'Report')['VariableNames'] ['[Clock].Today', '[Maize].Phenology.CurrentStageName', '[Maize].AboveGround.Wt', '[Maize].AboveGround.N', '[Maize].Grain.Total.Wt*10 as Yield', '[Maize].Grain.Wt', '[Maize].Grain.Size', '[Maize].Grain.NumberFunction', '[Maize].Grain.Total.Wt', '[Maize].Grain.N', '[Maize].Total.Wt', '[Clock].Today as Date'] >>> model.remove_report_variable(variable_spec='[Clock].Today as Date', report_name='Report') >>> model.inspect_model_parameters('Models.Report', 'Report')['VariableNames'] ['[Clock].Today', '[Maize].Phenology.CurrentStageName', '[Maize].AboveGround.Wt', '[Maize].AboveGround.N', '[Maize].Grain.Total.Wt*10 as Yield', '[Maize].Grain.Wt', '[Maize].Grain.Size', '[Maize].Grain.NumberFunction', '[Maize].Grain.Total.Wt', '[Maize].Grain.N', '[Maize].Total.Wt']
See also
Related APIs:
add_report_variable()andadd_db_table().- remove_model(self, model_type: 'Models', model_name) (inherited)
Removes a model from the APSIM Models.Simulations namespace.
- model_type: Models
The type of the model to remove (e.g.,
Models.Clock). This parameter is required.- model_name: str, optional
The name of the specific model instance to remove (e.g.,
"Clock"). If not provided, all models of the specified type may be removed.
Returns:
None
Example:
from apsimNGpy import core from apsimNGpy.core.core import Models model = core.base_data.load_default_simulations(crop = 'Maize') model.remove_model(Models.Clock) #deletes the clock node model.remove_model(Models.Climate.Weather) #deletes the weather node
See also
Related APIs:
clone_model()andadd_model().- move_model(self, model_type: 'Models', new_parent_type: 'Models', model_name: 'str' = None, new_parent_name: 'str' = None, verbose: 'bool' = False, simulations: 'Union[str, list]' = None) (inherited)
Args:
- model_type: Models
type of model tied to Models Namespace
- new_parent_type: Models.
New model parent type (Models)
- model_name: str
Name of the model e.g., Clock, or Clock2, whatever name that was given to the model
- new_parent_name``: str
The new parent names =Field2, this field is optional but important if you have nested simulations
Returns:
returns instance of apsimNGpy.core.core.apsim.ApsimModel or apsimNGpy.core.core.apsim.CoreModel
- replicate_file(self, k: 'int', path: 'os.PathLike' = None, suffix: 'str' = 'replica') (inherited)
Replicates a file
ktimes. Parameters ———- path:str default is NoneIf specified, the copies will be placed in that dir_path with incremented filenames. If no path is specified, copies are created in the same dir_path as the original file, also with incremented filenames.
- k int:
The number of copies to create.
- suffix: str, optional
a suffix to attach with the copies. Default to “replicate”
Returns:
A generator(str) is returned.
- get_crop_replacement(self, Crop) (inherited)
- param Crop:
crop to get the replacement
- return:
System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerable APSIM plant object
- inspect_model_parameters(self, model_type: 'Union[Models, str]', model_name: 'str', simulations: 'Union[str, list]' = <UserOptionMissing>, parameters: 'Union[list, set, tuple, str]' = 'all', exclude: 'list | set | tuple | str' = None, **kwargs) (inherited)
Inspect the input parameters of a specific
APSIMmodel type instance within selected simulations.This method consolidates functionality previously spread across
examine_management_info,read_cultivar_params, and other inspectors, allowing a unified interface for querying parameters of interest across a wide range of APSIM models.Parameters
- model_type: str required
The name of the model class to inspect (e.g., ‘Clock’, ‘Manager’, ‘Physical’, ‘Chemical’, ‘Water’, ‘Solute’). Shorthand names are accepted (e.g., ‘Clock’, ‘Weather’) as well as fully qualified names (e.g., ‘Models.Clock’, ‘Models.Climate.Weather’).
- simulations: Union[str, list]
A single simulation name or a list of simulation names within the APSIM context to inspect.
- model_name: str
The name of the specific model instance within each simulation. For example, if
model_class='Solute',model_namemight be ‘NH4’, ‘Urea’, or another solute name.- parameters: Union[str, set, list, tuple], optional
A specific parameter or a collection of parameters to inspect. Defaults to
'all', in which case all accessible attributes are returned. For layered models like Solute, valid parameters includeDepth,InitialValues,SoluteBD,Thickness, etc.- exclude: Union[str, list, tuple], optional
used to exclude a few simulations and include only the rest of the simulations Added in v0.39.10.20+
- kwargs:
Reserved for future compatibility; currently unused.
Returns
Union[dict, list, pd.DataFrame, Any] The format depends on the model type as shown below:
- Weather:
file path(s) as string(s)
- Clock:
dictionary with start and end datetime objects (or a single datetime if only one is requested).
- Manager:
dictionary of script parameters.
- Soil-related:
pandas DataFrame of layered values.
- Report:
A dictionary with
VariableNamesandEventNames.
Cultivar: dictionary of parameter strings.
Raises
ValueErrorIf the specified model or simulation is not found or arguments are invalid.
NotImplementedErrorIf the model type is unsupported by the current interface.
Requirements
APSIM Next Generation Python bindings (
apsimNGpy)Python 3.10+
Examples:
from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel model_instance = ApsimModel('Maize')
Inspect full soil
Organicprofile:model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Organic', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Organic') CNR Carbon Depth FBiom ... FOM Nitrogen SoilCNRatio Thickness 0 12.0 1.20 0-150 0.04 ... 347.129032 0.100 12.0 150.0 1 12.0 0.96 150-300 0.02 ... 270.344362 0.080 12.0 150.0 2 12.0 0.60 300-600 0.02 ... 163.972144 0.050 12.0 300.0 3 12.0 0.30 600-900 0.02 ... 99.454133 0.025 12.0 300.0 4 12.0 0.18 900-1200 0.01 ... 60.321981 0.015 12.0 300.0 5 12.0 0.12 1200-1500 0.01 ... 36.587131 0.010 12.0 300.0 6 12.0 0.12 1500-1800 0.01 ... 22.191217 0.010 12.0 300.0 [7 rows x 9 columns]
Inspect soil
Physicalprofile:model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Physical', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Physical') AirDry BD DUL ... SWmm Thickness ThicknessCumulative 0 0.130250 1.010565 0.521000 ... 78.150033 150.0 150.0 1 0.198689 1.071456 0.496723 ... 74.508522 150.0 300.0 2 0.280000 1.093939 0.488438 ... 146.531282 300.0 600.0 3 0.280000 1.158613 0.480297 ... 144.089091 300.0 900.0 4 0.280000 1.173012 0.471584 ... 141.475079 300.0 1200.0 5 0.280000 1.162873 0.457071 ... 137.121171 300.0 1500.0 6 0.280000 1.187495 0.452332 ... 135.699528 300.0 1800.0 [7 rows x 17 columns]
Inspect soil
Chemicalprofile:model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Chemical', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Chemical') Depth PH Thickness 0 0-150 8.0 150.0 1 150-300 8.0 150.0 2 300-600 8.0 300.0 3 600-900 8.0 300.0 4 900-1200 8.0 300.0 5 1200-1500 8.0 300.0 6 1500-1800 8.0 300.0
Inspect one or more specific parameters:
model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Organic', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Organic', parameters='Carbon') Carbon 0 1.20 1 0.96 2 0.60 3 0.30 4 0.18 5 0.12 6 0.12
Inspect more than one specific properties:
model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Organic', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Organic', parameters=['Carbon', 'CNR']) Carbon CNR 0 1.20 12.0 1 0.96 12.0 2 0.60 12.0 3 0.30 12.0 4 0.18 12.0 5 0.12 12.0 6 0.12 12.0
Inspect Report module attributes:
model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Report', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Report') {'EventNames': ['[Maize].Harvesting'], 'VariableNames': ['[Clock].Today', '[Maize].Phenology.CurrentStageName', '[Maize].AboveGround.Wt', '[Maize].AboveGround.N', '[Maize].Grain.Total.Wt*10 as Yield', '[Maize].Grain.Wt', '[Maize].Grain.Size', '[Maize].Grain.NumberFunction', '[Maize].Grain.Total.Wt', '[Maize].Grain.N', '[Maize].Total.Wt']}
Specify only EventNames:
model_instance.inspect_model_parameters(‘Report’, simulations=’Simulation’, model_name=’Report’, parameters=’EventNames’) {‘EventNames’: [‘[Maize].Harvesting’]}
Inspect a weather file path:
model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Weather', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Weather') '%root%/Examples/WeatherFiles/AU_Dalby.met'
Inspect manager script parameters:
model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Manager', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Sow using a variable rule') {'Crop': 'Maize', 'StartDate': '1-nov', 'EndDate': '10-jan', 'MinESW': '100.0', 'MinRain': '25.0', 'RainDays': '7', 'CultivarName': 'Dekalb_XL82', 'SowingDepth': '30.0', 'RowSpacing': '750.0', 'Population': '10'}
Inspect manager script by specifying one or more parameters:
model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Manager', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Sow using a variable rule', parameters='Population') {'Population': '10'}
Inspect cultivar parameters:
model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Cultivar', simulations='Simulation', model_name='B_110') # lists all path specifications for B_110 parameters abd their values model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Cultivar', simulations='Simulation', model_name='B_110', parameters='[Phenology].Juvenile.Target.FixedValue') {'[Phenology].Juvenile.Target.FixedValue': '210'}
Inspect surface organic matter module:
model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Models.Surface.SurfaceOrganicMatter', simulations='Simulation', model_name='SurfaceOrganicMatter') {'NH4': 0.0, 'InitialResidueMass': 500.0, 'StandingWt': 0.0, 'Cover': 0.0, 'LabileP': 0.0, 'LyingWt': 0.0, 'InitialCNR': 100.0, 'P': 0.0, 'InitialCPR': 0.0, 'SurfOM': <System.Collections.Generic.List[SurfOrganicMatterType] object at 0x000001DABDBB58C0>, 'C': 0.0, 'N': 0.0, 'NO3': 0.0}
Inspect a few parameters as needed:
model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Models.Surface.SurfaceOrganicMatter', simulations='Simulation', ... model_name='SurfaceOrganicMatter', parameters={'InitialCNR', 'InitialResidueMass'}) {'InitialCNR': 100.0, 'InitialResidueMass': 500.0}
Inspect a clock:
model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Clock', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Clock') {'End': datetime.datetime(2000, 12, 31, 0, 0), 'Start': datetime.datetime(1990, 1, 1, 0, 0)}
Inspect a few Clock parameters as needed:
model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Clock', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Clock', parameters='End') datetime.datetime(2000, 12, 31, 0, 0)
Access specific components of the datetime object e.g., year, month, day, hour, minute:
model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Clock', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Clock', parameters='Start').year # gets the start year only 1990
Inspect solute models:
model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Solute', simulations='Simulation', model_name='Urea') Depth InitialValues SoluteBD Thickness 0 0-150 0.0 1.010565 150.0 1 150-300 0.0 1.071456 150.0 2 300-600 0.0 1.093939 300.0 3 600-900 0.0 1.158613 300.0 4 900-1200 0.0 1.173012 300.0 5 1200-1500 0.0 1.162873 300.0 6 1500-1800 0.0 1.187495 300.0 model_instance.inspect_model_parameters('Solute', simulations='Simulation', model_name='NH4', parameters='InitialValues') InitialValues 0 0.1 1 0.1 2 0.1 3 0.1 4 0.1 5 0.1 6 0.1
See also
Related API:
inspect_model_parameters_by_path()- inspect_model_parameters_by_path(self, path, *, parameters: 'Union[list, set, tuple, str]' = None) (inherited)
Inspect and extract parameters from a model component specified by its path.
Parameters:
- path: str required
The path relative to the Models.Core.Simulations Node
- parameters: Union[str, set, list, tuple], optional
A specific parameter or a collection of parameters to inspect. Defaults to
'all', in which case all accessible attributes are returned. For layered models like Solute, valid parameters includeDepth,InitialValues,SoluteBD,Thickness, etc.- kwargs:
Reserved for future compatibility; currently unused.
Returns
Union[dict, list, pd.DataFrame, Any] The format depends on the model type as shown below:
- Weather:
file path(s) as string(s)
- Clock:
dictionary with start and end datetime objects (or a single datetime if only one is requested).
- Manager:
dictionary of script parameters.
- Soil-related:
pandas DataFrame of layered values.
- Report:
A dictionary with
VariableNamesandEventNames.
Cultivar: dictionary of parameter strings.
Raises
ValueErrorIf the specified model or simulation is not found or arguments are invalid.
NotImplementedErrorIf the model type is unsupported by the current interface.
Requirements
APSIM Next Generation Python bindings (
apsimNGpy)Python 3.10+
See also
Related API:
inspect_model_parameters()Others:inspect_model(),inspect_file()- edit_cultivar(self, *, CultivarName: 'str', commands: 'str', values: 'Any', **kwargs) (inherited)
@deprecated Edits the parameters of a given cultivar. we don’t need a simulation name for this unless if you are defining it in the manager section, if that it is the case, see update_mgt.
- Requires:
required a replacement for the crops
Args:
CultivarName (str, required): Name of the cultivar (e.g., ‘laila’).
variable_spec (str, required): A strings representing the parameter paths to be edited.
Returns: instance of the class CoreModel or ApsimModel
Example:
('[Grain].MaximumGrainsPerCob.FixedValue', '[Phenology].GrainFilling.Target.FixedValue') - values: values for each command (e.g., (721, 760)).
- update_cultivar(self, *, parameters: 'dict', simulations: 'Union[list, tuple]' = None, clear=False, **kwargs) (inherited)
Update cultivar parameters
- parameters: (dict, required)
dictionary of cultivar parameters to update.
- simulationsstr optional
List or tuples of simulation names to update if
Noneupdate all simulations.- clear (bool, optional)
If
Trueremove all existing parameters, by defaultFalse.
- recompile_edited_model(self, out_path: 'os.PathLike') (inherited)
Args:
out_path: os.PathLike object this method is called to convert the simulation object from ConverterReturnType to model like objectreturn:self- update_mgt_by_path(self, *, path: 'str', fmt='.', **kwargs) (inherited)
Parameters
- path: str
A complete node path to the script manager e.g. ‘.Simulations.Simulation.Field.Sow using a variable rule’
- fmt: str
seperator for formatting the path e.g., “.”. Other characters can be used with caution, e.g., / and clearly declared in fmt argument. If you want to use the forward slash, it will be ‘/Simulations/Simulation/Field/Sow using a variable rule’, fmt = ‘/’
- **kwargs:
Corresponding keyword arguments representing the paramters in the script manager and their values. Values is what you want to change to; Example here
Population=8.2, values should be entered with their corresponding data types e.g., int, float, bool,str etc.
Returns:
Instance of apsimNgpy.core.ApsimModel or apsimNgpy.core.experimentmanager.ExperimentManager
- replace_model_from(self, model, model_type: 'str', model_name: 'str' = None, target_model_name: 'str' = None, simulations: 'str' = None) (inherited)
@deprecated and will be removed function has not been maintained for a long time, use it at your own risk
Replace a model, e.g., a soil model with another soil model from another APSIM model. The method assumes that the model to replace is already loaded in the current model and the same class as a source model. e.g., a soil node to soil node, clock node to clock node, et.c
Parameters:
model: Path to the APSIM model file or a CoreModel instance.
- model_type: (str):
Class name (as string) of the model to replace (e.g., “Soil”).
- model_name: (str, optional)
Name of the model instance to copy from the source model. If not provided, the first match is used.
- target_model_name: (str, optional)
Specific simulation name to target for replacement. Only used when replacing Simulation-level objects.
- simulations (str, optional):
Simulation(s) to operate on. If None, applies to all.
- Returns:
self: To allow method chaining.
- Raises:
ValueError: Ifmodel_classis “Simulations” which is not allowed for replacement.
- update_mgt(self, *, management: 'Union[dict, tuple]', simulations: '[list, tuple]' = <UserOptionMissing>, out: '[Path, str]' = None, reload: 'bool' = True, **kwargs) (inherited)
Update management settings in the model. This method handles one management parameter at a time.
Parameters
- management: dict or tuple
A dictionary or tuple of management parameters to update. The dictionary should have ‘Name’ as the key for the management script’s name and corresponding values to update. Lists are not allowed as they are mutable and may cause issues with parallel processing. If a tuple is provided, it should be in the form (param_name, param_value).
- simulations: list of str, optional
List of simulation names to update. If
None, updates all simulations. This is not recommended for large numbers of simulations as it may result in a high computational load.- out: str or pathlike, optional
Path to save the edited model. If
None, uses the default output path specified inself.out_pathorself.model_info.path. No need to callsave_edited_fileafter updating, as this method handles saving.
Returns
Returns the instance of the respective model class for method chaining.
..note:
Ensure that the `management` parameter is provided in the correct format to avoid errors. - This method does not perform `validation` on the provided `management` dictionary beyond checking for key existence. - If the specified management script or parameters do not exist, they will be ignored.
- preview_simulation(self, watch=False) (inherited)
Open the current simulation in the APSIM Next Gen GUI.
This first saves the in-memory simulation to
out_pathand then launches the APSIM Next Gen GUI (viaget_apsim_bin_path()) so you can inspect the model tree and make quick edits side by side.Parameters
- watchbool, default False
If True, Python will listen for GUI edits and sync them back into the model instance in (near) real time. This feature is experimental.
Returns
- None
This function performs a side effect (opening the GUI) and does not return a value.
Raises
- FileNotFoundError
If the file does not exist after
save().- RuntimeError
If the APSIM Next Gen executable cannot be located or the GUI fails to start.
Tip
The file opened in the GUI is a saved copy of this Python object. Changes made in the GUI are not propagated back to the
ApsimModelinstance unless you setwatch=True. Otherwise, to continue working in Python with GUI edits, save the file in APSIM and re-load it, for example:ApsimModel("gui_edited_file_path.apsimx")
Examples
1. Preview only
from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel model = ApsimModel("Maize", out_path="test_.apsimx") model.preview_simulation()

2. Preview and edit simultaneously
After opening the APSIMX file in the GUI via the watching mode (
watch=True), you can modify any parameters using GUI interface. The Example given below involved changing parameters such as Plant population (/m²), Cultivar to be sown, and Row spacing (mm) in the Sow using a variable rule script and finally, checked whether the changes were successful by inspecting the model.model.preview_simulation(watch=True)

Example console output when
watch=True:2025-10-24 13:05:08,480 - INFO - Watching for GUI edits... Save in APSIM to sync back. 2025-10-24 13:05:08,490 - INFO - Press Ctrl+C in this cell to stop. APSIM GUI saved. Syncing model... 2025-10-24 13:05:24,112 - INFO - Watching terminated successfully.
Tip
When
watch=True, follow the console instructions. One critical step is that you must pressCtrl+Cto stop watching.Checking if changes were successfully propagated back
model.inspect_model_parameters("Models.Manager", "Sow using a variable rule")
{'Crop': '[Maize]', 'StartDate': '1-nov', 'EndDate': '10-jan', 'MinESW': '100', 'MinRain': '25', 'RainDays': '7', 'CultivarName': 'B_95', 'SowingDepth': '25', 'RowSpacing': '700', 'Population': '4'}Tip
Depending on your environment, you may need to close the GUI window to continue or follow the prompts shown after termination.
- replace_met_file(self, *, weather_file: 'Union[Path, str]', simulations=<UserOptionMissing>, exclude: 'set | str | tuple | list' = None, **kwargs) (inherited)
Deprecated since version 0.**x**: This helper will be removed in a future release. Prefer newer weather configuration utilities or set the
FileNameproperty on weather nodes directly.Replace the
FileNameof everyModels.Climate.Weathernode under one or more simulations so they point to a new.metfile.This method traverses the APSIM NG model tree under each selected simulation and updates the weather component(s) in-place. Version-aware traversal is used:
If
APSIM_VERSION_NO > BASE_RELEASE_NOorAPSIM_VERSION_NO == GITHUB_RELEASE_NO: useModelTools.find_all_in_scope()to findModels.Climate.Weathernodes.Otherwise: fall back to
sim.FindAllDescendants[Models.Climate.Weather]().
Parameters
- weather_fileUnion[pathlib.Path, str]
Path to the
.metfile. May be absolute or relative to the current working directory. The path must exist at call time; otherwise aFileNotFoundErroris raised.- simulationsAny, optional
Simulation selector forwarded to
find_simulations(). If left asMissingOption(default) (or if your implementation acceptsNone), all simulations yielded byfind_simulations()are updated. Acceptable types depend on yourfind_simulations()contract (e.g., iterable of names, single name, or sentinel).- exclude: (str, tuple, list), optional
used to eliminate a given simulation from getting updated Added in 0.39.10.20+
- **kwargs
Ignored. Reserved for backward compatibility and future extensions.
Returns
- Self
The current model/manager instance to support method chaining.
Raises
- FileNotFoundError
If
weather_filedoes not exist.- Exception
Any exception raised by
find_simulations()or underlying APSIM traversal utilities is propagated unchanged.
Side Effects
Mutates the model by setting
met.FileName = os.path.realpath(weather_file)for each matchedModels.Climate.Weathernode.Notes
No-op safety: If a simulation has no Weather nodes, that simulation is silently skipped.
Path normalization: The stored path is the canonical real path (
os.path.realpath).Thread/process safety: This operation mutates in-memory model state and is not inherently thread-safe. Coordinate external synchronization if calling concurrently.
Examples
Update all simulations to use a local
Ames.met:model.replace_met_file(weather_file="data/weather/Ames.met")
Update only selected simulations:
model.replace_met_file( weather_file=Path("~/wx/Boone.met").expanduser(), simulations=("Sim_A", "Sim_B") )
See Also
find_simulations : Resolve and yield simulation objects by name/selector. ModelTools.find_all_in_scope : Scope-aware traversal utility. Models.Climate.Weather : APSIM NG weather component.
- get_weather_from_file(self, weather_file, simulations=None)
Point targeted APSIM Weather nodes to a local
.metfile.The function name mirrors the semantics of
get_weather_from_webbut sources the weather from disk. If the provided path lacks the.metsuffix, it is appended. The file must exist on disk.Parameters
- weather_file: str | Path
Path (absolute or relative) to a
.metfile. If the suffix is missing,.metis appended. AFileNotFoundErroris raised if the final path does not exist. The path is resolved to an absolute path to avoid ambiguity.- simulations: None | str | Iterable[str], optional
Which simulations to update: -
None(default): update all Weather nodes found underSimulations. -stror iterable of names: only update Weather nodes within the namedsimulation(s). A
ValueErroris raised if a requested simulation has no Weather nodes.
Returns
Instance of the model for method chaining
Raises
- FileNotFoundError
If the resolved
.metfile does not exist.- ValueError
If any requested simulation exists but contains no Weather nodes.
Side Effects
Sets
w.FileNamefor each targetedModels.Climate.Weathernode to the resolved path ofweather_file. The file is not copied; only the path inside the APSIM document is changed.Notes
APSIM resolves relative paths relative to the
.apsimxfile. Using an absolute path (the default here) reduces surprises across working directories.Replacement folders that contain Weather nodes are also updated when
simulationsisNone(i.e., “update everything in scope”).
Examples
Update all Weather nodes:
from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel model = ApsimModel("Maize") model.get_weather_from_file("data/ames_2020.met")
Update only two simulations (suffix added automatically):
model.get_weather_from_file("data/ames_2020", simulations=("Simulation",))
See also
Related APIs:
edit_model()andedit_model_by_path().- get_weather_from_web(self, lonlat: 'tuple', start: 'int', end: 'int', simulations=<UserOptionMissing>, source='nasa', filename=None) (inherited)
Replaces the weather (met) file in the model using weather data fetched from an online source. Internally, calls get_weather_from_file after downloading the weather
Parameters:
- lonlat: tuple
A tuple containing the longitude and latitude coordinates.
- start: int
Start date for the weather data retrieval.
- end: int
End date for the weather data retrieval.
- simulations: str | list[str] default is all or None list of simulations or a singular simulation
name, where to place the weather data, defaults to None, implying
allthe available simulations- source: str default is ‘nasa’
Source of the weather data.
- filename: str default is generated using the base name of the apsimx file in use, and the start and
end years Name of the file to save the retrieved data. If None, a default name is generated.
- Returns:
model object with the corresponding file replaced with the fetched weather data.
Examples
>>> from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel >>> model = ApsimModel(model= "Maize") >>> model.get_weather_from_web(lonlat = (-93.885490, 42.060650), start = 1990, end = 2001)
Changing weather data with non-matching start and end dates in the simulation will lead to RuntimeErrors. To avoid this, first check the start and end date before proceeding as follows:
>>> dt = model.inspect_model_parameters(model_class='Clock', model_name='Clock', simulations='Simulation') >>> start, end = dt['Start'].year, dt['End'].year # output: 1990, 2000
- change_report(self, *, command: 'str', report_name='Report', simulations=None, set_DayAfterLastOutput=None, **kwargs) (inherited)
Set APSIM report _variables for specified simulations.
This function allows you to set the variable names for an APSIM report in one or more simulations.
Parameters
- command: str
The new report string that contains variable names.
- report_name: str
The name of the APSIM report to update defaults to Report.
- simulations: list of str, optional
A list of simulation names to update. If
None, the function will update the report for all simulations.
Returns
None
- extract_soil_physical(self, simulations: '[tuple, list]' = None) (inherited)
Find physical soil
Parameters
simulation, optionalSimulation name, if
Noneuse the first simulation.
Returns
APSIM Models.Soils.Physical object
- extract_any_soil_physical(self, parameter, simulations: '[list, tuple]' = <UserOptionMissing>) (inherited)
Extracts soil physical parameters in the simulation
- Args::
parameter(_string_): string e.g. DUL, SATsimulations(string, optional): Targeted simulation name. Defaults to None.
- inspect_model(self, model_type: 'Union[str, Models]', fullpath=True, **kwargs) (inherited)
Inspect the model types and returns the model paths or names.
When is it needed?
useful if you want to identify the paths or name of the model for further editing the model e.g., with the
in edit_modelmethod.Parameters
- model_classtype | str
The APSIM model type to search for. You may pass either a class (e.g., Models.Clock, Models.Manager) or a string. Strings can be short names (e.g., “Clock”, “Manager”) or fully qualified (e.g., “Models.Core.Simulation”, “Models.Climate.Weather”, “Models.Core.IPlant”). Please see from The list of classes or model types from the Models Namespace below. Red represents the modules, and this method
will throw an error if only a module is supplied. The list constitutes the classes or model types under each module
- Models:
Models.Clock
Models.Fertiliser
Models.Irrigation
Models.Manager
Models.Memo
Models.MicroClimate
Models.Operations
Models.Report
Models.Summary
- Models.Climate:
Models.Climate.Weather
- Models.Core:
Models.Core.Folder
Models.Core.Simulation
Models.Core.Simulations
Models.Core.Zone
- Models.Factorial:
Models.Factorial.Experiment
Models.Factorial.Factors
Models.Factorial.Permutation
- Models.PMF:
Models.PMF.Cultivar
Models.PMF.Plant
- Models.Soils:
Models.Soils.Arbitrator.SoilArbitrator
Models.Soils.CERESSoilTemperature
Models.Soils.Chemical
Models.Soils.Nutrients.Nutrient
Models.Soils.Organic
Models.Soils.Physical
Models.Soils.Sample
Models.Soils.Soil
Models.Soils.SoilCrop
Models.Soils.Solute
Models.Soils.Water
- Models.Storage:
Models.Storage.DataStore
- Models.Surface:
Models.Surface.SurfaceOrganicMatter
- Models.WaterModel:
Models.WaterModel.WaterBalance
- fullpathbool, optional (default: False)
If False, return the model name only. If True, return the model’s full path relative to the Simulations root.
Returns
- list[str]
A list of model names or full paths, depending on
fullpath.
Examples:
from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel from apsimNGpy.core.core import Models
load default
maizemodule:model = ApsimModel('Maize')
Find the path to all the manager scripts in the simulation:
model.inspect_model(Models.Manager, fullpath=True) [.Simulations.Simulation.Field.Sow using a variable rule', '.Simulations.Simulation.Field.Fertilise at sowing', '.Simulations.Simulation.Field.Harvest']
Inspect the full path of the Clock Model:
model.inspect_model(Models.Clock) # gets the path to the Clock models ['.Simulations.Simulation.Clock']
Inspect the full path to the crop plants in the simulation:
model.inspect_model(Models.Core.IPlant) # gets the path to the crop model ['.Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize']
Or use the full string path as follows:
model.inspect_model(Models.Core.IPlant, fullpath=False) # gets you the name of the crop Models ['Maize']
Get the full path to the fertilizer model:
model.inspect_model(Models.Fertiliser, fullpath=True) ['.Simulations.Simulation.Field.Fertiliser']
The models from APSIM Models namespace are abstracted to use strings. All you need is to specify the name or the full path to the model enclosed in a stirng as follows:
model.inspect_model('Clock') # get the path to the clock model ['.Simulations.Simulation.Clock']
Alternatively, you can do the following:
model.inspect_model('Models.Clock') ['.Simulations.Simulation.Clock']
Repeat inspection of the plant model while using a
string:model.inspect_model('IPlant') ['.Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize']
Inspect using the full model namespace path:
model.inspect_model('Models.Core.IPlant')
What about the weather model?:
model.inspect_model('Weather') # inspects the weather module ['.Simulations.Simulation.Weather']
Alternative:
# or inspect using full model namespace path model.inspect_model('Models.Climate.Weather') ['.Simulations.Simulation.Weather']
Try finding the path to the cultivar model:
model.inspect_model('Cultivar', fullpath=False) # list all available cultivar names ['Hycorn_53', 'Pioneer_33M54', 'Pioneer_38H20','Pioneer_34K77', 'Pioneer_39V43','Atrium', 'Laila', 'GH_5019WX']
# we can get only the names of the cultivar models using the full string path:
model.inspect_model('Models.PMF.Cultivar', fullpath = False) ['Hycorn_53','Pioneer_33M54', 'Pioneer_38H20','Pioneer_34K77', 'Pioneer_39V43','Atrium', 'Laila', 'GH_5019WX']
Tip
- Models can be inspected either by importing the Models namespace or by using string paths. The most reliable
approach is to provide the full model path—either as a string or as the
Modelsobject.- However, remembering full paths can be tedious, so allowing partial model names or references can significantly
save time during development and exploration.
Note
You do not need to import
Modelsif you pass a string; both short and fully qualified names are supported.“Full path” is the APSIM tree path relative to the Simulations node (be mindful of the difference between Simulations (root) and an individual Simulation).
See also
Related APIs:
inspect_file(),inspect_model_parameters(),inspect_model_parameters_by_path()- property configs(inherited)
records activities or modifications to the model including changes to the file
- replace_soils_values_by_path(self, node_path: 'str', indices: 'list' = None, **kwargs) (inherited)
set the new values of the specified soil object by path. only layers parameters are supported.
Unfortunately, it handles one soil child at a time e.g.,
Physicalat a goParameters:
- node_path: (str, required):
complete path to the soil child of the Simulations e.g.,Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Organic. Use`copy path to node function in the GUI to get the real path of the soil node.
- indices: (list, optional)
defaults to none but could be the position of the replacement values for arrays
- **kwargs: (key word arguments)
This carries the parameter and the values e.g., BD = 1.23 or BD = [1.23, 1.75] if the child is
Physical, orCarbonif the child isOrganicraises: `ValueError if none of the key word arguments, representing the paramters are specified
- returns:
Instance of the model object
Example:
from apsimNGpy.core.base_data import load_default_simulations model = load_default_simulations(crop ='Maize', simulations_object=False) # initiate model. model = CoreModel(model) # ``replace`` with your intended file path model.replace_soils_values_by_path(node_path='.Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Organic', indices=[0], Carbon =1.3) sv= model.get_soil_values_by_path('.Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Organic', 'Carbon') output # {'Carbon': [1.3, 0.96, 0.6, 0.3, 0.18, 0.12, 0.12]}
- replace_soil_property_values(self, *, parameter: 'str', param_values: 'list', soil_child: 'str', simulations: 'list' = <UserOptionMissing>, indices: 'list' = None, crop=None, **kwargs) (inherited)
Replaces values in any soil property array. The soil property array.
parameter: str: parameter name e.g., NO3, ‘BD’param_values: list or tuple: values of the specified soil property name to replacesoil_child: str: sub child of the soil component e.g., organic, physical etc.simulations: list: list of simulations to where the child is found ifnot found, all current simulations will receive the new values, thus defaults to None
indices: list. Positions in the array which will be replaced. Please note that unlike C#, python satrt counting from 0crop(str, optional): string for soil water replacement. Default is None- clean_up(self, db=True, verbose=False, csv=True) (inherited)
Clears the file cloned the datastore and associated csv files are not deleted if db is set to False defaults to True.
- Returns:
>>None: This method does not return a value.
Caution
Please proceed with caution, we assume that if you want to clear the model objects, then you don’t need them, but by making copy compulsory, then, we are clearing the edited files
- create_experiment(self, permutation: 'bool' = True, base_name: 'str' = None, **kwargs) (inherited)
@deprecated and will be removed in future versions for this class.
Initialize an
ExperimentManagerinstance, adding the necessary models and factors.Args:
kwargs: Additional parameters for CoreModel.permutation(bool). If True, the experiment uses a permutation node to run unique combinations of the specified factors for the simulation. For example, if planting population and nitrogen fertilizers are provided, each combination of planting population level and fertilizer amount is run as an individual treatment.base_name(str, optional): The name of the base simulation to be moved into the experiment setup. if notprovided, it is expected to be Simulation as the default.
Warning
base_nameis optional but the experiment may not be created if there are more than one base simulations. Therefore, an error is likely.- refresh_model(self) (inherited)
for methods that will alter the simulation objects and need refreshing the second time we call @return: self for method chaining
- add_factor(self, specification: 'str', factor_name: 'str' = None, **kwargs) (inherited)
Adds a factor to the created experiment. Thus, this method only works on factorial experiments
It could raise a value error if the experiment is not yet created.
Under some circumstances, experiment will be created automatically as a permutation experiment.
Parameters:
- specification``: (str), required*
- A specification can be:
multiple values or categories e.g., “[Sow using a variable rule].Script.Population =4, 66, 9, 10”
Range of values e.g, “[Fertilise at sowing].Script.Amount = 0 to 200 step 20”,
- factor_name: (str), required
expected to be the user-desired name of the factor being specified e.g., population
This method is overwritten in
ExperimentManagerclass.@deprecated and will be removed in future versions for this class.
Example:
from apsimNGpy.core import base_data apsim = base_data.load_default_simulations(crop='Maize') apsim.create_experiment(permutation=False) apsim.add_factor(specification="[Fertilise at sowing].Script.Amount = 0 to 200 step 20", factor_name='Nitrogen') apsim.add_factor(specification="[Sow using a variable rule].Script.Population =4 to 8 step 2", factor_name='Population') apsim.run() # doctest: +SKIP
- add_fac(self, model_type, parameter, model_name, values, factor_name=None) (inherited)
Add a factor to the initiated experiment. This should replace add_factor. which has less abstractionn @param model_type: model_class from APSIM Models namespace @param parameter: name of the parameter to fill e.g CNR @param model_name: name of the model @param values: values of the parameter, could be an iterable for case of categorical variables or a string e.g, ‘0 to 100 step 10 same as [0, 10, 20, 30, …]. @param factor_name: name to identify the factor in question @return:
- set_continuous_factor(self, factor_path, lower_bound, upper_bound, interval, factor_name=None) (inherited)
Wraps around
add_factorto add a continuous factor, just for clarity- Args:
factor_path: (str): The path of the factor definition relative to its child node,e.g.,
"[Fertilise at sowing].Script.Amount".
factor_name: (str): The name of the factor.lower_bound: (int or float): The lower bound of the factor.upper_bound: (int or float): The upper bound of the factor.interval: (int or float): The distance between the factor levels.Returns:ApsimModelorCoreModel: An instance ofapsimNGpy.core.core.apsim.ApsimModelorCoreModel.
Example:
from apsimNGpy.core import base_data apsim = base_data.load_default_simulations(crop='Maize') apsim.create_experiment(permutation=False) apsim.set_continuous_factor(factor_path = "[Fertilise at sowing].Script.Amount", lower_bound=100, upper_bound=300, interval=10)
- set_categorical_factor(self, factor_path: 'str', categories: 'Union[list, tuple]', factor_name: 'str' = None) (inherited)
wraps around
add_factor()to add a continuous factor, just for clarity.factor_path: (str, required): path of the factor definition relative to its child node “[Fertilise at sowing].Script.Amount”factor_name: (str) name of the factor.categories: (tuple, list, required): multiple values of a factorreturns:ApsimModelorCoreModel: An instance ofapsimNGpy.core.core.apsim.ApsimModelorCoreModel.
Example:
from apsimNGpy.core import base_data apsim = base_data.load_default_simulations(crop='Maize') apsim.create_experiment(permutation=False) apsim.set_continuous_factor(factor_path = "[Fertilise at sowing].Script.Amount", lower_bound=100, upper_bound=300, interval=10)
- add_crop_replacements(self, _crop: 'str') (inherited)
Adds a replacement folder as a child of the simulations.
Useful when you intend to edit cultivar parameters.
- Args:
_crop(str): Name of the crop to be added to the replacement folder.Returns:ApsimModel: An instance of
apsimNGpy.core.core.apsim.ApsimModelorCoreModel.
Raises:ValueError: If the specified crop is not found.
- get_model_paths(self, cultivar=False)
Select out a few model types to use for building the APSIM file inspections
- inspect_file(self, *, cultivar=False, console=True, **kwargs) (inherited)
Inspects the file by traversing the entire simulation tree, using
inspect_model()under the hoodThis method is important in inspecting the
whole fileand also getting thescripts paths.Parameters
- cultivar: (bool)
To include cultivar paths.
- console: (bool)
Prints to the console if True
Examples
from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel model = ApsimModel('Maize') model.inspect_file(cultivar=False)
# output
└── Models.Core.Simulations: .Simulations ├── Models.Storage.DataStore: .Simulations.DataStore ├── Models.Core.Folder: .Simulations.Replacements │ └── Models.PMF.Plant: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize └── Models.Core.Simulation: .Simulations.Simulation ├── Models.Clock: .Simulations.Simulation.Clock ├── Models.Core.Zone: .Simulations.Simulation.Field │ ├── Models.Manager: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Fertilise at sowing │ ├── Models.Fertiliser: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Fertiliser │ ├── Models.Manager: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Harvest │ ├── Models.PMF.Plant: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize │ ├── Models.Report: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Report │ ├── Models.Soils.Soil: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Chemical: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Chemical │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Solute: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.NH4 │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Solute: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.NO3 │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Organic: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Organic │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Physical: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Physical │ │ │ └── Models.Soils.SoilCrop: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Physical.MaizeSoil │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Solute: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Urea │ │ └── Models.Soils.Water: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Water │ ├── Models.Manager: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Sow using a variable rule │ └── Models.Surface.SurfaceOrganicMatter: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.SurfaceOrganicMatter ├── Models.Graph: .Simulations.Simulation.Graph │ └── Models.Series: .Simulations.Simulation.Graph.Series ├── Models.MicroClimate: .Simulations.Simulation.MicroClimate ├── Models.Soils.Arbitrator.SoilArbitrator: .Simulations.Simulation.SoilArbitrator ├── Models.Summary: .Simulations.Simulation.Summary └── Models.Climate.Weather: .Simulations.Simulation.WeatherTurn cultivar paths on as follows:
model.inspect_file(cultivar=True)
# output
└── Models.Core.Simulations: .Simulations ├── Models.Storage.DataStore: .Simulations.DataStore ├── Models.Core.Folder: .Simulations.Replacements │ └── Models.PMF.Plant: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize │ └── Models.Core.Folder: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Atrium │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.CG4141 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Dekalb_XL82 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.GH_5009 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.GH_5019WX │ ├── Models.Core.Folder: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_100 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_103 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_105 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_108 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_110 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_112 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_115 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_120 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_130 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_80 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_90 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_95 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_100 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_103 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_105 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_108 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_110 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_112 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_115 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_120 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_130 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_80 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_90 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_95 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.HY_110 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.LY_110 │ │ └── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.P1197 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Hycorn_40 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Hycorn_53 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Katumani │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Laila │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Makueni │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Melkassa │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.NSCM_41 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_3153 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_33M54 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_34K77 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_38H20 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_39G12 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_39V43 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.malawi_local │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh12 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh16 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh17 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh18 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh19 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.r201 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.r215 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc401 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc501 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc601 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc623 │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc625 │ └── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Replacements.Maize.CultivarFolder.sr52 └── Models.Core.Simulation: .Simulations.Simulation ├── Models.Clock: .Simulations.Simulation.Clock ├── Models.Core.Zone: .Simulations.Simulation.Field │ ├── Models.Manager: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Fertilise at sowing │ ├── Models.Fertiliser: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Fertiliser │ ├── Models.Manager: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Harvest │ ├── Models.PMF.Plant: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize │ │ └── Models.Core.Folder: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Atrium │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.CG4141 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Dekalb_XL82 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.GH_5009 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.GH_5019WX │ │ ├── Models.Core.Folder: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_100 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_103 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_105 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_108 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_110 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_112 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_115 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_120 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_130 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_80 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_90 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.A_95 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_100 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_103 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_105 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_108 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_110 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_112 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_115 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_120 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_130 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_80 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_90 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.B_95 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.HY_110 │ │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.LY_110 │ │ │ └── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Generic.P1197 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Hycorn_40 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Hycorn_53 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Katumani │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Laila │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Makueni │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Melkassa │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.NSCM_41 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_3153 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_33M54 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_34K77 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_38H20 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_39G12 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Pioneer_39V43 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.malawi_local │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh12 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh16 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh17 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh18 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.mh19 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.r201 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.r215 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc401 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc501 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc601 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc623 │ │ ├── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.sc625 │ │ └── Models.PMF.Cultivar: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.sr52 │ ├── Models.Report: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Report │ ├── Models.Soils.Soil: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Chemical: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Chemical │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Solute: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.NH4 │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Solute: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.NO3 │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Organic: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Organic │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Physical: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Physical │ │ │ └── Models.Soils.SoilCrop: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Physical.MaizeSoil │ │ ├── Models.Soils.Solute: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Urea │ │ └── Models.Soils.Water: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Water │ ├── Models.Manager: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.Sow using a variable rule │ └── Models.Surface.SurfaceOrganicMatter: .Simulations.Simulation.Field.SurfaceOrganicMatter ├── Models.Graph: .Simulations.Simulation.Graph │ └── Models.Series: .Simulations.Simulation.Graph.Series ├── Models.MicroClimate: .Simulations.Simulation.MicroClimate ├── Models.Soils.Arbitrator.SoilArbitrator: .Simulations.Simulation.SoilArbitrator ├── Models.Summary: .Simulations.Simulation.Summary └── Models.Climate.Weather: .Simulations.Simulation.WeatherSee also
Related APIs:
inspect_model(),inspect_model_parameters()
- summarize_numeric(self, data_table: 'Union[str, tuple, list]' = None, columns: 'list' = None, percentiles=(0.25, 0.5, 0.75), round=2)
Summarize numeric columns in a simulated pandas DataFrame. Useful when you want to quickly look at the simulated data
Parameters:
data_table (list, tuple, str): The names of the data table attached to the simulations. defaults to all data tables.
specific (list) columns to summarize.
percentiles (tuple): Optional percentiles to include in the summary.
round (int): number of decimal places for rounding off.
Returns:
pd.DataFrame: A summary DataFrame with statistics for each numeric column.
- add_db_table(self, variable_spec: 'list' = None, set_event_names: 'list' = None, rename: 'str' = None, simulation_name: 'Union[str, list, tuple]' = <UserOptionMissing>) (inherited)
Adds a new database table, which
APSIMcallsReport(Models.Report) to theSimulationunder a Simulation Zone.This is different from
add_report_variablein that it creates a new, named report table that collects data based on a given list of _variables and events. actuParameters:
- variable_spec: (list or str)
A list of APSIM variable paths to include in the report table. If a string is passed, it will be converted to a list.
- set_event_names: (list or str, optional):
- A list of APSIM events that trigger the recording of _variables.
Defaults to [‘[Clock].EndOfYear’] if not provided. other examples include ‘[Clock].StartOfYear’, ‘[Clock].EndOfsimulation’, ‘[crop_name].Harvesting’ etc.
rename: (str): The name of the report table to be added. Defaults to ‘my_table’.
- simulation_name: (str,tuple, or list, Optional)
if specified, the name of the simulation will be searched and will become the parent candidate for the report table. If it is none, all Simulations in the file will be updated with the new db_table
Raises:
ValueError: If no variable_spec is provided.RuntimeError: If no Zone is found in the current simulation scope.Examples:
from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel model = ApsimModel('Maize') model.add_db_table(variable_spec=['[Clock].Today', '[Soil].Nutrient.TotalC[1]/1000 as SOC1'], rename='report2') model.add_db_table(variable_spec=['[Clock].Today', '[Soil].Nutrient.TotalC[1]/1000 as SOC1', '[Maize].Grain.Total.Wt*10 as Yield'], rename='report2', set_event_names=['[Maize].Harvesting','[Clock].EndOfYear' ])
See also
Related APIs:
remove_report_variables()andadd_report_variables().- plot_mva(self, table: pandas.core.frame.DataFrame, time_col: Hashable, response: Hashable, *, expression: str = None, window: int = 5, min_period: int = 1, grouping: Hashable | collections.abc.Sequence[Hashable] | NoneType = None, preserve_start: bool = True, kind: str = 'line', estimator='mean', plot_raw: bool = False, raw_alpha: float = 0.35, raw_linewidth: float = 1.0, auto_datetime: bool = False, ylabel: str | None = None, return_data: bool = False, **kwargs)
Plot a centered moving-average (MVA) of a response using
seaborn.relplot.Enhancements over a direct
relplotcall: - Computes and plots a smoothed series viaapsimNGpy.stats.data_insights.mva(). - Supports multi-column grouping; will auto-construct a composite hue if needed. - Optional overlay of the raw (unsmoothed) series for comparison. - Stable (mergesort) time ordering.Parameters
- tablepandas.DataFrame or str
Data source or table name; if
None, use :pyattr:`results`.- time_colhashable
Time (x-axis) column.
- responsehashable
Response (y) column to smooth.
- expression: str default is None
simple mathematical expression to create new columns from existing columns
- windowint, default=5
MVA window size.
- min_periodint, default=1
Minimum periods for the rolling mean.
- groupinghashable or sequence of hashable, optional
One or more grouping columns.
- preserve_startbool, default=True
Preserve initial values when centering.
- kind{“line”,”scatter”}, default=”line”
Passed to
sns.relplot.- estimatorstr or None, default=”mean”
Passed to
sns.relplot(set toNoneto plot raw observations).- plot_rawbool, default=False
Overlay the raw series on each facet.
- raw_alphafloat, default=0.35
Alpha for the raw overlay.
- raw_linewidthfloat, default=1.0
Line width for the raw overlay.
- auto_datetimebool, default=False
Attempt to convert
time_colto datetime.- ylabelstr, optional
Custom y-axis label; default is generated from window/response.
- return_databool, default=False
If
True, return(FacetGrid, smoothed_df).
Returns
- seaborn.FacetGrid
The relplot grid, or
(grid, smoothed_df)ifreturn_data=True.
Notes
This function calls
seaborn.relplot()and accepts its keyword arguments via**kwargs. See link below for details:https://seaborn.pydata.org/generated/seaborn/relplot.html
- boxplot(self, column, *, table=None, expression: str = None, by=None, figsize=(10, 8), grid=False, **kwargs) (inherited)
Plot a boxplot from simulation results using
pandas.DataFrame.boxplot.Parameters
- columnstr
Column to plot.
- tablestr or pandas.DataFrame, optional
Table name or DataFrame; if omitted, use :pyattr:`results`.
- bystr, optional
Grouping column.
figsize : tuple, default=(10, 8) grid : bool, default=False **kwargs
Forwarded to
pandas.DataFrame.boxplot().Returns
matplotlib.axes.Axes
See also
Related APIs:
cat_plot().- distribution(self, x, *, table=None, expression: str = None, **kwargs) (inherited)
Plot a uni-variate distribution/histogram using
seaborn.histplot().Parameters
- xstr
Numeric column to plot.
- tablestr or pandas.DataFrame, optional
Table name or DataFrame; if omitted, use :pyattr:`results`.
- expression: str default is None
simple mathematical expression to create new columns from existing columns
- **kwargs
Forwarded to
seaborn.histplot().
Raises
- ValueError
If
xis a string-typed column.
Notes
This function calls
seaborn.histplot()and accepts its keyword arguments via**kwargs. See link below for details:https://seaborn.pydata.org/generated/seaborn/histplot.html
- series_plot(self, table=None, expression: str = None, *, x: str = None, y: Union[str, list] = None, hue=None, size=None, style=None, units=None, weights=None, palette=None, hue_order=None, hue_norm=None, sizes=None, size_order=None, size_norm=None, dashes=True, markers=None, style_order=None, estimator='mean', errorbar=('ci', 95), n_boot=1000, seed=None, orient='x', sort=True, err_style='band', err_kws=None, legend='auto', ci='deprecated', ax=None, **kwargs) (inherited)
Just a wrapper for seaborn.lineplot that supports multiple y columns that could be provided as a list
- tablestr | [str] |None | None| pandas.DataFrame, optional. Default is None
If the table names are provided, results are collected from the simulated data, using that table names. If None, results will be all the table names inside concatenated along the axis 0 (not recommended).
- expression: str default is None
simple mathematical expression to create new columns from existing columns
If
yis a list of columns, the data are melted into long form and
the different series are colored by variable name.
- **Kwargs
Additional keyword args and all other arguments are for Seaborn.lineplot. See the reference below for all the kwargs.
reference; https://seaborn.pydata.org/generated/seaborn.lineplot.html
Examples
>>> model.series_plot(x='Year', y='Yield', table='Report') >>> model.series_plot(x='Year', y=['SOC1', 'SOC2'], table='Report')
Examples:
>>> from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel >>> model = ApsimModel(model= 'Maize') # run the results >>> model.run(report_names='Report') >>>model.series_plot(x='Maize.Grain.Size', y='Yield', table='Report') >>>model.render_plot(show=True, ylabel = 'Maize yield', xlabel ='Maize grain size')
Plot two variables:
>>>model.series_plot(x=’Yield’, y=[‘Maize.Grain.N’, ‘Maize.Grain.Size’], table= ‘Report’)
Notes
This function calls
seaborn.lineplot()and accepts its keyword arguments via**kwargs. See link below for detailed explanations:https://seaborn.pydata.org/generated/seaborn/lineplot.html
See also
Related APIs:
plot_mva().- scatter_plot(self, table=None, expression: str = None, *, x=None, y=None, hue=None, size=None, style=None, palette=None, hue_order=None, hue_norm=None, sizes=None, size_order=None, size_norm=None, markers=True, style_order=None, legend='auto', ax=None, **kwargs) (inherited)
Scatter plot using
seaborn.scatterplot()with flexible aesthetic mappings.Parameters
- tablestr | [str] |None | None| pandas.DataFrame, optional. Default is None
If the table names are provided, results are collected from the simulated data, using that table names. If None, results will be all the table names inside concatenated along the axis 0 (not recommended).
- x, y, hue, size, style, palette, hue_order, hue_norm, sizes, size_order, size_norm, markers, style_order, legend, ax
Passed through to
seaborn.scatterplot().- expression: str default is None
simple mathematical expression to create new columns from existing columns
- ** Kwargs
Additional keyword args for Seaborn.
See the reference below for all the kwargs. reference; https://seaborn.pydata.org/generated/seaborn.scatterplot.html
- cat_plot(self, table=None, expression=None, *, x=None, y=None, hue=None, row=None, col=None, kind='strip', estimator='mean', errorbar=('ci', 95), n_boot=1000, seed=None, units=None, weights=None, order=None, hue_order=None, row_order=None, col_order=None, col_wrap=None, height=5, aspect=1, log_scale=None, native_scale=False, formatter=None, orient=None, color=None, palette=None, hue_norm=None, legend='auto', legend_out=True, sharex=True, sharey=True, margin_titles=False, facet_kws=None, **kwargs) (inherited)
Categorical plot wrapper over
seaborn.catplot().
Parameters
table : str or pandas.DataFrame, optional
- expression: str default is None
simple mathematical expression to create new columns from existing columns
x, y, hue, row, col, kind, estimator, errorbar, n_boot, seed, units, weights, order, hue_order, row_order, col_order, col_wrap, height, aspect, log_scale, native_scale, formatter, orient, color, palette, hue_norm, legend, legend_out, sharex, sharey, margin_titles, facet_kws
Passed through to
seaborn.catplot().- **kwargs
Additional keyword args for Seaborn.
Returns
seaborn.axisgrid.FacetGrid
reference https://seaborn.pydata.org/generated/seaborn.catplot.html
Related APIs:
distribution().- reg_plot(self, table=None, expression=None, **kwargs) (inherited)
Wrapper around seaborn.lmplot. V 0.39.10.19+
Kwargs passed to seaborn.lmplot
- xstr or None, optional
Name of column in
datato plot on the x-axis.- ystr or None, optional
Name of column in
datato plot on the y-axis.- huestr or None, optional
Grouping variable that will produce elements with different colors.
- colstr or None, optional
Variable that defines columns of the facet grid.
- rowstr or None, optional
Variable that defines rows of the facet grid.
- palettestr, list, dict, or None, optional
Color palette for different
huelevels.- col_wrapint or None, optional
Wrap the column facets after this many columns.
- heightfloat, default=5
Height (in inches) of each facet.
- aspectfloat, default=1
Aspect ratio of each facet, so width = aspect * height.
- markersstr or list, default=’o’
Marker(s) used for the scatter plot points.
- sharexbool or None, optional
If True, share x-axis limits across facets.
- shareybool or None, optional
If True, share y-axis limits across facets.
- hue_orderlist or None, optional
Order to plot the levels of
hue.- col_orderlist or None, optional
Order to plot the levels of
col.- row_orderlist or None, optional
Order to plot the levels of
row.- legendbool, default=True
If True, add a legend for the
huevariable.- legend_outbool or None, optional
If True, place the legend outside the grid.
- x_estimatorcallable or None, optional
Function to compute a central tendency of
yfor each uniquex(e.g.np.mean). Plot points at that value instead of raw data.- x_binsint or None, optional
Bin the
xvariable into discrete bins before plotting.- x_ci‘ci’, ‘sd’, float, or None, default=’ci’
Size/definition of the confidence band around the estimator in
x_estimator.- scatterbool, default=True
If True, draw the scatter points.
- fit_regbool, default=True
If True, fit and plot a regression line.
- ciint or None, default=95
Size of the bootstrap confidence interval for the regression estimate.
- n_bootint, default=1000
Number of bootstrap samples to compute
ci.- unitsstr or None, optional
Column in
dataidentifying sampling units. Used for clustered bootstrap.- seedint, RandomState, or None, optional
Random seed for reproducible bootstrapping.
- orderint, default=1
Polynomial order of the regression (1 = linear).
- logisticbool, default=False
If True, fit a logistic regression.
- lowessbool, default=False
If True, fit a locally weighted regression (LOWESS).
- robustbool, default=False
If True, use a robust regression estimator.
- logxbool, default=False
If True, estimate the model in log10(x) space.
- x_partialstr, list of str, or None, optional
Columns in
datato regress out ofxbefore plotting.- y_partialstr, list of str, or None, optional
Columns in
datato regress out ofybefore plotting.- truncatebool, default=True
If True, limit the regression line to the data range.
- x_jitterfloat or None, optional
Amount of horizontal jitter to add to scatter points.
- y_jitterfloat or None, optional
Amount of vertical jitter to add to scatter points.
- scatter_kwsdict or None, optional
Additional keyword args passed to the scatter plot (e.g. alpha, s).
- line_kwsdict or None, optional
Additional keyword args passed to the regression line plot.
- facet_kwsdict or None, optional
Additional keyword args passed to seaborn.FacetGrid.
See Also
- seaborn.lmplotHigh-level interface for plotting linear models with faceting.
Tutorial: https://seaborn.pydata.org/tutorial/regression.html#regression-tutorial
- relplot(self, table=None, **kwargs) (inherited)
Plots a relation plot
apsimNGpy.core_utils.database_utils
Interface to APSIM simulation models using Python.NET
Module attributes
- apsimNGpy.core_utils.database_utils.T
Default value:
~T
Functions
- apsimNGpy.core_utils.database_utils.chunker(data: 'Iterable[T]', *, chunk_size: 'Optional[int]' = None, n_chunks: 'Optional[int]' = None, pad: 'bool' = False, fillvalue: 'Optional[T]' = None) 'Iterator[List[T]]'
Yield chunks from
data.- Choose exactly one of:
chunk_size: yield consecutive chunks of lengthchunk_size(last chunk may be shorter unlesspad=True)n_chunks: split data inton_chunksnearly equal parts (sizes differ by at most 1)
Args
- dataIterable[T]
The input data (list, generator, etc.)
- chunk_sizeint, optional
Fixed size for each chunk (>=1).
- n_chunksint, optional
Number of chunks to create (>=1). Uses nearly equal sizes.
- padbool, default False
If True and using
chunk_size, pad the last chunk to lengthchunk_size.- fill valueT, optional
Value to use when padding.
Yields
- List[T]
Chunks of the input data.
Raises
- ValueError
If neither or both of
chunk_sizeandn_chunksare provided, or if provided values are invalid.
- apsimNGpy.core_utils.database_utils.clear_all_tables(db)
Deletes all rows from all user-defined tables in the given SQLite database.
Parameters
- dbstr | Path
Path to the SQLite database file.
Returns
- None
This function does not return a value.
See also
Related API:
clear_table()
- apsimNGpy.core_utils.database_utils.clear_table(db: 'Union[str, Path]', table_name: 'str')
Deletes all rows from all user-defined tables in the given SQLite database.
Parameters
- dbstr | Path
Path to the SQLite database file.
- table_namestr
Name of the target table to delete from the database
db
Returns
- None
This function does not return a value.
See also
Related API:
clear_all_tables()
- apsimNGpy.core_utils.database_utils.dataview_to_dataframe(_model, reports)
Convert .NET System.Data.DataView to Pandas DataFrame. report (str, list, tuple) of the report to be displayed. these should be in the simulations :param apsimng model: CoreModel object or instance :return: Pandas DataFrame
- apsimNGpy.core_utils.database_utils.delete_all_tables(db: 'str') 'None'
Deletes all tables in the specified SQLite database.
⚠️ Proceed with caution: this operation is irreversible.
- Args:
db (str): Path to the SQLite database file.
- apsimNGpy.core_utils.database_utils.delete_table(db, table_name)
deletes the table in a database.
⚠️ Proceed with caution: this operation is irreversible.
- apsimNGpy.core_utils.database_utils.get_db_table_names(db)
Parameter
db : database name or path.
- return: list of table names
All names
SQLdatabase tablenamesexisting within the database
- apsimNGpy.core_utils.database_utils.read_db_table(db: 'Union[str, Path]', report_name: 'str' = None, sql_query=None)
Connects to a specified SQLite database, retrieves the entire contents of a specified table, and returns the results as a pandas DataFrame.
Parameters
- dbstr | Path, database connection object
Path to the SQLite database file.
- report_namestr
Name of the table in the database from which to retrieve data.
- sql_query: str default is None
if it is none, we assume a table
Returns
- pandas.DataFrame
A DataFrame containing all records from the specified table.
Examples
>>> database_path = 'your_database.sqlite' # or connection object >>> table_name = 'your_table' >>> ddf = read_db_table(database_path, table_name) >>> print(ddf)
Notes
Establishes a connection to the SQLite database, executes
SELECT *on the specified table, loads the result into a DataFrame, and then closes the connection.Ensure that the database path and table name are correct.
This function retrieves all records; use with caution for very large tables.
- apsimNGpy.core_utils.database_utils.read_with_query(db, query)
Executes an SQL query on a specified SQLite database and returns the result as a pandas DataFrame.
Parameters
- dbstr
Database file path or identifier to connect to.
- querystr
SQL query string to execute. Must be a valid
SELECTstatement.
Returns
- pandas.DataFrame
A DataFrame containing the results of the SQL query.
Examples
Define the database and the query
database_path = 'your_database.sqlite' sql_query = 'SELECT * FROM your_table WHERE condition = values' # Get the query result as a DataFrame df = read_with_query(database_path, sql_query)
Notes
Opens a connection to the SQLite database, executes the given query, loads the results into a DataFrame, and then closes the connection.
Ensure that the database path and query are correct and that the query is a proper SQL
SELECTstatement.Uses
sqlite3for the connection; confirm it is appropriate for your database.
See also
Related API:
read_db_table()
- apsimNGpy.core_utils.database_utils.write_results_to_sql(db_path: 'Union[str, Path]', table: 'str' = 'Report', *, if_exists: "Literal['fail', 'replace', 'append']" = 'append', insert_fn: 'InsertFn | None' = None, ensure_parent: 'bool' = True) 'Callable'
Decorator factory: collect the wrapped function’s returned data and insert it or saves it into SQLite database.
After the wrapped function executes, its return value is normalized to a list of
(table, DataFrame)pairs via_normalize_resultand inserted intodb_pathusing either the providedinsert_fnor the default_default_insert_fn(which relies onpandas.DataFrame.to_sql+ SQLAlchemy). The original return value is passed through unchanged to the caller.Accepted return shapes
pd.DataFrame-> appended totable(table_name: str, df: pd.DataFrame)-> appended totable_namelist[pd.DataFrame]-> each appended totablelist[(table_name, df)]-> routed per pair{"data": <df|list[dict]|dict-of-cols>, "table": "MyTable"}-> to “MyTable”{"TblA": df_or_records, "TblB": df2}-> multiple tableslist[dict]ordict-of-columns-> coerced to DataFrame -> appended totableNone-> no-op
Parameters
- db_pathstr | pathlib.Path
Destination SQLite file. A
.dbsuffix is enforced if missing. Ifensure_parentis True, parent directories are created.- tablestr, default “Report”
Default table name when the return shape does not carry one.
- if_exists: {“fail”, “replace”, “append”}, default “append”
Passed to
to_sqlby the inserter. See panda docs for semantics.- insert_fncallable, optional
Custom inserter
(db_path, df, table, if_exists) -> None. Use this to: - reuse a single connection/transaction across multiple tables, - enable SQLite WAL mode and retry on lock, - control dtype mapping or target a different DBMS.- ensure_parentbool, default True
If True, create missing parent directories for
db_path.
Returns
- Callable
A decorator that, when applied to a function, performs the persistence step after the function returns and then yields the original result.
Raises
- TypeError
If the wrapped function’s result cannot be normalized by
_normalize_result.- RuntimeError
If any insert operation fails (original exception is chained as
__cause__).- OSError
On path or filesystem errors when creating the database directory/file.
Side Effects
Creates parent directories for
db_path(whenensure_parent=True).Creates/opens the SQLite database and writes one or more tables.
Skips empty frames: pairs where
dfisNoneordf.emptyare ignored.May DROP + CREATE the table when
if_exists="replace".
Cautions
**SQLite concurrency: ** Concurrent writers can trigger “database is locked”. Consider a custom
insert_fnenabling WAL mode, retries, and transactional batching for robustness.**Table name safety: ** Avoid propagating untrusted table names; identifier quoting is driver-dependent.
Schema drift:
to_sqlinfers SQL schema from the DataFrame’s dtypes each call. Ensure stable dtypes or manage schema explicitly in yourinsert_fn.**Timezones: ** Pandas may localize/naivify datetime on writing; verify round-trips if timezone fidelity matters.
**Performance: ** Creating a new engine/connection per insert is simple but not optimal. For high-volume pipelines, supply an
insert_fnthat reuses a connection and commits once per batch.
Design rationale
Separates computation from persistence. The decorator is explicit about where data goes (db path, table names) and flexible about what callers return, reducing boilerplate in the business logic while still allowing power users to override insertion strategy.
Examples
Basic usage, single table with default appends:
@collect_returned_results("outputs/results.db", table="Report") def run_analysis(...): return df # a DataFrame
Multiple tables using a mapping shape:
@collect_returned_results("outputs/results.db") def summarize(...): return {"Summary": df1, "Metrics": df2}
Custom inserter enabling WAL mode and a single transaction:
def wal_insert(db, df, table, if_exists): import sqlite3 con = sqlite3.connect(db, isolation_level="DEFERRED") try: con.execute("PRAGMA journal_mode=WAL;") df.to_sql(table, con, if_exists=if_exists, index=False) con.commit() finally: con.close()
Examples:
>>> from pandas import DataFrame >>> from apsimNGpy.core_utils.database_utils import write_results_to_sql, read_db_table >>> @write_results_to_sql(db_path="db.db", table="Report", if_exists="replace") ... def get_report(): ... # Return a DataFrame to be written to SQLite ... return DataFrame({"x": [2], "y": [4]})
>>> _ = get_report() # executes and writes to db.db::Report >>> db = read_db_table("db.db", report_name="Report") >>> print(db.to_string(index=False)) x y 2 4
See also
Related API:
save_tosql(),insert_data()
- apsimNGpy.core_utils.database_utils.write_schema_grouped_tables(schema_to_df: 'Dict[SchemaKey, pd.DataFrame]', engine: 'Engine', *, base_table_prefix: 'str' = 'group', schema_table_name: 'str' = '_schema', chunksize=None, dtype=None, if_exists='append', index=False, schema=None) 'None'
- For each (schema, DataFrame) pair:
create a dedicated SQL table and insert the DataFrame,
record its schema and table name in a separate schema table.
Parameters
- schema_to_dfdict
Mapping from schema signature to concatenated DataFrame. Schema signature format: ((column_name, dtype_str), …).
- enginesqlalchemy.engine.Engine or DB-API connection
Database connection/engine to write to.
- base_table_prefixstr, optional
Prefix for generated table names (e.g., ‘apsim_group_1’, ‘apsim_group_2’, …).
- schema_table_namestr, optional
Name of the schema metadata table.
apsimNGpy.exceptions
Classes
- class apsimNGpy.exceptions.ApsimBinPathConfigError
Raised when the APSIM bin path is misconfigured or incomplete.
- with_traceback() (inherited)
Exception.with_traceback(tb) – set self.__traceback__ to tb and return self.
- add_note() (inherited)
Exception.add_note(note) – add a note to the exception
- args(inherited)
Default:
<attribute 'args' of 'BaseException' objects>
- class apsimNGpy.exceptions.ApsimNGpyError
Base class for all apsimNGpy-related exceptions. These errors are more descriptive than just rising a value error
- with_traceback() (inherited)
Exception.with_traceback(tb) – set self.__traceback__ to tb and return self.
- add_note() (inherited)
Exception.add_note(note) – add a note to the exception
- args(inherited)
Default:
<attribute 'args' of 'BaseException' objects>
- class apsimNGpy.exceptions.ApsimNotFoundError
Raised when the APSIM executable or directory is not found.
- with_traceback() (inherited)
Exception.with_traceback(tb) – set self.__traceback__ to tb and return self.
- add_note() (inherited)
Exception.add_note(note) – add a note to the exception
- args(inherited)
Default:
<attribute 'args' of 'BaseException' objects>
- class apsimNGpy.exceptions.ApsimRuntimeError
occurs when an error occurs during running APSIM models with Models.exe or Models on Mac and linnux
- with_traceback() (inherited)
Exception.with_traceback(tb) – set self.__traceback__ to tb and return self.
- add_note() (inherited)
Exception.add_note(note) – add a note to the exception
- args(inherited)
Default:
<attribute 'args' of 'BaseException' objects>
- class apsimNGpy.exceptions.CastCompilationError
Raised when the C# cast helper DLL fails to compile.
- with_traceback() (inherited)
Exception.with_traceback(tb) – set self.__traceback__ to tb and return self.
- add_note() (inherited)
Exception.add_note(note) – add a note to the exception
- args(inherited)
Default:
<attribute 'args' of 'BaseException' objects>
- class apsimNGpy.exceptions.EmptyDateFrameError
Raised when a DataFrame is unexpectedly empty.
- with_traceback() (inherited)
Exception.with_traceback(tb) – set self.__traceback__ to tb and return self.
- add_note() (inherited)
Exception.add_note(note) – add a note to the exception
- args(inherited)
Default:
<attribute 'args' of 'BaseException' objects>
- class apsimNGpy.exceptions.ForgotToRunError
Raised when a required APSIM model run was skipped or forgotten.
- with_traceback() (inherited)
Exception.with_traceback(tb) – set self.__traceback__ to tb and return self.
- add_note() (inherited)
Exception.add_note(note) – add a note to the exception
- args(inherited)
Default:
<attribute 'args' of 'BaseException' objects>
- class apsimNGpy.exceptions.InvalidInputErrors
Raised when the input provided is invalid or improperly formatted.
- with_traceback() (inherited)
Exception.with_traceback(tb) – set self.__traceback__ to tb and return self.
- add_note() (inherited)
Exception.add_note(note) – add a note to the exception
- args(inherited)
Default:
<attribute 'args' of 'BaseException' objects>
- class apsimNGpy.exceptions.ModelNotFoundError
Raised when a specified model cannot be found.
- with_traceback() (inherited)
Exception.with_traceback(tb) – set self.__traceback__ to tb and return self.
- add_note() (inherited)
Exception.add_note(note) – add a note to the exception
- args(inherited)
Default:
<attribute 'args' of 'BaseException' objects>
- class apsimNGpy.exceptions.NodeNotFoundError
Raised when a specified model node cannot be found.
- with_traceback() (inherited)
Exception.with_traceback(tb) – set self.__traceback__ to tb and return self.
- add_note() (inherited)
Exception.add_note(note) – add a note to the exception
- args(inherited)
Default:
<attribute 'args' of 'BaseException' objects>
- class apsimNGpy.exceptions.TableNotFoundError
the table was not found error.
- with_traceback() (inherited)
Exception.with_traceback(tb) – set self.__traceback__ to tb and return self.
- add_note() (inherited)
Exception.add_note(note) – add a note to the exception
- args(inherited)
Default:
<attribute 'args' of 'BaseException' objects>
apsimNGpy.optimizer.minimize.single_mixed
Classes
- class apsimNGpy.optimizer.minimize.single_mixed.MixedVariableOptimizer
List of Public Attributes:
(none)
List of Public Methods
- __init__(self, problem)
@param problem:
- minimize_with_local(self, **kwargs)
Run a local optimization solver (e.g., Powell, L-BFGS-B, etc.) on given defined problem.
This method wraps
scipy.optimize.minimizeand handles mixed-variable encoding internally using theObjectivewrapper fromwrapdisc. It supports any method supported by SciPy’sminimizefunction and uses the encoded starting values and variable bounds. This decoding implies that you can optimize categorical variable such as start dates or cultivar paramter with xy numerical values.Progress is tracked using a progress bar, and results are automatically decoded and stored in
self.outcomes.- Parameters:
- **kwargs: Keyword arguments passed directly to
scipy.optimize.minimize. - Important keys include:
method (str): Optimization algorithm (e.g., ‘Powell’, ‘L-BFGS-B’).options (dict): Dictionary of solver options like maxiter, disp, etc.
- **kwargs: Keyword arguments passed directly to
scipy.optimize.minimize provide a number of optimization algorithms see table below or for details check their website: https://docs.scipy.org/doc/scipy/reference/generated/scipy.optimize.minimize.html#scipy.optimize.minimize
Method
Type
Gradient Required
Handles Bounds
Handles Constraints
Notes
Nelder-Mead
Local (Derivative-free)
No
No
No
Simplex algorithm
Powell
Local (Derivative-free)
No
Yes
No
Direction set method
CG
Local (Gradient-based)
Yes
No
No
Conjugate Gradient
BFGS
Local (Gradient-based)
Yes
No
No
Quasi-Newton
Newton-CG
Local (Gradient-based)
Yes
No
No
Newton’s method
L-BFGS-B
Local (Gradient-based)
Yes
Yes
No
Limited memory BFGS
TNC
Local (Gradient-based)
Yes
Yes
No
Truncated Newton
COBYLA
Local (Derivative-free)
No
No
Yes
Constrained optimization by linear approx.
SLSQP
Local (Gradient-based)
Yes
Yes
Yes
Sequential Least Squares Programming
trust-constr
Local (Gradient-based)
Yes
Yes
Yes
Trust-region constrained
dogleg
Local (Gradient-based)
Yes
No
No
Requires Hessian
trust-ncg
Local (Gradient-based)
Yes
No
No
Newton-CG trust region
trust-exact
Local (Gradient-based)
Yes
No
No
Trust-region, exact Hessian
trust-krylov
Local (Gradient-based)
Yes
No
No
Trust-region, Hessian-free
- Returns:
- result (OptimizeResult): The result of the optimization, with an additional
x_varsattribute that provides a labeled dict of optimized control variable values.
- Raises:
Any exceptions raised by
scipy.optimize.minimize.
The following example shows how to use this method, the evaluation is very basic, but you can add a more advanced evaluation by adding a loss function e.g RMSE os NSE by comparing with the observed and predicted, and changing the control variables:
- class Problem(MixedVarProblem):
- def __init__(self, model=None, simulation=’Simulation’):
super().__init__(model, simulation) self.simulation = simulation
- def evaluate(self, x, **kwargs):
# All evlauations can be defined inside here, by taking into accound the fact that the results object returns a data frame # Also, you can specify the database table or report name holding the
resultsreturn -self.run(verbose=False).results.Yield.mean() # A return is based on your objective definition, but as I said this could aRRMSEerror or any other loss function
# Ready to initialize the problem
problem.add_control( path='.Simulations.Simulation.Field.Fertilise at sowing', Amount="?", bounds=[50, 300], v_type="float", start_value =50 ) problem.add_control( path='.Simulations.Simulation.Field.Sow using a variable rule', Population="?", bounds=[4, 14], v_type="float", start_value=5 ) Attributes of the returned object
- xndarray
The solution of the optimization.
- successbool
Whether or not the optimizer exited successfully.
- statusint
Termination status of the optimizer. Its value depends on the underlying solver. Refer to
messagefor details.- messagestr
Description of the cause of the termination.
- fun, jac, hess: ndarray
Values of objective function, its Jacobian and its Hessian (if available). The Hessians may be approximations, see the documentation of the function in question.
- hess_invobject
Inverse of the objective function’s Hessian; may be an approximation. Not available for all solvers. The type of this attribute may be either np.ndarray or scipy.sparse.linalg.LinearOperator.
- nfev, njev, nhevint
Number of evaluations of the objective functions and of its Jacobian and Hessian.
- nitint
Number of iterations performed by the optimizer.
- maxcvfloat
The maximum constraint violation.
- data: DataFrame
This DataFrame represents the index columns, with the predicted and observed values
Depending on the specific solver being used,
OptimizeResultmay not have all attributes listed here, and they may have additional attributes not listed here. Since this class is essentially a subclass of dict with attribute accessors, one can see which attributes are available using theOptimizeResult.keysmethod.- minimize_with_de(self, use_threads=False, args=(), strategy='rand1bin', maxiter=1000, popsize=None, tol=0.01, mutation=(0.5, 1), recombination=0.9, rng=None, callback=None, disp=True, polish=True, init='latinhypercube', atol=0, updating='deffered', workers=1, constraints=(), x0=None, seed=1, *, integrality=None, vectorized=False)
Run differential evolution on the wrapped APSIM objective function. Finds the global minimum of a multivariate function.
The differential evolution method [1]_ is stochastic in nature. It does not use gradient methods to find the minimum, and can search large areas of candidate space, but often requires larger numbers of function evaluations than conventional gradient-based techniques.
The algorithm is due to Storn and Price [2]_.
Parameters
- funccallable
The objective function to be minimized. Must be in the form
f(x, *args), wherexis the argument in the form of a 1-D array andargsis a tuple of any additional fixed parameters needed to completely specify the function. The number of parameters, N, is equal tolen(x).- boundssequence or
Bounds Bounds for variables. There are two ways to specify the bounds:
Instance of
Boundsclass.(min, max)pairs for each element inx, defining the finite lower and upper bounds for the optimizing argument offunc.
The total number of bounds is used to determine the number of parameters, N. If there are parameters whose bounds are equal the total number of free parameters is
N - N_equal.- argstuple, optional
Any additional fixed parameters needed to completely specify the objective function.
- strategy{str, callable}, optional
The differential evolution strategy to use. Should be one of:
‘best1bin’
‘best1exp’
‘rand1bin’
‘rand1exp’
‘rand2bin’
‘rand2exp’
‘randtobest1bin’
‘randtobest1exp’
‘currenttobest1bin’
‘currenttobest1exp’
‘best2exp’
‘best2bin’
The default is ‘best1bin’. Strategies that may be implemented are outlined in ‘Notes’. Alternatively the differential evolution strategy can be customized by providing a callable that constructs a trial vector. The callable must have the form
strategy(candidate: int, population: np.ndarray, rng=None), wherecandidateis an integer specifying which entry of the population is being evolved,populationis an array of shape(S, N)containing all the population members (where S is the total population size), andrngis the random number generator being used within the solver.candidatewill be in the range[0, S).strategymust return a trial vector with shape(N,). The fitness of this trial vector is compared against the fitness ofpopulation[candidate].Changed in version 1.12.0: Customization of evolution strategy via a callable.
- maxiterint, optional
The maximum number of generations over which the entire population is evolved. The maximum number of function evaluations (with no polishing) is:
(maxiter + 1) * popsize * (N - N_equal)- popsizeint, optional
A multiplier for setting the total population size. The population has
popsize * (N - N_equal)individuals. This keyword is overridden if an initial population is supplied via theinitkeyword. When usinginit='sobol'the population size is calculated as the next power of 2 afterpopsize * (N - N_equal).- tolfloat, optional
Relative tolerance for convergence, the solving stops when
np.std(pop) <= atol + tol * np.abs(np.mean(population_energies)), where andatolandtolare the absolute and relative tolerance respectively.- mutationfloat or tuple(float, float), optional
The mutation constant. In the literature this is also known as differential weight, being denoted by F. If specified as a float it should be in the range [0, 2]. If specified as a tuple
(min, max)dithering is employed. Dithering randomly changes the mutation constant on a generation by generation basis. The mutation constant for that generation is taken fromU[min, max). Dithering can help speed convergence significantly. Increasing the mutation constant increases the search radius, but will slow down convergence.- recombinationfloat, optional
The recombination constant, should be in the range [0, 1]. In the literature this is also known as the crossover probability, being denoted by CR. Increasing this value allows a larger number of mutants to progress into the next generation, but at the risk of population stability.
- seed{None, int,
numpy.random.Generator,numpy.random.RandomState}, optional If
seedis None (ornp.random), thenumpy.random.RandomStatesingleton is used. Ifseedis an int, a newRandomStateinstance is used, seeded withseed. Ifseedis already aGeneratororRandomStateinstance then that instance is used. Specifyseedfor repeatable minimizations.- dispbool, optional
Prints the evaluated
funcat every iteration.- callbackcallable, optional
A callable called after each iteration. Has the signature:
callback(intermediate_result: OptimizeResult)where
intermediate_resultis a keyword parameter containing anOptimizeResultwith attributesxandfun, the best solution found so far and the objective function. Note that the name of the parameter must beintermediate_resultfor the callback to be passed anOptimizeResult.The callback also supports a signature like:
callback(x, convergence: float=val)valrepresents the fractional value of the population convergence. Whenvalis greater than1.0, the function halts.Introspection is used to determine which of the signatures is invoked.
Global minimization will halt if the callback raises
StopIterationor returnsTrue; any polishing is still carried out.Changed in version 1.12.0: callback accepts the
intermediate_resultkeyword.- polishbool, optional
If True (default), then
scipy.optimize.minimizewith theL-BFGS-Bmethod is used to polish the best population member at the end, which can improve the minimization slightly. If a constrained problem is being studied then thetrust-constrmethod is used instead. For large problems with many constraints, polishing can take a long time due to the Jacobian computations.- initstr or array-like, optional
Specify which type of population initialization is performed. Should be one of:
‘latinhypercube’
‘sobol’
‘halton’
‘random’
array specifying the initial population. The array should have shape
(S, N), where S is the total population size and N is the number of parameters.initis clipped toboundsbefore use.
The default is ‘latinhypercube’. Latin Hypercube sampling tries to maximize coverage of the available parameter space.
‘sobol’ and ‘halton’ are superior alternatives and maximize even more the parameter space. ‘sobol’ will enforce an initial population size which is calculated as the next power of 2 after
popsize * (N - N_equal). ‘halton’ has no requirements but is a bit less efficient. Seescipy.stats.qmcfor more details.‘random’ initializes the population randomly - this has the drawback that clustering can occur, preventing the whole of parameter space being covered. Use of an array to specify a population could be used, for example, to create a tight bunch of initial guesses in an location where the solution is known to exist, thereby reducing time for convergence.
- atolfloat, optional
Absolute tolerance for convergence, the solving stops when
np.std(pop) <= atol + tol * np.abs(np.mean(population_energies)), where andatolandtolare the absolute and relative tolerance respectively.- updating{‘immediate’, ‘deferred’}, optional
If
'immediate', the best solution vector is continuously updated within a single generation [4]_. This can lead to faster convergence as trial vectors can take advantage of continuous improvements in the best solution. With'deferred', the best solution vector is updated once per generation. Only'deferred'is compatible with parallelization or vectorization, and theworkersandvectorizedkeywords can over-ride this option.Added in version 1.2.0.
- workersint or map-like callable, optional
If
workersis an int the population is subdivided intoworkerssections and evaluated in parallel (usesmultiprocessing.Pool <multiprocessing>). Supply -1 to use all available CPU cores. Alternatively supply a map-like callable, such asmultiprocessing.Pool.mapfor evaluating the population in parallel. This evaluation is carried out asworkers(func, iterable). This option will override theupdatingkeyword toupdating='deferred'ifworkers != 1. This option overrides thevectorizedkeyword ifworkers != 1. Requires thatfuncbe pickleable.Added in version 1.2.0.
- constraints{NonLinearConstraint, LinearConstraint, Bounds}
Constraints on the solver, over and above those applied by the
boundskwd. Uses the approach by Lampinen [5]_.Added in version 1.4.0.
- x0None or array-like, optional
Provides an initial guess to the minimization. Once the population has been initialized this vector replaces the first (best) member. This replacement is done even if
initis given an initial population.x0.shape == (N,).Added in version 1.7.0.
- integrality1-D array, optional
For each decision variable, a boolean value indicating whether the decision variable is constrained to integer values. The array is broadcast to
(N,). If any decision variables are constrained to be integral, they will not be changed during polishing. Only integer values lying between the lower and upper bounds are used. If there are no integer values lying between the bounds then aValueErroris raised.Added in version 1.9.0.
- vectorizedbool, optional
If
vectorized is True,funcis sent anxarray withx.shape == (N, S), and is expected to return an array of shape(S,), whereSis the number of solution vectors to be calculated. If constraints are applied, each of the functions used to construct aConstraintobject should accept anxarray withx.shape == (N, S), and return an array of shape(M, S), whereMis the number of constraint components. This option is an alternative to the parallelization offered byworkers, and may help in optimization speed by reducing interpreter overhead from multiple function calls. This keyword is ignored ifworkers != 1. This option will override theupdatingkeyword toupdating='deferred'. See the notes section for further discussion on when to use'vectorized', and when to use'workers'.Added in version 1.9.0.
Returns
- resOptimizeResult
The optimization result represented as a
OptimizeResultobject. Important attributes are:xthe solution array,successa Boolean flag indicating if the optimizer exited successfully,messagewhich describes the cause of the termination,populationthe solution vectors present in the population, andpopulation_energiesthe value of the objective function for each entry inpopulation. SeeOptimizeResultfor a description of other attributes. Ifpolishwas employed, and a lower minimum was obtained by the polishing, then OptimizeResult also contains thejacattribute. If the eventual solution does not satisfy the applied constraintssuccesswill beFalse.
Notes
Differential evolution is a stochastic population based method that is useful for global optimization problems. At each pass through the population the algorithm mutates each candidate solution by mixing with other candidate solutions to create a trial candidate. There are several strategies [3]_ for creating trial candidates, which suit some problems more than others. The ‘best1bin’ strategy is a good starting point for many systems. In this strategy two members of the population are randomly chosen. Their difference is used to mutate the best member (the ‘best’ in ‘best1bin’), \(x_0\), so far:
\[b' = x_0 + mutation * (x_{r_0} - x_{r_1})\]A trial vector is then constructed. Starting with a randomly chosen ith parameter the trial is sequentially filled (in modulo) with parameters from
b'or the original candidate. The choice of whether to useb'or the original candidate is made with a binomial distribution (the ‘bin’ in ‘best1bin’) - a random number in [0, 1) is generated. If this number is less than therecombinationconstant then the parameter is loaded fromb', otherwise it is loaded from the original candidate. The final parameter is always loaded fromb'. Once the trial candidate is built its fitness is assessed. If the trial is better than the original candidate then it takes its place. If it is also better than the best overall candidate it also replaces that.The other strategies available are outlined in Qiang and Mitchell (2014) [3]_.
\[ \begin{align}\begin{aligned}rand1* : b' = x_{r_0} + mutation*(x_{r_1} - x_{r_2})\\rand2* : b' = x_{r_0} + mutation*(x_{r_1} + x_{r_2} - x_{r_3} - x_{r_4})\\best1* : b' = x_0 + mutation*(x_{r_0} - x_{r_1})\\best2* : b' = x_0 + mutation*(x_{r_0} + x_{r_1} - x_{r_2} - x_{r_3})\\currenttobest1* : b' = x_i + mutation*(x_0 - x_i + x_{r_0} - x_{r_1})\\randtobest1* : b' = x_{r_0} + mutation*(x_0 - x_{r_0} + x_{r_1} - x_{r_2})\end{aligned}\end{align} \]where the integers \(r_0, r_1, r_2, r_3, r_4\) are chosen randomly from the interval [0, NP) with
NPbeing the total population size and the original candidate having indexi. The user can fully customize the generation of the trial candidates by supplying a callable tostrategy.To improve your chances of finding a global minimum use higher
popsizevalues, with highermutationand (dithering), but lowerrecombinationvalues. This has the effect of widening the search radius, but slowing convergence.By default the best solution vector is updated continuously within a single iteration (
updating='immediate'). This is a modification [4]_ of the original differential evolution algorithm which can lead to faster convergence as trial vectors can immediately benefit from improved solutions. To use the original Storn and Price behaviour, updating the best solution once per iteration, setupdating='deferred'. The'deferred'approach is compatible with both parallelization and vectorization ('workers'and'vectorized'keywords). These may improve minimization speed by using computer resources more efficiently. The'workers'distribute calculations over multiple processors. By default the Pythonmultiprocessingmodule is used, but other approaches are also possible, such as the Message Passing Interface (MPI) used on clusters [6]_ [7]_. The overhead from these approaches (creating new Processes, etc) may be significant, meaning that computational speed doesn’t necessarily scale with the number of processors used. Parallelization is best suited to computationally expensive objective functions. If the objective function is less expensive, then'vectorized'may aid by only calling the objective function once per iteration, rather than multiple times for all the population members; the interpreter overhead is reduced.Added in version 0.15.0:
apsimNGpy.optimizer.moo
Classes
- class apsimNGpy.optimizer.moo.MultiObjectiveProblem
List of Public Attributes:
indicatorslabelsoutcomes
List of Public Methods
Parameters
- apsim_runnerapsimNGpy.core.cal.OptimizationBase
Instance to run APSIM simulations.
- objectiveslist of callable.
List of functions that take simulation output (DataFrame) and return scalar objective values.
- decision_varslist of dict, optional
Each dict must have: ‘path’, ‘bounds’, ‘v_type’, ‘kwargs’.
- optimization_type(self)
Must be implemented as a property in subclass
- is_mixed_type_vars(self)
Detect if decision vars contain types other than float or int.
- minimize(self, **kwargs)
Minimization of function of one or more variables, objectives and constraints. wraps around Pymoo
Parameters
- kwargsdict
- problem: instance of
pymoo.core.problem.Problem A problem object which is defined using pymoo.
- problem: instance of
- algorithm: instance of
pymoo.core.algorithm.Algorithm The algorithm object that should be used for the optimization.
- algorithm: instance of
- termination:
pymoo.core.termination.Terminationor tuple default is None Usually the termination criterion that is used to stop the algorithm.
- termination:
- seedinteger
The random seed to be used.
- verbosebool
Whether output should be printed or not.
- display
Display Each algorithm has a default display object for printouts. However, it can be overwritten if desired.
- display
- callback
pymoo.core.callback.Callback A callback object which is called each iteration of the algorithm.
- callback
- save_historybool
Whether the history should be stored or not.
- copy_algorithmbool
Whether the algorithm object should be copied before optimization.
- add_control(self, path: str, *, bounds, v_type, q=None, start_value=None, categories=None, **kwargs) (inherited)
Adds a single APSIM parameter to be optimized.
Parameters
- pathstr
APSIM component path.
- v_typetype
The Python type of the variable. Should be either
intorfloatfor continous variable problem or ‘uniform’, ‘choice’, ‘grid’, ‘categorical’, ‘qrandint’, ‘quniform’ for mixed variable problem
- start_valueany (type determined by the variable type.
The initial value to use for the parameter in optimization routines. Only required for single objective optimizations
- boundstuple of (float, float), optional
Lower and upper bounds for the parameter (used in bounded optimization). Must be a tuple like (min, max). If None, the variable is considered unbounded or categorical or the algorithm to be used do not support bounds
- kwargs: dict
One of the key-value pairs must contain a value of ‘?’, indicating the parameter to be filled during optimization. Keyword arguments are used because most APSIM models have unique parameter structures, and this approach allows flexible specification of model-specific parameters. It is also possible to pass other parameters associated with the model in question to be changed on the fly.
Returns
- selfobject
Returns self to support method chaining.
Warning
- Raises a
ValueError If the provided arguments do not pass validation via
_evaluate_args.
Note
This method is typically used before running optimization to define which parameters should be tuned.
Example:
from apsimNGpy.core.apsim import ApsimModel from apsimNGpy.core.optimizer import MultiObjectiveProblem runner = ApsimModel("Maize") _vars = [ {'path': '.Simulations.Simulation.Field.Fertilise at sowing', 'Amount': "?", "bounds": [50, 300], "v_type": "float"}, {'path': '.Simulations.Simulation.Field.Sow using a variable rule', 'Population': "?", 'v_type': 'float', 'bounds': [4, 14]} ] problem = MultiObjectiveProblem(runner, objectives=objectives, decision_vars=_vars) # or problem = MultiObjectiveProblem(runner, objectives=objectives, None) problem.add_control( **{'path': '.Simulations.Simulation.Field.Fertilise at sowing', 'Amount': "?", "bounds": [50, 300], "v_type": "float"}) problem.add_control( **{'path': '.Simulations.Simulation.Field.Sow using a variable rule', 'Population': "?", 'v_type': 'float', 'bounds': [4, 14]})
apsimNGpy.optimizer.problems.back_end
Functions
- apsimNGpy.optimizer.problems.back_end.detect_range(metric: str, bounds: tuple)
Check whether user-defined bounds fall within the allowed metric range.
Parameters
- metricstr
Name of the metric (e.g., “rmse”, “wia”, “r2”).
- boundstuple
User-specified (lower, upper) bounds.
Returns
- bool
True if the user-specified bounds are valid and within the global metric range. False otherwise.
Raises
- KeyError
If the metric is unknown.
- ValueError
If bounds is not a valid 2-tuple.
- apsimNGpy.optimizer.problems.back_end.eval_observed(obs: pandas.core.frame.DataFrame, pred: pandas.core.frame.DataFrame, index: str | list | tuple | set, pred_col: str, obs_col: str, method: str = 'rmse', exp: str | None = None) float
Evaluate observed and predicted values using a selected performance metric.
- This function:
validates and aligns the datasets,
computes the selected metric through
Validate,applies the metric’s optimization direction (min/max),
returns a single scalar performance value.
Supported Metrics
Metric
Description
Preferred Direction
Sign
RMSE
Root Mean Square Error
Smaller
+1
MAE
Mean Absolute Error
Smaller
+1
MSE
Mean Square Error
Smaller
+1
RRMSE
Relative RMSE
Smaller
+1
BIAS
Mean Bias
Closer to 0
+1
ME
Modeling Efficiency
Larger
-1
WIA
Willmott’s Index of Agreement
Larger
-1
R2
Coefficient of Determination
Larger
-1
CCC
Concordance Correlation Coefficient
Larger
-1
SLOPE
Regression Slope
Closer to 1
-1
- float
Metric value multiplied by the optimization direction.
- apsimNGpy.optimizer.problems.back_end.final_eval(obs: pandas.core.frame.DataFrame, pred: pandas.core.frame.DataFrame, index: str | tuple | list, pred_col: str, obs_col: str, exp: str | None = None) dict
Evaluate observed and predicted values and return the full suite of performance metrics supported by the: class:
Validateclass.- This function:
prepares and validates the input data (shared utility),
runs all metrics, not just one,
returns both the metric dictionary and the aligned dataset.
Returns
- dict
- {
“metrics”: {metric_name: value, …}, “data”: pd.DataFrame (aligned observed/predicted pairs)
}
apsimNGpy.optimizer.problems.smp
MixedProblem: a reusable interface for defining mixed-variable optimization problems with APSIM Next Generation models and wrapdisc-compatible variable types.
This module supports dynamic factor definition, parameter validation, and objective wrapping for use with Python-based optimization solvers such as scipy.Optimize and differential evolution.
Author: Richard Magala
Classes
- class apsimNGpy.optimizer.problems.smp.MixedProblem
Defines a single-objective mixed-variable optimization problem for APSIM models.
This class integrates APSIM simulations, observed data comparison, and user-defined factors (parameters) into a single reusable problem description suitable for optimization with scipy or pymoo solvers.
- modelstr
APSIM model identifier or path to the .apsimx file.
- trainer_datasetpd.DataFrame or None
Observed dataset for calibration or evaluation.
- pred_colstr
Column in APSIM output corresponding to predicted values.
- trainer_colstr
Column in observed dataset corresponding to observed values.
- indexstr
Column used for aligning predicted and observed values (e.g., ‘year’).
- metricstr, default=’RMSE’
Evaluation metric to use (e.g., ‘RMSE’, ‘R2’, ‘WIA’).
- tablestr or None, optional
APSIM output table name (if applicable).
- funccallable or None, optional
Custom evaluation function to override the built-in validation workflow. if provided should leave room for predicted argument
Each factor defines a modifiable APSIM node parameter and can have its own variable type (e.g., continuous, integer, categorical).
The resulting object can be wrapped into a callable Objective via
wrap_objectives()for integration with optimization solvers.
List of Public Attributes:
List of Public Methods
- __init__(self, model: str, trainer_dataset: pandas.core.frame.DataFrame | None = None, pred_col: str = None, trainer_col: str = None, index: str | tuple | set | list = None, metric: str = 'RMSE', table: str | None = None, func: Any | None = None)
Initialize self. See help(type(self)) for accurate signature.
- property n_apsim_nodes
Number of submitted optimization APSIM factors nodes.
- property n_factors
Number of submitted optimization factors.
- submit_factor(self, *, path, start_value, candidate_param, vtype=None, cultivar=False, bounds=None, other_params=None)
Add a new factor (parameter) to be optimized.
Each factor corresponds to a modifiable APSIM node attribute and its variable type (e.g.,
UniformVar,RandintVar,ChoiceVar). Factors define the search space and initial values for parameter optimization.Parameters
- pathstr
APSIM node path where the parameter resides, e.g.
".Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Organic". This node typically contains attributes such asFBiom,Carbon, andFINert.- vtypelist or tuple of wrapdisc.var
Variable types defining the search domain for each candidate parameter. These can include discrete, quantized, or continuous domains (see table below).
- start_valuelist or tuple of (str | int | float)
Initial values for each parameter, in the same order as
candidate_param.- candidate_paramlist or tuple of str
Names of APSIM variables (e.g.,
"FOM","FBiom") to be optimized. These must exist within the APSIM node path.- cultivarbool, optional, default=False
Indicates whether the parameter belongs to a cultivar node. Set to
Truewhen defining cultivar-related optimization factors.- other_paramsdict, optional
Additional APSIM constants to fix during optimization (non-optimized). These must belong to the same APSIM node. For example, when optimizing
FBiombut also modifyingCarbon, supplyCarbonunderother_params(see Example 1).
Tip
As a rule of thumb, group all parameters belonging to the same APSIM node into a single factor by providing them as lists. Submitting parameters from the same node as separate factors triggers a validation error.
Values must be provided using keyword-style arguments to support JSON-based cross-platform data structures.
Note
All submitted factors are validated using Pydantic to ensure adherence to expected data structures and variable types — for example checking that
vtypeincludes valid variable types (UniformVar,GridVar), ensuringpathis a valid string, and that numeric constraints follow their expected conventions.After Pydantic validation, an additional structural check ensures that the lengths of
vtype,start_value, andcandidate_paramare identical. Each candidate parameter must have a matching variable type and initial value.Optimization methods that do not require bounded or initialized start values allow for dummy entries in
start_value. These placeholders are accepted without affecting the optimization process. The system remains flexible across both stochastic and deterministic search methods.Variable Types (wrapdisc)
Each variable type below defines how sampling and decoding occur during optimization.
Supported Variable Types
ChoiceVar(items) Nominal (unordered categorical) Example:
ChoiceVar(["USA", "Panama", "Cayman"])GridVar(values) Ordinal (ordered categorical) Example:
GridVar([2, 4, 8, 16])RandintVar(lower, upper) Integer in
[lower, upper]Example:RandintVar(0, 6)QrandintVar(lower, upper, q) Quantized integer with step
qExample:QrandintVar(0, 12, 3)UniformVar(lower, upper) Continuous float range Example:
UniformVar(0.0, 5.11)QuniformVar(lower, upper, q) Quantized float with step
qExample:QuniformVar(0.0, 5.1, 0.3)
Below is a list of available string for each variable
ALLOWED_VARIABLES = { # Original canonical names "UniformVar": UniformVar, "QrandintVar": QrandintVar, "QuniformVar": QuniformVar, "GridVar": GridVar, "ChoiceVar": ChoiceVar, "RandintVar": RandintVar, # Short aliases "uniform": UniformVar, "quniform": QuniformVar, "qrandint": QrandintVar, "grid": GridVar, "choice": ChoiceVar, "randint": RandintVar, # Descriptive aliases (readable English) "continuous": UniformVar, "quantized_continuous": QuniformVar, "quantized_int": QrandintVar, "ordinal": GridVar, "categorical": ChoiceVar, "integer": RandintVar, # Alternative descriptive (for domain users) "step_uniform_float": QuniformVar, "step_random_int": QrandintVar, "ordered_var": GridVar, "choice_var": ChoiceVar}
Reference
wrapdisc documentation: https://pypi.org/project/wrapdisc/
Examples
Initialise a mixed-variable problem:
from apsimNGpy.optimizer.problems.variables import QrandintVar from apsimNGpy.tests.unittests.test_factory import obs from optimizer.problems.smp import MixedProblem mp = MixedProblem( model='Maize', trainer_dataset=obs, pred_col='Yield', metric='RRMSE', index='year', trainer_col='observed' )
Example 1 — Continuous variable (
UniformVar)mp.submit_factor( path=".Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Organic", vtype=[UniformVar(1, 2)], start_value=["1"], candidate_param=["FOM"], other_params={"FBiom": 2.3, "Carbon": 1.89}, )
Example 2 — Quantized continuous (
QuniformVar)mp.submit_factor( path=".Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Organic", vtype=[QuniformVar(0.0, 1.0, 0.005)], start_value=["0.035"], candidate_param=["FBiom"], )
Example 3 — Integer variable (
RandintVar)mp.submit_factor( path=".Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Plant", vtype=[RandintVar(1, 10)], start_value=[5], candidate_param=["Population"], )
Example 4 — Quantized integer (
QrandintVar)mp.submit_factor( path=".Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Labile", vtype=[QrandintVar(0, 12, 3)], start_value=[3], candidate_param=["Carbon"], )
Example 5 — Categorical variable (
ChoiceVar)mp.submit_factor( path=".Simulations.Simulation.Sow using a variable rule", vtype=[ChoiceVar(["B_100", "A90", "B110"])], start_value=["B_100"], candidate_param=["CultivarName"], )
Example 6 — Ordinal grid variable (
GridVar)mp.submit_factor( path=".Simulations.Simulation.Field.Management", vtype=[GridVar(["Low", "Medium", "High"])], start_value=["Medium"], candidate_param=["FertilizerRate"], )
Submitting more than one parameter on a single node
You must specify complete lists for
vtype,start_value, andcandidate_param. Each list must align so that the element at index i corresponds to the same variable across all lists.cultivar_params = { "path": ".Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Dekalb_XL82", "vtype": [ QrandintVar(400, 600, q=5), QrandintVar(400, 900, q=5) ], "start_value": [500, 550], "candidate_param": [ "[Grain].MaximumGrainsPerCob.FixedValue", "[Phenology].GrainFilling.Target.FixedValue" ], "other_params": {"sowed": True}, "cultivar": True, } mp.submit_factor(**cultivar_params)
- It is possible to describe your data type using string characters uisng any of the description below,
implying no variable descriptor namespace import needed.
Skip variable typing
You can skip typing variables, implying that only continuous variables will be allowed.
cultivar_params = { "path": ".Simulations.Simulation.Field.Maize.CultivarFolder.Dekalb_XL82", "bounds": [ (400, 600), (400, 900) ], "start_value": [500, 550], "candidate_param": [ "[Grain].MaximumGrainsPerCob.FixedValue", "[Phenology].GrainFilling.Target.FixedValue" ], "other_params": {"sowed": True}, "cultivar": True} mp.submit_factor(**cultivar_params)
Added in version 0.39.12.21.
Warning
The use of both vtype-specified variables and unrestricted continuous variables within the same configuration is unsupported and will not satisfy Pydantic validation requirements.
Variable Type Classification
- Continuous (UniformVar)
UniformVaruniformcontinuous
Represents real-valued continuous parameters.
- Quantized Continuous (QuniformVar)
QuniformVarquniformquantized_continuousstep_uniform_float
Continuous parameters restricted to fixed step sizes.
- Quantized Integer (QrandintVar)
QrandintVarqrandintquantized_intstep_random_int
Integer parameters with fixed quantization.
- Ordinal / Grid (GridVar)
GridVargridordinalordered_var
Ordered categorical variables with ranked classes.
- Categorical / Nominal (ChoiceVar)
ChoiceVarchoicecategoricalchoice_var
Unordered categorical classes.
- Integer (RandintVar)
RandintVarrandintinteger
Integer-valued variables.
Batch-add multiple factors for optimization.
This method provides a convenient way to register several parameter factors (e.g., multiple APSIM node attributes) at once, instead of calling
submit_factor()repeatedly for each parameter. Each item in the input list must follow the same structure expected bysubmit_factor().Parameters
- all_factorslist of dict
A list (or tuple) of dictionaries, where each dictionary defines a single optimization factor with the following required keys:
- path: str
The APSIM node path where the variable resides.
- vtype: list or tuple of wrapdisc.var
The variable type(s) defining the sampling space (e.g.,
UniformVar,ChoiceVar).- start_value: list or tuple of str, int, or float
The starting value(s) corresponding to each candidate parameter.
- candidate_paramlist or tuple of str
The APSIM variable names to optimize.
- other_params: dict, optional
Any additional parameters belonging to the same APSIM node that should remain constant during optimization.
- cultivar: bool, default=False
Whether the factor being submitted is cultivar specific or resides on the cultivar node
Notes
This method internally calls
submit_factor()for each element inall_factors. Each factor is individually validated using Pydantic type checks and structural consistency rules to ensure that all required fields are properly defined.Returns
- selfMixedProblem
Returns the same instance for method chaining. This enables expressions like:
mp.submit_all(factors).wrap_objectives().minimize_with_de()
Examples
# Define multiple parameter factors all_factors = [ { "path": ".Simulations.Simulation.Field.Soil.Organic", "vtype": [UniformVar(1, 2)], "start_value": ["1.0"], "candidate_param": ["FOM"], "other_params": {"FBiom": 2.3, "Carbon": 1.89}, }, { "path": ".Simulations.Simulation.Field.Plant", "vtype": [RandintVar(1, 10)], "start_value": [5], "candidate_param": ["Population"], }, ] # Batch register all factors at once mp.submit_all(all_factors)
- evaluate_objectives(self, x)
Evaluate the APSIM model’s objective function for a given parameter vector.
This method inserts the provided input parameters into the APSIM model, executes the simulation, and evaluates the predicted outputs against the observed dataset using a selected performance metric (e.g., RMSE, R², ME, CCC). It serves as the core evaluation routine for optimization and sensitivity analysis workflows.
Parameters
- xarray-like
A numeric vector (list, tuple, or NumPy array) representing parameter values to be inserted into the APSIM model. The vector must match the order and dimensionality of the defined optimization factors (as specified through
submit_factor()orsubmit_all()).
Workflow
The provided parameter vector
xis mapped onto APSIM input variables using the internal_insert_x_vars()method.The model is executed via the
runner()interface, which runs the APSIM simulation with the updated parameters.Simulation outputs (predicted data) are compared against the reference observations (
self.obs) using theeval_observed()evaluator.The chosen performance metric, defined in
self.method, is computed and returned.
Notes
The supported evaluation metrics include:
RMSE: Root Mean Square ErrorMAE: Mean Absolute ErrorRRMSE: Relative Root Mean Square ErrorR2: Coefficient of DeterminationME: Modeling EfficiencyWIA: Willmott’s Index of AgreementCCC: Concordance Correlation CoefficientBIAS: Mean Bias Error
These metrics are implemented in the
apsimNGpy.validation.evaluator.Validatemodule and are used to assess how well the simulated values replicate observed data.Returns
- float
The computed performance score based on the selected metric. For metrics such as RMSE or MAE, lower values indicate better performance, whereas for R², WIA, or CCC, higher values indicate better model fit.
The size of the minimization is determined automatically in the back_end.py, thus if you are using eval_observed method, no need to worry about multiplying with -1 for loss function indices such as CCC
Examples
# Evaluate APSIM model performance using a sample parameter vector x = [1.5, 0.8, 3.2, 0.1] score = mp.evaluate_objectives(x) print(f"Model evaluation ({mp.method}):", score)
- wrap_objectives(self) wrapdisc.wrapdisc.Objective
Wrap the evaluation function into a
wrapdisc.Objectiveinstance compatible with mixed-variable optimizers.Returns
- Objective
A callable objective that accepts encoded variable vectors.
apsimNGpy.parallel.process
Functions
- apsimNGpy.parallel.process.custom_parallel(func, iterable: 'Iterable', *args, **kwargs)
Run a function in parallel using threads or processes.
- funccallable
The function to run in parallel.
- iterableiterable
An iterable of items to be processed by
func.- *args
Additional positional arguments to pass to
func.
- Any
The result of
funcfor each item initerable.
- kwargs
- use_threadbool, optional, default=False
If
True, use threads; ifFalse, use processes (recommended for CPU-bound work).- ncoresint, optional
Number of worker threads/processes. Defaults to ~50% of available CPU cores.
- verbosebool, optional, default=True
Whether to display a progress indicator.
- progress_messagestr, optional
Message shown alongside the progress indicator. Defaults to
f"Processing multiple jobs via {func.__name__}, please wait!".- voidbool, optional, default=False
If
True, consume results internally (do not yield). Useful for side-effect–only functions.- unitstr, optional, default=”iteration”
Label for the progress indicator (cosmetic only).
Run with processes (CPU-bound):
>>> list(run_parallel(work, range(5), use_thread=False, ncores=4))
Run with threads (I/O-bound):
>>> for _ in run_parallel(download, urls, use_thread=True, verbose=True): ... pass
See also
- apsimNGpy.parallel.process.custom_parallel_chunks(func: 'Callable[..., Any]', jobs: 'Iterable[Iterable[Any]]', *args, **kwargs)
Run a function in parallel using threads or processes. The iterable is automatically divided into chunks, and each chunk is submitted to worker processes or threads.
Parameters
- funccallable
The function to run in parallel.
- iterableiterable
An iterable of items that will be processed by
func.- *args
Additional positional arguments to pass to
func.
Yields
- Any
The results of
funcfor each item in the iterable. IffuncreturnsNone, the results will be a sequence ofNone. Note: The function returns a generator, which must be consumed to retrieve results.
Other Parameters
- use_threadbool, optional, default=False
If
True, use threads for parallel execution; ifFalse, use processes (recommended for CPU-bound tasks).- ncoresint, optional
Number of worker processes or threads to use. Defaults to 50% of available CPU cores.
- verbosebool, optional, default=True
Whether to display a progress bar.
- progress_messagestr, optional
Message to display alongside the progress bar. Defaults to
f"Processing multiple jobs via {func.__name__}, please wait!".- voidbool, optional, default=False
If
True, results are consumed internally (not yielded). Useful for functions that operate with side effects and do not return results.- unitstr, optional, default=”iteration”
Label for the progress bar unit (cosmetic only).
- n_chunksint, optional
Number of chunks to divide the iterable into. For example, if the iterable length is 100 and
n_chunks=10, each chunk will have 10 items.- chunk_sizeint, optional
Size of each chunk. If specified,
n_chunksis determined automatically. For example, if the iterable length is 100 andchunk_size=10, thenn_chunks=10.
Examples
Run with processes (CPU-bound): >>> def worker(): … pass
>>> list(run_parallel(work, range(5), use_thread=False, ncores=4))
Run with threads (I/O-bound):
>>> for _ in run_parallel(download, urls, use_thread=True, verbose=True): ... pass
See also
apsimNGpy.validation.evaluator
Evaluate predicted vs. observed data using statistical and mathematical metrics.
Implements standard model evaluation metrics used in crop modeling and other environmental simulation contexts. For detailed metric definitions, see:
Archontoulis, S. V., & Miguez, F. E. (2015). Nonlinear regression models and applications in agricultural research. Agronomy Journal, 107(2), 786–798.
Classes
- class apsimNGpy.validation.evaluator.Validate
Compare predicted and observed values using statistical performance metrics.
Parameters
- actualArrayLike
Observed (measured) values.
- predictedArrayLike
Model-predicted values of the same length as
actual.
Notes
This class provides a consistent interface for evaluating model performance using commonly used metrics such as RMSE, MAE, R², Willmott’s Index of Agreement, and the Concordance Correlation Coefficient (CCC).
Metric
Description
Preferred Direction
RMSE
Root Mean Square Error
Smaller
MAE
Mean Absolute Error
Smaller
MSE
Mean Square Error
Smaller
RRMSE
Relative RMSE
Smaller
BIAS
Mean Bias
Closer to 0
ME
Modeling Efficiency
Larger
WIA
Willmott’s Index of Agreement
Larger
R2
Coefficient of Determination
Larger
CCC
Concordance Correlation Coefficient
Larger
SLOPE
Regression Slope
Closer to 1
Examples
from apsimNGpy.optimizer.problems.validation import Validate import numpy as np obs = np.array([1.2, 2.4, 3.6, 4.8, 5.0]) pred = np.array([2.0, 3.5, 4.2, 5.7, 6.0]) val = Validate(obs, pred) print(val.RMSE()) print(val.evaluate_all(verbose=True))
- __init__(self, actual: numpy.ndarray | List[float] | pandas.core.series.Series, predicted: numpy.ndarray | List[float] | pandas.core.series.Series) None
Method generated by attrs for class Validate.
- METRICS
Default:
['RMSE', 'MAE', 'MSE', 'RRMSE', 'bias', 'ME', 'WIA', 'R2', 'CCC', 'SLOPE']Mean Square Error.
Root Mean Square Error.
Mean Absolute Error.
Relative Root Mean Square Error (normalized by mean of observed).
Mean Bias (positive = overestimation, negative = underestimation).
Modeling Efficiency (Nash–Sutcliffe Efficiency).
Willmott’s Index of Agreement.
Coefficient of Determination.
Regression slope between observed and predicted.
Concordance Correlation Coefficient.
Compute a single metric value.
Parameters
- metricstr, default=”RMSE”
Name of the metric to compute (case-insensitive).
Returns
- float
Metric value.
Raises
- ValueError
If the metric name is not recognized.
Compute all available metrics at once.
Parameters
- verbosebool, default=False
If True, print metrics to console.
Returns
- dict
Dictionary mapping metric names to their computed values.